Is A Hawk A Secondary Consumer

Secondary Consumers In The Food Chain You Probably Don T Know Yes, hawks are considered secondary consumers in most ecosystems. as predatory birds, they primarily feed on smaller animals like rodents, reptiles, birds, and insects. secondary consumers occupy the second level in the food chain and obtain energy by consuming primary consumers. hawks play a crucial role in regulating populations of their prey. Learn why hawks are secondary consumers and how they fit into the food web. find out what they eat, how they help regulate ecosystems, and what threats they face.
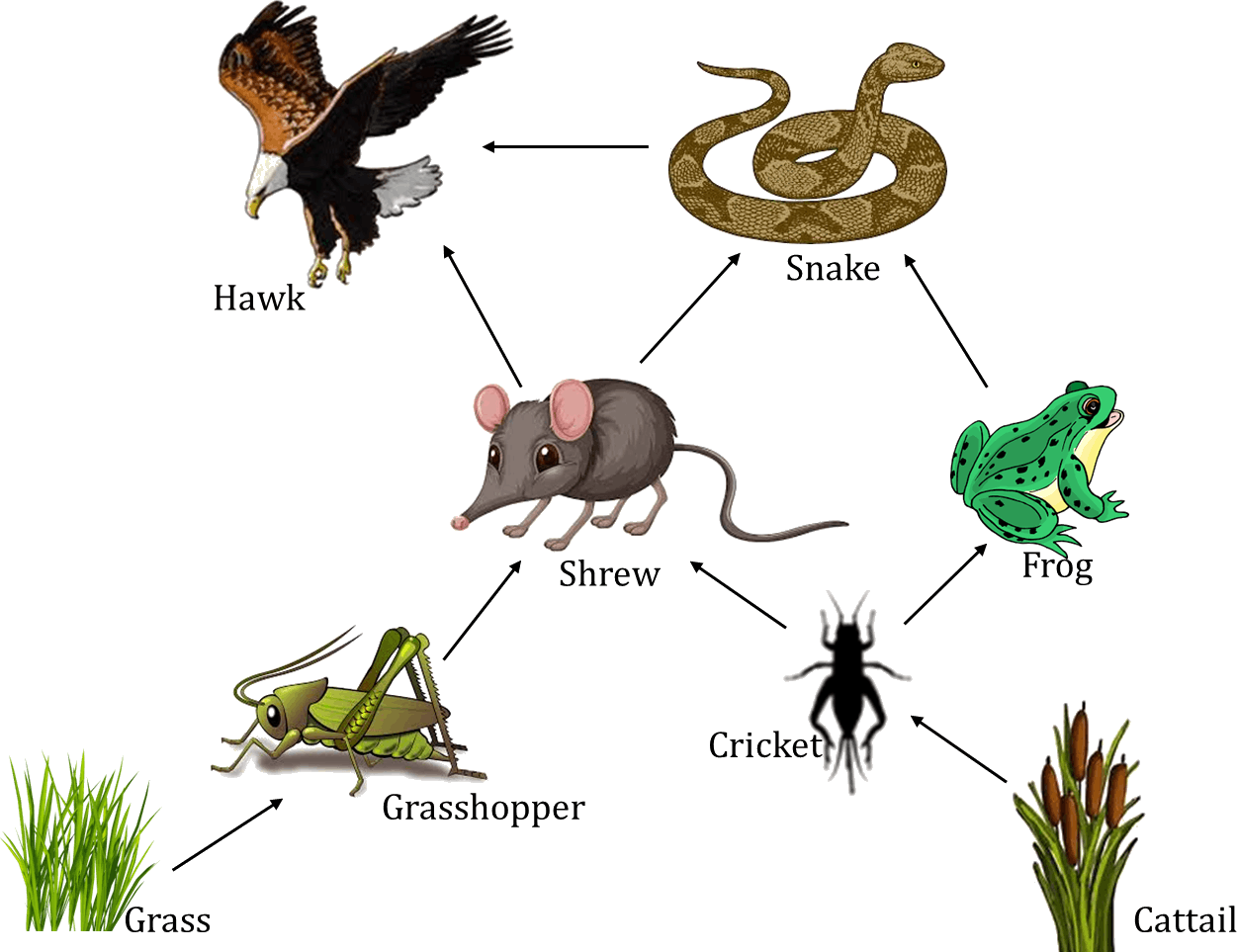
Hawk Clipart Secondary Consumer Picture 1307352 Hawk Clipart Who is a secondary consumer in this diagram? we could say the coyote's a secondary consumer. the hawk is also a secondary consumer. the vulture is a secondary consumer. and so is the snake. and as you can see, that's okay, even in a situation where some secondary consumers eat other secondary consumers. the coyote might eat a hawk, or a vulture. We can see examples of these levels in the diagram below. the green algae are primary producers that get eaten by mollusks—the primary consumers. the mollusks then become lunch for the slimy sculpin fish, a secondary consumer, which is itself eaten by a larger fish, the chinook salmon—a tertiary consumer. Learn how food chains show the feeding relationships and energy transfer in ecosystems. a hawk is a predator that eats other animals, such as frogs, thrushes and voles. these are the primary and secondary consumers in the food chain. Spiders, snakes, and seals are all examples of carnivorous secondary consumers. omnivores are the other type of secondary consumer. they eat both plant and animal materials for energy. bears and skunks are examples of omnivorous secondary consumers that both hunt prey and eat plants. however, some omnivores are simply scavengers.

Are Hawks Secondary Consumers Exploring Their Vital Role Learn Bird Learn how food chains show the feeding relationships and energy transfer in ecosystems. a hawk is a predator that eats other animals, such as frogs, thrushes and voles. these are the primary and secondary consumers in the food chain. Spiders, snakes, and seals are all examples of carnivorous secondary consumers. omnivores are the other type of secondary consumer. they eat both plant and animal materials for energy. bears and skunks are examples of omnivorous secondary consumers that both hunt prey and eat plants. however, some omnivores are simply scavengers. The mollusks then become lunch for the slimy sculpin fish, a secondary consumer, which is itself eaten by a larger fish, the chinook salmon (tertiary consumer). image credit: " ecology of ecosystems: figure 3 ," by openstax college, biology, cc by 4.0 . The organisms that consume the producers are herbivores: the primary consumers. secondary consumers are usually carnivores that eat the primary consumers. tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the.

Are Hawks Secondary Consumers Exploring Their Vital Role Learn Bird The mollusks then become lunch for the slimy sculpin fish, a secondary consumer, which is itself eaten by a larger fish, the chinook salmon (tertiary consumer). image credit: " ecology of ecosystems: figure 3 ," by openstax college, biology, cc by 4.0 . The organisms that consume the producers are herbivores: the primary consumers. secondary consumers are usually carnivores that eat the primary consumers. tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the.

Comments are closed.