Linear Algebra Ch 2 Determinants 23 Of 48 Non Invertible Matrix

Linear Algebra Ch 2 Determinants 23 Of 48 Non Invertible Matrix Visit ilectureonline for more math and science lectures!in this video i will find a13=? of a 3x3 matix the determinant of that matrix is non inver. Visit ilectureonline for more math and science lectures!in this video i will demonstrate if the inverse of a matrix does not exist then the determ.

Linear Algebra Ch 2 Determinants 18 Of 48 Example Of Rule 12 Share your videos with friends, family, and the world. 2 linear equations 6 3 matrix algebra 8 4 determinants 11 5 eigenvalues and eigenvectors 13 6 linear transformations 16 7 dimension 17 8 similarity and diagonalizability 18 9 complex numbers 23 10 projection theorem 28 11 gram schmidt orthonormalization 29 12 qr factorization 31 13 least squares approximation 32 14 orthogonal (unitary. First, since we’re looking at $2\times2$ (presumably real) matrices, we’re talking about linear transformations of the plane $\mathbb r^2$: linear transformations that map from a vector space to one with a different dimension aren’t directly relevant. The inverse of a matrix exists if and only if the determinant is nonzero. to find the inverse of a matrix, we write a new extended matrix with the identity on the right. then we completely row reduce, the resulting matrix on the right will be the inverse matrix. example \ (\pageindex {4}\).
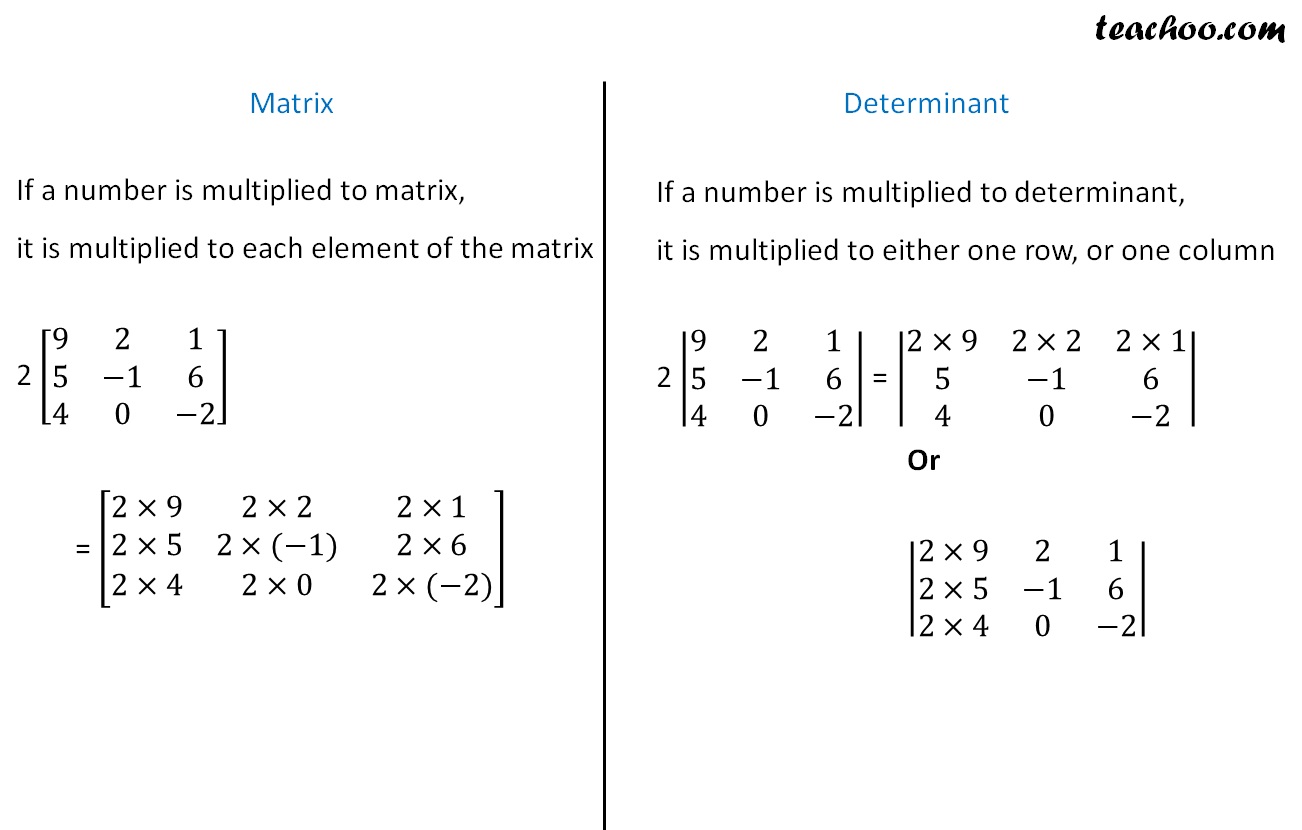
Matrices And Determinants Formula Sheet And Summary Teachoo First, since we’re looking at $2\times2$ (presumably real) matrices, we’re talking about linear transformations of the plane $\mathbb r^2$: linear transformations that map from a vector space to one with a different dimension aren’t directly relevant. The inverse of a matrix exists if and only if the determinant is nonzero. to find the inverse of a matrix, we write a new extended matrix with the identity on the right. then we completely row reduce, the resulting matrix on the right will be the inverse matrix. example \ (\pageindex {4}\). Summary. determinant is an important scale in linear algebra. that’s why it has a lot of properties. you don’t need to remember everything line by line. first, try to get the ideas. then play. Using definition 3.1.1, the determinant is given by det (a) = 1 × 4 − 2 × 2 = 0. however notice that the second row is equal to 2 times the first row. then by the discussion above following theorem 3.2.4 the determinant will equal 0. until now, our focus has primarily been on row operations.

Linear Algebra Ch 2 Determinants 2 Of 48 What Is A Determi Summary. determinant is an important scale in linear algebra. that’s why it has a lot of properties. you don’t need to remember everything line by line. first, try to get the ideas. then play. Using definition 3.1.1, the determinant is given by det (a) = 1 × 4 − 2 × 2 = 0. however notice that the second row is equal to 2 times the first row. then by the discussion above following theorem 3.2.4 the determinant will equal 0. until now, our focus has primarily been on row operations.

Linear Algebra Ch 2 Determinants 3 Of 48 What Is A Determinant

Comments are closed.