Law Of Reflection Ray Diagrams For Spherical Mirrors
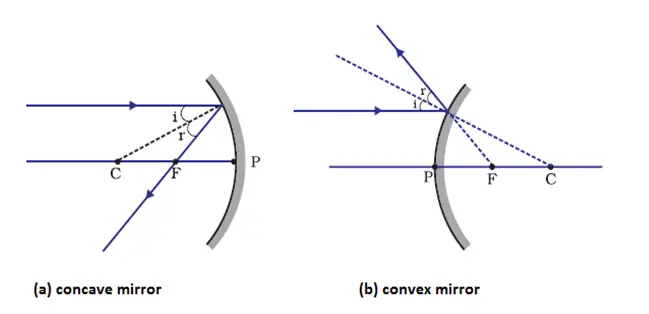
Image Formation By Spherical Mirrors Class 10 Reflection Of Light Notes 2.3: spherical mirrors. Laws of reflection. in the diagram given above, the ray of light that approaches the mirror is the “incident ray”. the ray that leaves the mirror is the “reflected ray”. at the point of incidence where the incident ray strikes the mirror, a perpendicular line is drawn is the “normal”.
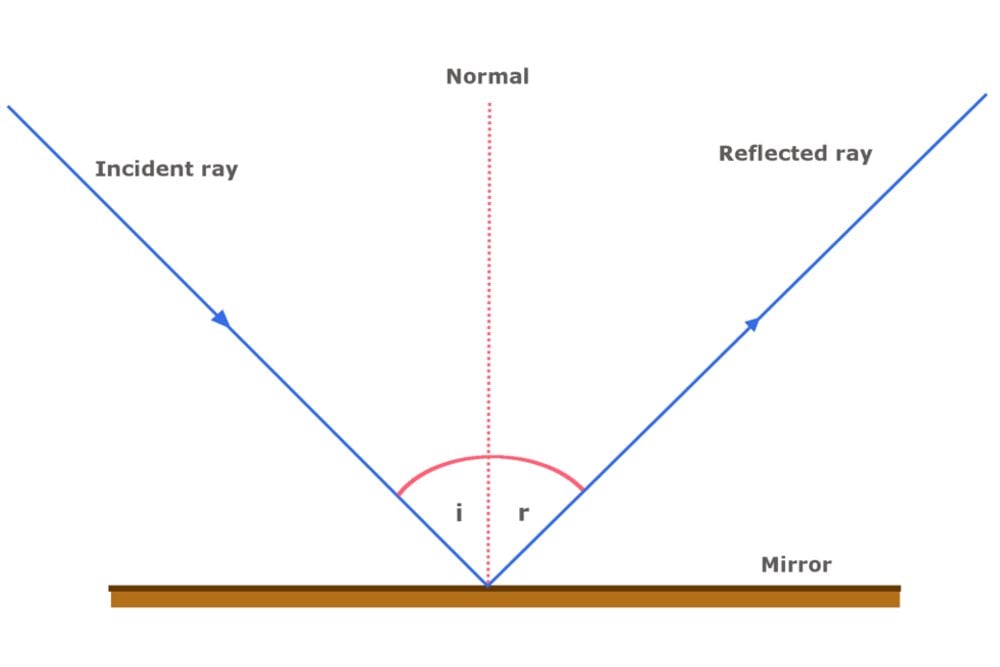
What Is The Law Of Reflection Definition And A Simple Explanation 23 2 the law of reflection; plane mirrors a ray of light that reflects from a surface obeys a very simple rule, known as the law of reflection. see, also, the illustrations in figure 23.7. a surface acts as a mirror when the law of reflection is followed on a large scale, as shown in figure 23.8 (a). in that case, the whole beam of light,. Exploration 23.3 – ray diagram for a convex mirror. we will follow a process similar to that for plane mirrors to draw a ray diagram for a convex (diverging) mirror. step 1 – first, locate the mirror’s focal point. then, draw a light ray that leaves the tip of the object (its top) and goes parallel to the principal axis. By the end of this section, you will be able to: describe image formation by spherical mirrors. use ray diagrams and the mirror equation to calculate the properties of an image in a spherical mirror. the image in a plane mirror has the same size as the object, is upright, and is the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of. 2.2 spherical mirrors university physics volume 3.

Comments are closed.