Marcus Gunn Pupil Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect Grepm

Marcus Gunn Pupil Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect Grepm Marcus gunn pupil (mgp) is the term given to an abnormal pupil showing aberrant pupillary response in certain ocular disorders. in literature, the term is often used synonymously with marcus gunn phenomenon or relative afferent pupillary defect (rapd).[1] after exposure to bright light, a normal pupil constricts.[2]a marcus gunn pupil, on the other hand, has a relative weakness of the afferent. Marcus gunn pupil: what is it, causes, treatment, and more.
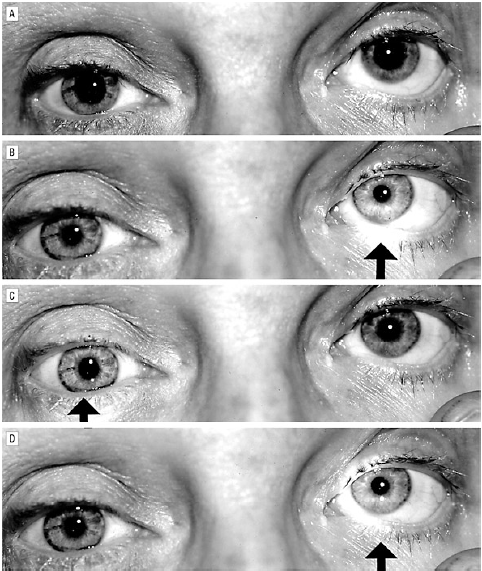
Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect Marcus Gunn Pupil Mrcp It might also be called relative afferent pupillary defect (rapd), gunn’s syndrome or marcus gunn sign. types of marcus gunn pupil or rapd. there are different ways to classify rapd. sometimes, professionals refer to a clinical grading system ranging from one to five based on how much your pupil contracts or dilates when exposed to light. A relative afferent pupillary defect (rapd) also known as a marcus gunn pupil, is a critically important ophthalmological examination finding that defines a defect ( pathology) in the pupil pathway on the afferent side. an rapd is relative to the fellow eye and occurs because of the bilateral and equal innervation of the pupils in normal. Relative afferent pupillary defect. Marcus gunn pupil: causes, treatments, types and more.

Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect Stepwards Relative afferent pupillary defect. Marcus gunn pupil: causes, treatments, types and more. Definition. the relative afferent pupillary defect (rapd) is a clinical sign. the rapd is caused by asymmetrical input to the edinger westphal nuclei from the afferent limb of the visual pathway (e.g., retina, optic nerve, chiasm, optic tract, and pretectal neurons). Relative afferent pupillary defect marcus gunn pupil, unilateral afferent pupillary defect. abbreviation: rapd. the presence of a unilateral afferent pupillary defect. if a flashlight is swung back and forth between the two eyes (swinging flashlight test), the eye with the afferent pupillary defect appears to dilate in response to illumination.

Comments are closed.