Learn What Is Diffusion How Does It Work What Factors Affect It 7ођ

What Is Diffusion How Does It Work What Factors Affect It 7 Yout This video covers what diffusion is how it works how it applies to cell membranes the 3 factors that affect the rate of diffusion (concentration gradi. 1) simple diffusion. it is the process in which substances move across a biologically active semi permeable membrane along the concentration gradient without the involvement of any other molecules. example: breathing in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide out of the body during respiration. 2) facilitated diffusion.
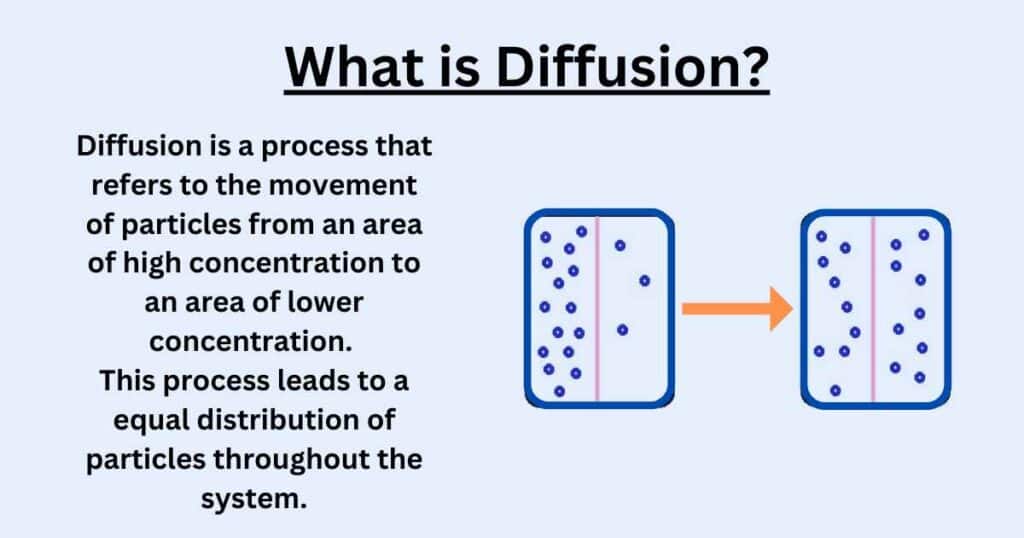
Diffusion Explained Types Examples And Factors Next video. general biology 6. the membrane concentration gradients and diffusion. 5m. what is diffusion? how does it work? what factors affect it? #7. cognito. Diffusion is a physical process that refers to the net movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to one of lower concentration. the material that diffuses could be a solid, liquid or gas. similarly, the medium in which diffusion occurs could also be in one of the three physical states. one of the main characteristics of. Diffusion is the process of movement of molecules under a concentration gradient. it is an important process occurring in all living beings. diffusion helps in the movement of substances in and out of the cells. the molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration until the concentration becomes equal. Two factors affect diffusion: the type of substance substances diffuse more quickly through gases than through liquids. this is because the particles in a gas are more spread out and move faster.
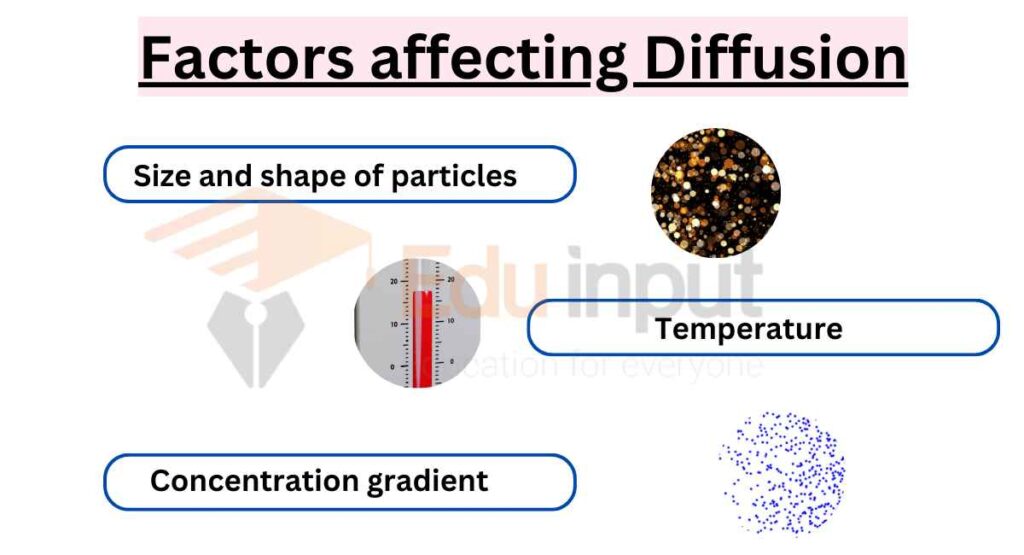
Diffusion Explained Types Examples And Factors Diffusion is the process of movement of molecules under a concentration gradient. it is an important process occurring in all living beings. diffusion helps in the movement of substances in and out of the cells. the molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration until the concentration becomes equal. Two factors affect diffusion: the type of substance substances diffuse more quickly through gases than through liquids. this is because the particles in a gas are more spread out and move faster. Diffusion is a passive process of transport. a single substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal across a space. you are familiar with diffusion of substances through the air. for example, think about someone opening a bottle of ammonia in a room filled with people. Diffusion is the tendency of molecules to spread out in order to occupy an available space. gasses and molecules in a liquid have a tendency to diffuse from a more concentrated environment to a less concentrated environment. passive transport is the diffusion of substances across a membrane. this is a spontaneous process and cellular energy is.

What Is Diffusion Factors Affecting Diffusion Youtube Diffusion is a passive process of transport. a single substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the concentration is equal across a space. you are familiar with diffusion of substances through the air. for example, think about someone opening a bottle of ammonia in a room filled with people. Diffusion is the tendency of molecules to spread out in order to occupy an available space. gasses and molecules in a liquid have a tendency to diffuse from a more concentrated environment to a less concentrated environment. passive transport is the diffusion of substances across a membrane. this is a spontaneous process and cellular energy is.

Comments are closed.