Introduction To Cartesian Coordinate Systems Skillsyouneed вђ Otosection

Introduction To Cartesian Coordinate Systems Skillsyouneed вђ Otose The origin of a three dimensional cartesian system is the point at which x, y and z are all equal to zero (0,0,0). in mathematical terms, a point p in a typical three dimensional cartesian coordinate system is shown in the diagram below. p is equivalent to the ball in our example. it is unlikely that you will need to use 3d cartesian coordinate. Cartesian coordinate system with a circle of radius 2 centered at the origin marked in red. the equation of a circle is (x − a)2 (y − b)2 = r2 where a and b are the coordinates of the center (a, b) and r is the radius. cartesian coordinates are named for rené descartes, whose invention of them in the 17th century revolutionized.
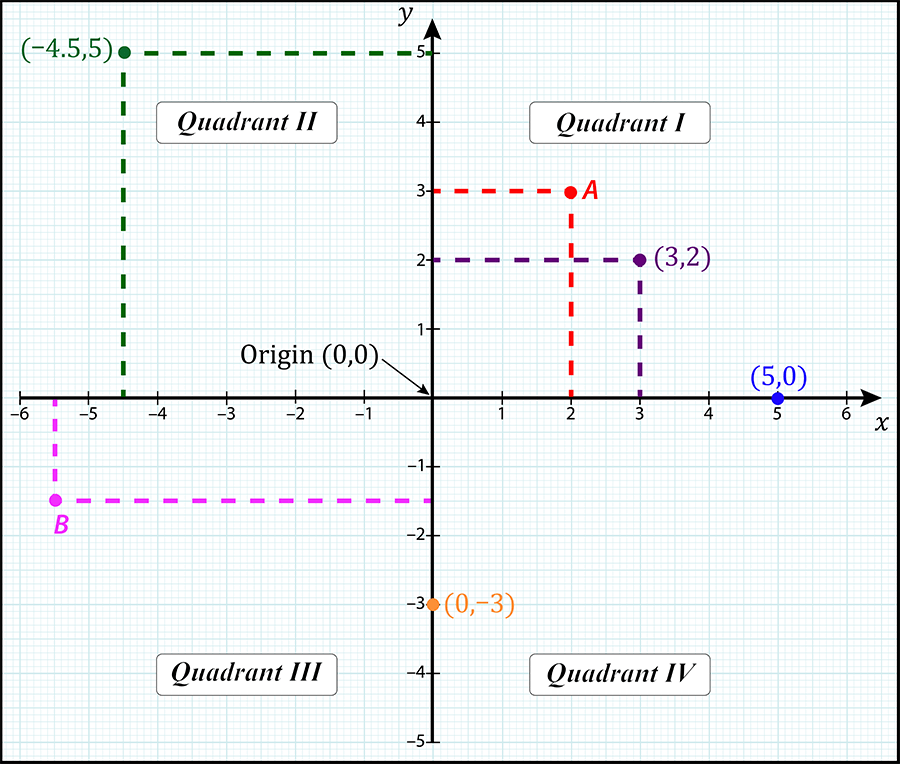
Introduction To Cartesian Coordinate Systems Skillsyouneed Geometry, n. that part of mathematics which treats the properties of points, lines, surfaces and solids…. chambers english dictionary, 1989 edition. geometry comes from the greek meaning ‘earth measurement’ and is the visual study of shapes, sizes and patterns, and how they fit together in space. you will find that our geometry pages. The cartesian coordinate systems is of one dimension, two dimensions, three dimension, and n dimension. the points in a cartesian coordinate system are expressed as (x, y), or (x, y, z). what is the cartesian coordinate system used for? the cartesian coordinate system can be used to represent points, lines, curves, planes. These systems are the three dimensional relatives of the two dimensional polar coordinate system. cylindrical coordinates are more straightforward to understand than spherical and are similar to the three dimensional cartesian system (x,y,z). in this case, the orthogonal x y plane is replaced by the polar plane and the vertical z axis remains. However, it becomes cumbersome when we need to describe the rotation of objects. when describing rotation, we usually work in the polar coordinate system. in the polar coordinate system, the location of point p in a plane is given by two polar coordinates (figure 2.20).
Intro To Cartesian Coordinate System Expii These systems are the three dimensional relatives of the two dimensional polar coordinate system. cylindrical coordinates are more straightforward to understand than spherical and are similar to the three dimensional cartesian system (x,y,z). in this case, the orthogonal x y plane is replaced by the polar plane and the vertical z axis remains. However, it becomes cumbersome when we need to describe the rotation of objects. when describing rotation, we usually work in the polar coordinate system. in the polar coordinate system, the location of point p in a plane is given by two polar coordinates (figure 2.20). To introduce the idea, consider the grid above. the columns of the grid are lettered a,b,c etc. the rows are numbered 1,2,3 etc from the top. we can see that the x is in box d3; that is, column d, row 3. d and 3 are called the coordinates of the box. it has two parts: the row and the column. there are many boxes in each row and many boxes in. The 3 dimensional coordinate system of euclidean space can be represented on a flat surface, such as this page or a blackboard, only by giving the illusion of three dimensions, in the manner shown in figure 12.1.1 . euclidean space has three mutually perpendicular coordinate axes (x, y and z), and three mutually perpendicular coordinate planes.

Introduction To Cartesian Coordinate Systems Skillsyouneed To introduce the idea, consider the grid above. the columns of the grid are lettered a,b,c etc. the rows are numbered 1,2,3 etc from the top. we can see that the x is in box d3; that is, column d, row 3. d and 3 are called the coordinates of the box. it has two parts: the row and the column. there are many boxes in each row and many boxes in. The 3 dimensional coordinate system of euclidean space can be represented on a flat surface, such as this page or a blackboard, only by giving the illusion of three dimensions, in the manner shown in figure 12.1.1 . euclidean space has three mutually perpendicular coordinate axes (x, y and z), and three mutually perpendicular coordinate planes.

Introduction To The Coordinate Plane Cartesian Plane Ejfullerton

Comments are closed.