Periodic Table Reactivity Arrows Periodic Table Timeline

Reactivity Shown In The Periodic Table Download Scientific Diagram Figure 1.6.1 1.6. 1: the periodic table. red elements are the alkali and alkaline earth metals (s block). yellow elements are the transition metals (d block). orange elements are the lanthanides and actinides (f block). green, blue and purple elements are the p block; together with the s block, they are called the main group elements. Problem example 5 5: draw an electron dot diagram for the element helium. helium has an atomic number of 2, so there are 2 electrons in the neon atom. as in the examples above, the electrons fill the energy levels starting at the lowest level, resulting in an electron distribution of: energy level 1: 2 electrons.
Periodic Table Reactivity Series Brokeasshome Atomic radius: atomic radius is a term describing the distance between an atom’s nucleus, and its outermost electron shell. several factors affect this distance; including the number of an element, and the number of electron shells. through periodic trends, the atomic radius increases in size further left of a period, and lower down a group. The redox properties of the elements very roughly follow the following general trends: as one moves towards the left of the periodic table, elements tend to act as good reductants, while those towards the right tend to act as increasingly good oxidants. as one moves down a group of the periodic table, elements tend to act as either weaker. Join me as we decode the periodic table and review what patterns we can use to identify groups and valence electrons, periods and energy levels, and reactivity!. Chemistry for the gifted and talented: trends in reactivity in the periodic table. bookmark. this could be used to follow up some work on the periodic table where the trends in reactivity in groups 1 and 7 have been identified. it can be used as a differentiated activity for the more able students within a group.
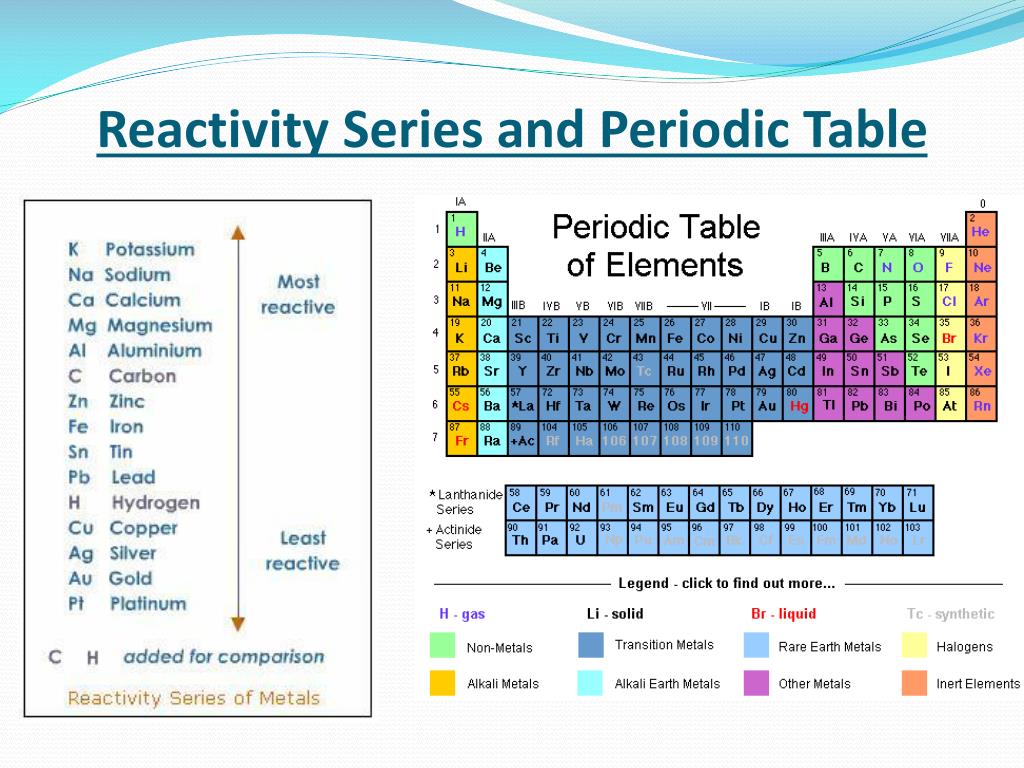
Reactivity Table Join me as we decode the periodic table and review what patterns we can use to identify groups and valence electrons, periods and energy levels, and reactivity!. Chemistry for the gifted and talented: trends in reactivity in the periodic table. bookmark. this could be used to follow up some work on the periodic table where the trends in reactivity in groups 1 and 7 have been identified. it can be used as a differentiated activity for the more able students within a group. In this article, you will learn about the reactivity series, including its significance and its applications. after reading this article, you will be able to understand the nature of the reactivity series as well as its uses and functions. topics covered in other articles. interactive periodic table; periodic trends made easy; atomic radius trend. Metallic and nonmetallic character. metallic character refers to the level of reactivity of a metal. metals tend to lose electrons in chemical reactions, as indicated by their low ionization energies. within a compound, metal atoms have relatively low attraction for electrons, as indicated by their low electronegativities.

Comments are closed.