Linear Algebra And Matrices Linear Equations And Matrices
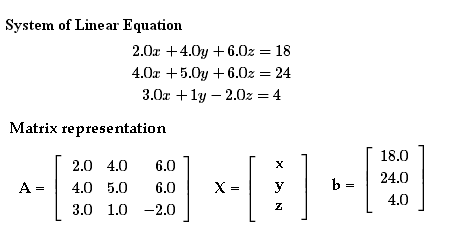
System Of Linear Equations Matrices W3schools Using the matrix calculator we get this: (i left the 1 determinant outside the matrix to make the numbers simpler) then multiply a 1 by b (we can use the matrix calculator again): and we are done! the solution is: x = 5. y = 3. z = −2. just like on the systems of linear equations page. 4.6: solve systems of equations using matrices.

Linear Algebra Lecture 9 Matrix Equations Youtube 4.1 introduction to linear algebra and matrices linear algebra is concerned mainly with: systems of linear equations, matrices, vector space, linear transformations, eigenvalues, and eigenvectors. linear and non linear functions and equations: linear functions: linear equations: 4x 1 3x 2 –2x 3 x 4 = 0 where x 1, x 2, x 3 and x 4 are. Therefore, when we include the constants, we often refer to the resulting matrix as an augmented matrix. we can use augmented matrices to find solutions to linear equations by using essentially the same steps we used above. every time we used the word “equation” above, substitute the word “row,” as we show below. Matrices. a matrix is a rectangular array of numbers that is usually named by a capital letter: a, b, c, and so on. each entry in a matrix is referred to as aij, such that i represents the row and j represents the column. matrices are often referred to by their dimensions: m × n indicating m rows and n columns. Solve systems of equations using matrices. to solve a system of equations using matrices, we transform the augmented matrix into a matrix in row echelon form using row operations. for a consistent and independent system of equations, its augmented matrix is in row echelon form when to the left of the vertical line, each entry on the diagonal is.

Linear Algebra Introduction And Matrix Operations Youtube Matrices. a matrix is a rectangular array of numbers that is usually named by a capital letter: a, b, c, and so on. each entry in a matrix is referred to as aij, such that i represents the row and j represents the column. matrices are often referred to by their dimensions: m × n indicating m rows and n columns. Solve systems of equations using matrices. to solve a system of equations using matrices, we transform the augmented matrix into a matrix in row echelon form using row operations. for a consistent and independent system of equations, its augmented matrix is in row echelon form when to the left of the vertical line, each entry on the diagonal is. So multiplication by matrix inverse solves a set of linear equations some comments: • x = a−1b makes solving set of 100 linear equations in 100 variables look simple, but the notation is hiding alot of work! • fortunately, it’s very easy (and fast) for a computer to compute x = a−1b (even when x has dimension 100, or much higher). In linear algebra, two matrices are row equivalent if one can be changed to the other by a sequence of elementary row operations. alternatively, two [latex]m \times n[ latex]matrices are row equivalent if and only if they have the same row space. the row space of a matrix is the set of all possible linear combinations of its row vectors. if the.
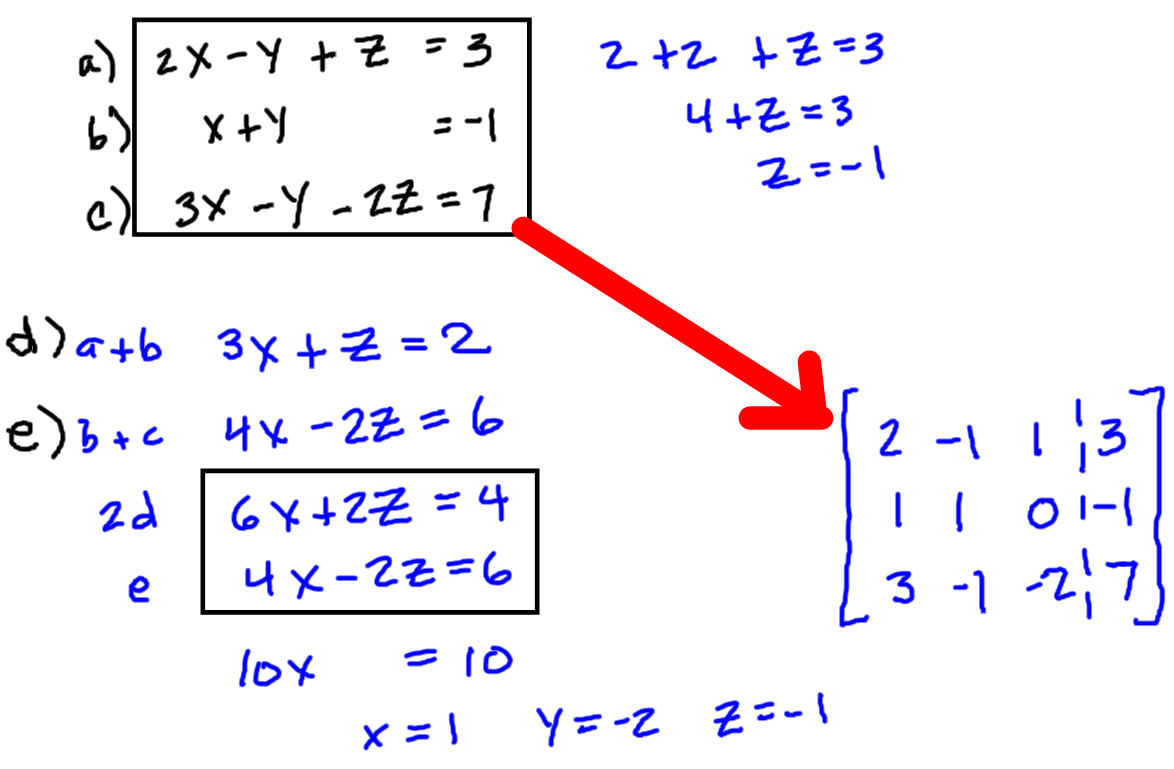
Solving Systems Of Linear Equations With Matrices вђ Db Excel So multiplication by matrix inverse solves a set of linear equations some comments: • x = a−1b makes solving set of 100 linear equations in 100 variables look simple, but the notation is hiding alot of work! • fortunately, it’s very easy (and fast) for a computer to compute x = a−1b (even when x has dimension 100, or much higher). In linear algebra, two matrices are row equivalent if one can be changed to the other by a sequence of elementary row operations. alternatively, two [latex]m \times n[ latex]matrices are row equivalent if and only if they have the same row space. the row space of a matrix is the set of all possible linear combinations of its row vectors. if the.

Comments are closed.