Part 5 Of 13 Dog Color Genetics Pied And Brindle Genes

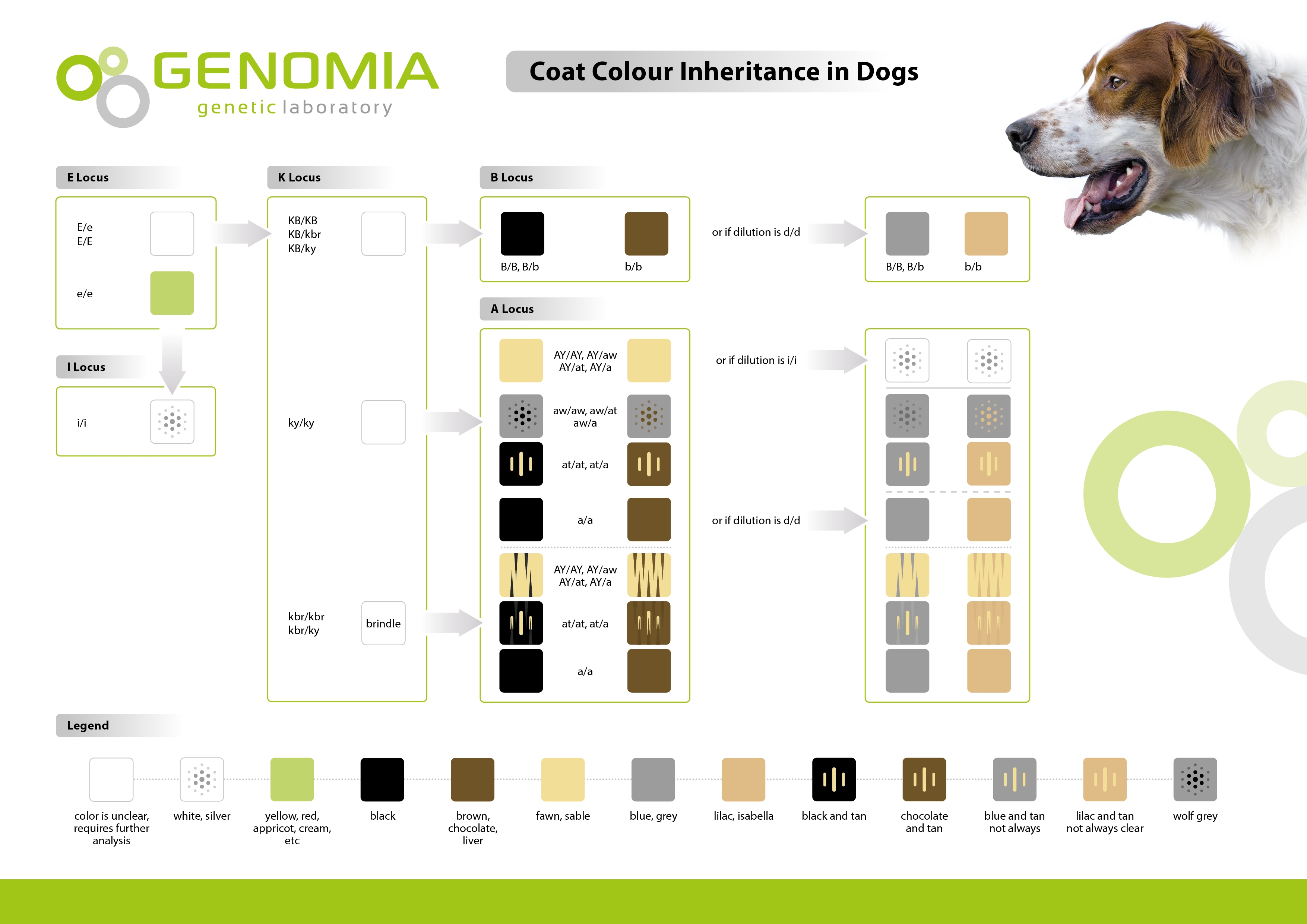
Part 5 Of 13 Dog Color Genetics Pied And Brindle Genes Youtube 13 part series all about color genetics all about dog breeding lovemypups don't forget, subscribe, like and make comments, our store: mybre. E (extension) locus. this locus creates the black facial mask of many dogs as well as yellow or red coats. the four alleles of this gene in order of dominance are: melanistic mask (em), grizzle (eg), black (e) and red (e). k (dominant black) locus. this gene controls dominant black, brindle, and fawn colors.
Dog Dna Color Chart Ponasa A dog with two piebald s alleles will display some extent of white patterning. a heterozygous ss dog may or may not have white patterning. a dog with two non piebald alleles will not have piebald markings, although they may have white fur due to other genes. negative health outcomes associated with coat color. Pheomelanin is a red pigment with yellow or gold as the default color. pheomelanin is responsible for reds that produce deep red, cream, orange, yellow, gold, or tan. various genes control the influence of pheomelanin; some make it weaker, and some make it stronger. pheomelanin only affects coat color, but eumelanin influences the nose and eye. As a reminder, each dog has two copies of each gene (or “ locus “). this results in each dog having two of the possible versions of each gene (or “ alleles “). dogs can have two copies of the same allele (e.g. b b), in which case they’re homozygous, or two different alleles (e.g. b b), in which case they’re heterozygous. Colors: black, yellow, and red. canines produce two types of pigment: eumelanin, which is black pigment; and phaeomelanin which is red yellow pigment. it is the combination of these pigments, along with dilutions, modifiers, and white patterns, that make up the entire spectrum of dog coat colors. in dogs and wolves there are four known alleles.

Dog Color Breeding Chart As a reminder, each dog has two copies of each gene (or “ locus “). this results in each dog having two of the possible versions of each gene (or “ alleles “). dogs can have two copies of the same allele (e.g. b b), in which case they’re homozygous, or two different alleles (e.g. b b), in which case they’re heterozygous. Colors: black, yellow, and red. canines produce two types of pigment: eumelanin, which is black pigment; and phaeomelanin which is red yellow pigment. it is the combination of these pigments, along with dilutions, modifiers, and white patterns, that make up the entire spectrum of dog coat colors. in dogs and wolves there are four known alleles. This is the color often associated with weimaraners. what embark reports for the s locus: the s locus (mitf) controls where pigment is produced in a dog’s coat and skin. an insertion near the mitf gene turns off pigment production in the coat and skin, resulting in white hair and or pink skin. Single tests: canine coat color and type background mammals have two pigments that are the basis of hair color: eumelanin (black) and phaeomelanin (red or yellow). one of the genes involved in the production of these pigments in many species including dogs is melanocortin 1 receptor (mc1r) which is also known as the extension locus.

Comments are closed.