Normal Pressures In The Heart
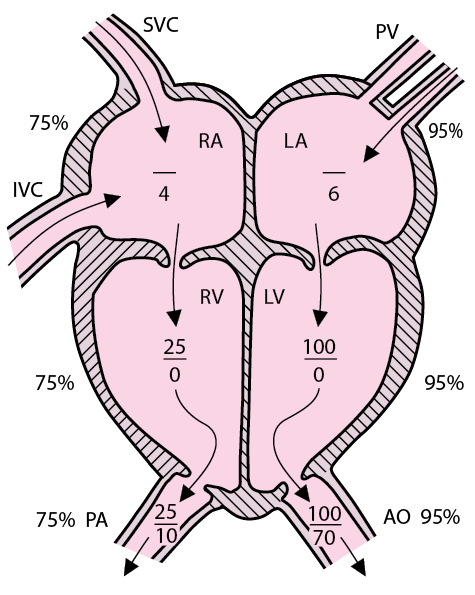
Table Normal Circulation With Representative Right And Left Cardiac Normal pressures in the heart and great vessels. type of pressure. average (mm hg) range (mm hg) right atrium. 3. 0–8. right ventricle. The cardiac cycle can be divided into four stages: filling phase – the ventricles fill during diastole and atrial systole. isovolumetric contraction – the ventricles contract, but as the heart valves are shut, the volume remains constant. this causes a build up of pressure, ready to propel blood into the aorta pulmonary trunk.

Medicowesome Normal Cardiac Pressures Mnemonic Normal Swan Ganz 1. images. overview. normal intracardiac pressures (see chart above) pulmonary wedge pressure (pwp) an approximation of left atrial pressure and left ventricular diastolic pressure. measured with swan ganz catheter. in mitral stenosis, pwp > left ventricular diastolic pressure. The cardiac cycle is a series of pressure changes within the heart. these pressure changes result in blood movement through different chambers of the heart and the body as a whole. these pressure changes originate as conductive electrochemical changes within the myocardium that result in the concentric contraction of cardiac muscle. valves within the heart direct blood movement, which leads to. Representative right heart oxygen saturation = 75%; representative left heart oxygen saturation = 95%. atrial pressures are mean pressures. atrial pressures are mean pressures. ao = aorta; ivc = inferior vena cava; la = left atrium; lv = left ventricle; pa = pulmonary artery; pv = pulmonary veins; ra = right atrium; rv = right ventricle; svc = superior vena cava. The bottom number is called diastolic pressure. this is pressure in the arteries between heartbeats. the top number minus the bottom number is the pulse pressure. so if the resting blood pressure is 120 80 mm hg, the pulse pressure is 40. this is considered a healthy pulse pressure. generally, a pulse pressure greater than 40 mm hg is unhealthy.

Normal Intracardiac Pressure Youtube Representative right heart oxygen saturation = 75%; representative left heart oxygen saturation = 95%. atrial pressures are mean pressures. atrial pressures are mean pressures. ao = aorta; ivc = inferior vena cava; la = left atrium; lv = left ventricle; pa = pulmonary artery; pv = pulmonary veins; ra = right atrium; rv = right ventricle; svc = superior vena cava. The bottom number is called diastolic pressure. this is pressure in the arteries between heartbeats. the top number minus the bottom number is the pulse pressure. so if the resting blood pressure is 120 80 mm hg, the pulse pressure is 40. this is considered a healthy pulse pressure. generally, a pulse pressure greater than 40 mm hg is unhealthy. Figure 19.3.3 – heart sounds and the cardiac cycle: in this illustration, the x axis reflects time with a recording of the heart sounds. the y axis represents pressure. the term murmur is used to describe an unusual sound coming from the heart that is caused by the turbulent flow of blood, usually due to valve problesms. for example an. At rest, a heart rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute is normal. when you exercise, your heart beats faster, and your heart rate speeds up to get more oxygen to your muscles. signals from your body’s nervous system and hormones from your endocrine system control how fast and hard your heart beats. these signals and hormones allow you to adapt.

11 Heart Rate Rhythm And Contractility Veterian Key Figure 19.3.3 – heart sounds and the cardiac cycle: in this illustration, the x axis reflects time with a recording of the heart sounds. the y axis represents pressure. the term murmur is used to describe an unusual sound coming from the heart that is caused by the turbulent flow of blood, usually due to valve problesms. for example an. At rest, a heart rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute is normal. when you exercise, your heart beats faster, and your heart rate speeds up to get more oxygen to your muscles. signals from your body’s nervous system and hormones from your endocrine system control how fast and hard your heart beats. these signals and hormones allow you to adapt.

Comments are closed.