Normal Force Physics Problems With Tension Inclined Planes Free Body Diagrams

Normal Force Physics Problems With Tension Inclined Planes This physics video explains how to calculate the normal force on a horizontal surface when a downward force is applied or when an upward tension force is use. This physics video tutorial explains how to draw free body diagrams for different situations particular those that involve constant velocity and constant acc ap physics 1: algebra based.

Free Body Diagram Inclined Plane 1) the weight w 1 exerted by the earth on the box. 2) the normal force n. 3) the force of friction f k. 4) the tension force t exerted by the string on the block m 1 . b) free body diagram of block m 2 (right of figure below) 1) the weight of the block w 2. 2) tension t '. tutorials on free body diagrams with several examples and detailed. Draw the free body diagram for the box. solution: to solve this problem, it is better to adopt a tilted coordinate system with the x x axis parallel to the inclined plane, whereas the positive y y axis is perpendicular to the incline. the free body diagram would include the following forces: 1. Draw the free body diagram of an object sliding down a plane inclined 30^\circ 30∘ above the horizontal and experiencing a force of kinetic friction. drawing the object & surface. we’ll start this free body diagram the same way we would any other by drawing in the surface and the object it’s resting on. In figure 5.8.1a 5.8. 1 a, a sled is pulled by force p p → at an angle of 30°. in part (b), we show a free body diagram for this situation, as described by steps 1 and 2 of the problem solving strategy. in part (c), we show all forces in terms of their x and y components, in keeping with step 3.
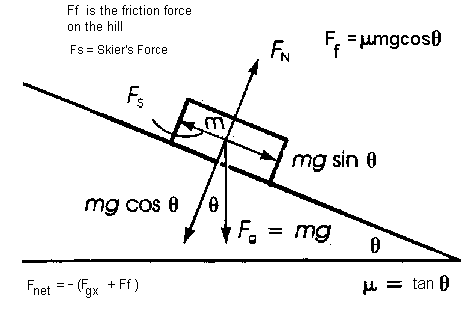
37 Free Body Diagram On Incline Diagram For You Draw the free body diagram of an object sliding down a plane inclined 30^\circ 30∘ above the horizontal and experiencing a force of kinetic friction. drawing the object & surface. we’ll start this free body diagram the same way we would any other by drawing in the surface and the object it’s resting on. In figure 5.8.1a 5.8. 1 a, a sled is pulled by force p p → at an angle of 30°. in part (b), we show a free body diagram for this situation, as described by steps 1 and 2 of the problem solving strategy. in part (c), we show all forces in terms of their x and y components, in keeping with step 3. Let’s apply the problem solving strategy in drawing a free body diagram for a sled. in figure 6.4.1a, a sled is pulled by force →p at an angle of 30°. in part (b), we show a free body diagram for this situation, as described by steps 1 and 2 of the problem solving strategy. in part (c), we show all forces in terms of their x and y. Once we have drawn an accurate free body diagram, we can apply newton’s first law if the body is in equilibrium (balanced forces; that is, f net = 0 f net = 0) or newton’s second law if the body is accelerating (unbalanced force; that is, f net ≠ 0 f net ≠ 0). in forces, we gave a brief problem solving strategy to help you understand.

How To Solve Inclined Plane Problems Youtube Let’s apply the problem solving strategy in drawing a free body diagram for a sled. in figure 6.4.1a, a sled is pulled by force →p at an angle of 30°. in part (b), we show a free body diagram for this situation, as described by steps 1 and 2 of the problem solving strategy. in part (c), we show all forces in terms of their x and y. Once we have drawn an accurate free body diagram, we can apply newton’s first law if the body is in equilibrium (balanced forces; that is, f net = 0 f net = 0) or newton’s second law if the body is accelerating (unbalanced force; that is, f net ≠ 0 f net ≠ 0). in forces, we gave a brief problem solving strategy to help you understand.

Comments are closed.