Lumbar Instability Tests A Prone Instability Test B Passive Lumbar

Prone Instability Test Lumbar Spine Instability Youtube Technique. the patient lies prone with the body on the examining table and legs over the edge and feet resting on the floor. while the patient rests in this position with the trunk muscles relaxed, the examiner applies posterior to anterior pressure to an individual spinous process of the lumbar spine. any provocation of pain is reported. Passive tests include the posterior shear test, 14 the prone instability test, 33 passive accessory intervertebral motion (paivm) tests, passive physiological intervertebral motion (ppivm) tests, 33, 35 and the passive lumbar extension (ple) test. 30 active tests for structural lsi have included symptom reproduction during the sit to stand 34.
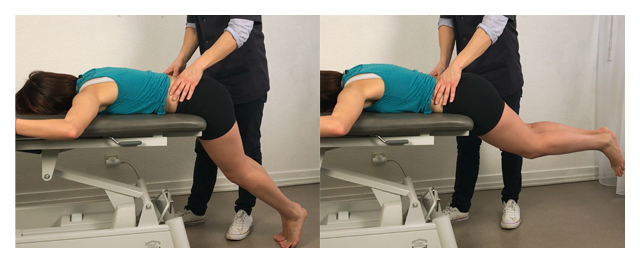
Prone Instability Test Piriforme Prone instability test positive test: pain provoked during the first part of the test decreases when the test is repeated with the legs off the floor. e: contraindications to radiographic assessment (e.g., current pregnancy), previous lumbar fusion surgery, inability (e.g., pain or muscle spasm) to actively flex and extend the spine adequately. The prone instability test is an orthopedic test to assess radiographic lumbar instability – one possible cause of chronic low back pain. several authors have evaluated this test regardings its inter rater reliability and have found kappa values between 0.46 (weak) and 0.87 (strong). however, when it was examined regardings its accuracy to. Introduction. lumbar instability is a pathology of the spine in which there is abnormal mobility or an abnormal joint between two or more contiguous vertebrae. when a patient suffers from lumbar instability, there is excessive movement between the vertebrae and, progressively, a degeneration of the intervertebral joints and can affect the. Several clinical tests, such as aberrant motion, sit to stand, lumbar flexion and prone instability tests, were not found to be associated with instability, as expected. as all the tests were active movement tests, it can be speculated that, when there is passive subsystem dysfunction, the remaining subsystems (active and neural control.
Lumbar And Si Joint Special Tests Lumbar Instability Test Prone Introduction. lumbar instability is a pathology of the spine in which there is abnormal mobility or an abnormal joint between two or more contiguous vertebrae. when a patient suffers from lumbar instability, there is excessive movement between the vertebrae and, progressively, a degeneration of the intervertebral joints and can affect the. Several clinical tests, such as aberrant motion, sit to stand, lumbar flexion and prone instability tests, were not found to be associated with instability, as expected. as all the tests were active movement tests, it can be speculated that, when there is passive subsystem dysfunction, the remaining subsystems (active and neural control. The prone instability test uses the pa glide to assess segmental stiffness and pain provocation with muscles in a resting state and during an active contraction. 27 the first portion of the test is performed with the patient in prone with the lower extremities in contact with the ground while a pa glide is performed at each lumbar segment to. “secondly, no clinical test can detect lumbar instability alone,” dr. ferrari said. “our experience suggests the use of a cluster of tests. the interspinous gap change could be one of these, together with the aberrant movements, passive lumbar extension test, prone instability test, and active straight leg raise test,” dr. ferrari said.

Comments are closed.