More Examples Of Differentiating From First Principles Youtube

More Examples Of Differentiating From First Principles Youtube In this a level maths video i show you how to differentiate from first principles. it's quite simple once you know how! time stamps: 0:00 intro 0:14 what is. A level maths revision tutorial video.for the full list of videos and more revision resources visit mathsgenie.co.uk.
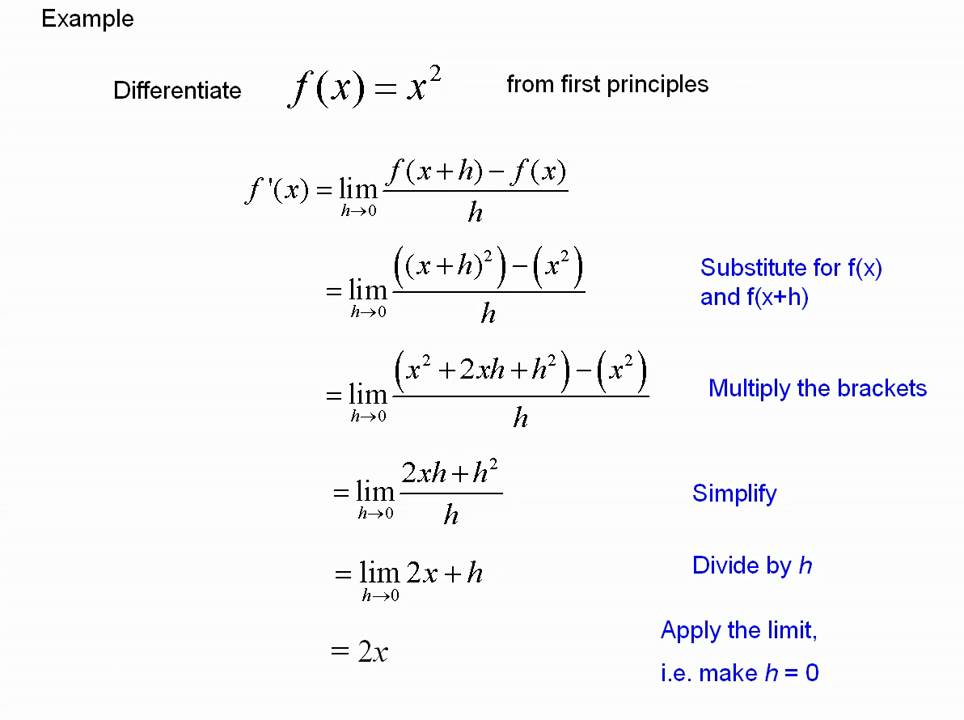
Differentiating From First Principles Youtube Learn the steps for differentiating functions from first principles. this is an important thing to remember for a level and ib maths, as well as some calculu. To do differentiation by first principles: find f (x h) by substituting x with x h in the f (x) equation. substitute f (x h) and f (x) into the first principles equation. simplify the numerator. divide all terms by h. substituting h=0 to evaluate the limit. The aim of differentiation is to find the gradient of the tangent lines to a curve. a tangent touches the curve at one point, and the gradient varies according to the touching coordinate. the tangents of the function f (x)=x² can be explored using the slider below. first principles differentiation first principles differentiation of x n maxima. Definition. the derivative of a function f(x) is denoted by f ′ (x) and is defined as f ′ (x) = lim h → 0f(x h) − f(x) h, h ≠ 0. using this definition is called differentiating from first principles. the result f ′ (x), is called the derivative of f(x). there are rules for differentiation that are far more convenient than using.

Finding The Derivative From First Principles As Level Year 12 The aim of differentiation is to find the gradient of the tangent lines to a curve. a tangent touches the curve at one point, and the gradient varies according to the touching coordinate. the tangents of the function f (x)=x² can be explored using the slider below. first principles differentiation first principles differentiation of x n maxima. Definition. the derivative of a function f(x) is denoted by f ′ (x) and is defined as f ′ (x) = lim h → 0f(x h) − f(x) h, h ≠ 0. using this definition is called differentiating from first principles. the result f ′ (x), is called the derivative of f(x). there are rules for differentiation that are far more convenient than using. Differentiation from first principles example questions. question 1: for f (x) = x f (x) = x, prove that the gradient is fixed at 1 1, using first principles. [2 marks] a level aqa edexcel ocr. show answer. question 2: prove that, for any constant c c where y = c y = c, the gradient \bigg (\dfrac {dy} {dx}\bigg) (dxdy) is 0 0, using first. This is the definition, for any function y = f (x), of the derivative, dy dx. note: given y = f (x), its derivative, or rate of change of y with respect to x is defined as. example. suppose we want to differentiate the function f (x) = 1 x from first principles. a sketch of part of this graph shown below.

Comments are closed.