Phase Change Cooler Diagram
Phase Change Diagrams вђ Overview Examples Expii Materials. to build a system we will need copper piping. the accepted pipe sizes are ¼” for discharge and 3 8″ for suction in most of the small systems we work with. the copper piping is purchased from a local refrigeration supplier, the ¼” pipe comes in 15 meter coiled lengths and the 3 8″ in 5 meter straight lengths. The science behind heat exchangers. phase change cooling involves harnessing a cooling fluid’s natural latent heat of vaporization, or the point at which it transitions from a liquid phase into a gaseous phase (and vice versa). instead of using chilled air to eradicate the electrical waste heat in an enclosure, a heat exchanger’s fluid can.

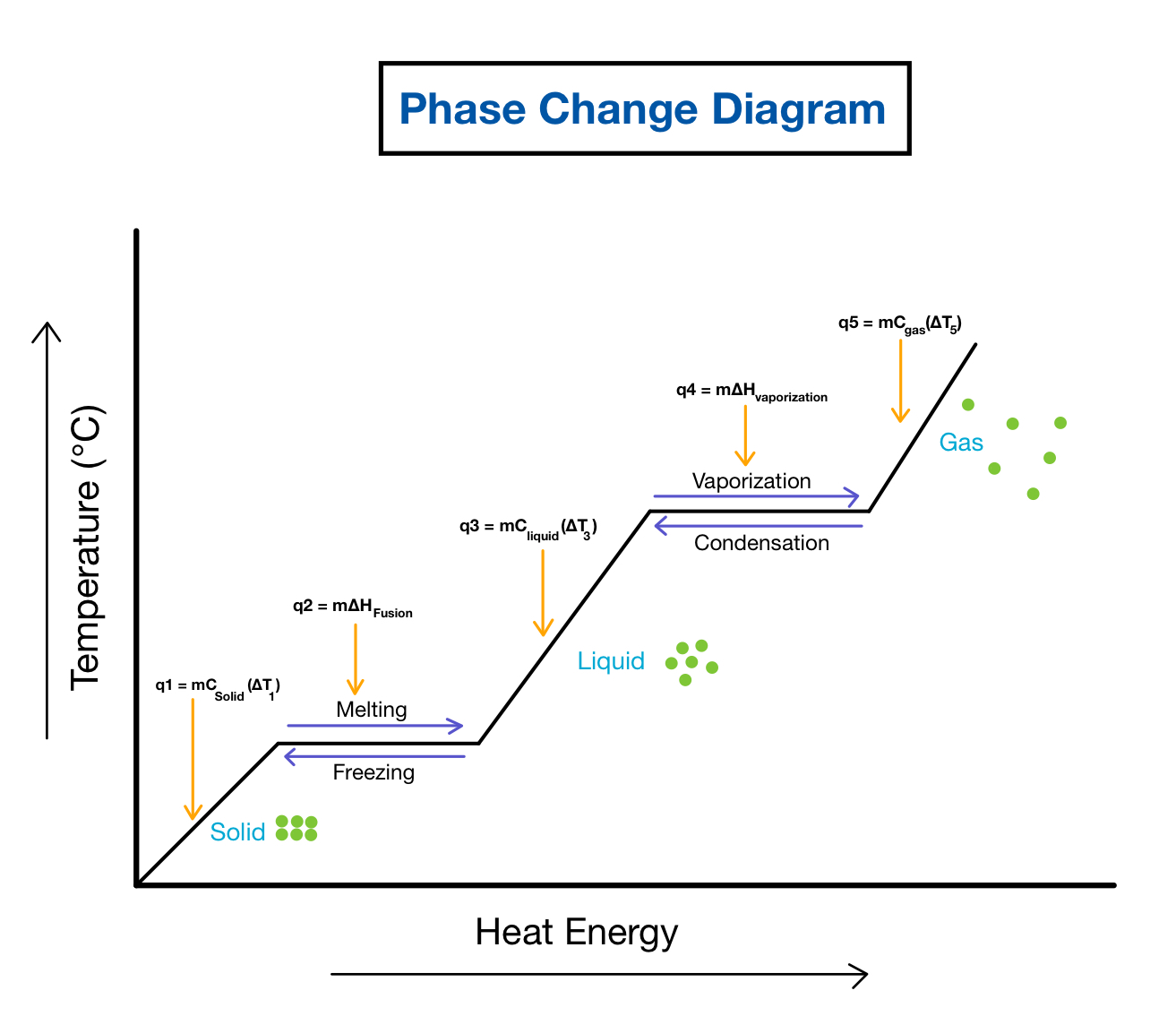
Extreme Cooling Part Ii Introduced and reviewed existing phase change cooing in data centers. compared and summarized the characteristics of phase change cooling systems. analyzed the application limitations of phase change cooling technologies. explored the future research direction of phase change cooling technologies. Table 11.3 latent heats of fusion and vaporization, along with melting and boiling points. let’s consider the example of adding heat to ice to examine its transitions through all three phases—solid to liquid to gas. a phase diagram indicating the temperature changes of water as energy is added is shown in figure 11.10. Solution: when two substances or objects at different temperatures are brought into contact, heat will flow from the warmer one to the cooler. the amount of heat that flows is given by. q = mcsΔt (16.3.1) (16.3.1) q = m c s Δ t. where q is heat, m is mass, cs is the specific heat, and Δ t is the temperature change. Heat exchanger calculations are based on the log mean temperature difference. = ∆ ∆ 2 − ∆ 1 ∆ = =. ∆ 2 Τ∆ 1. =. 1Τ h 1 Τ h. h, − , − h, − , h, − , ൗ h, − , hi and ho can be calculated using the nusselt number correlations shown earlier. another way to size a heat exchanger would be to use the effectiveness ntu method.

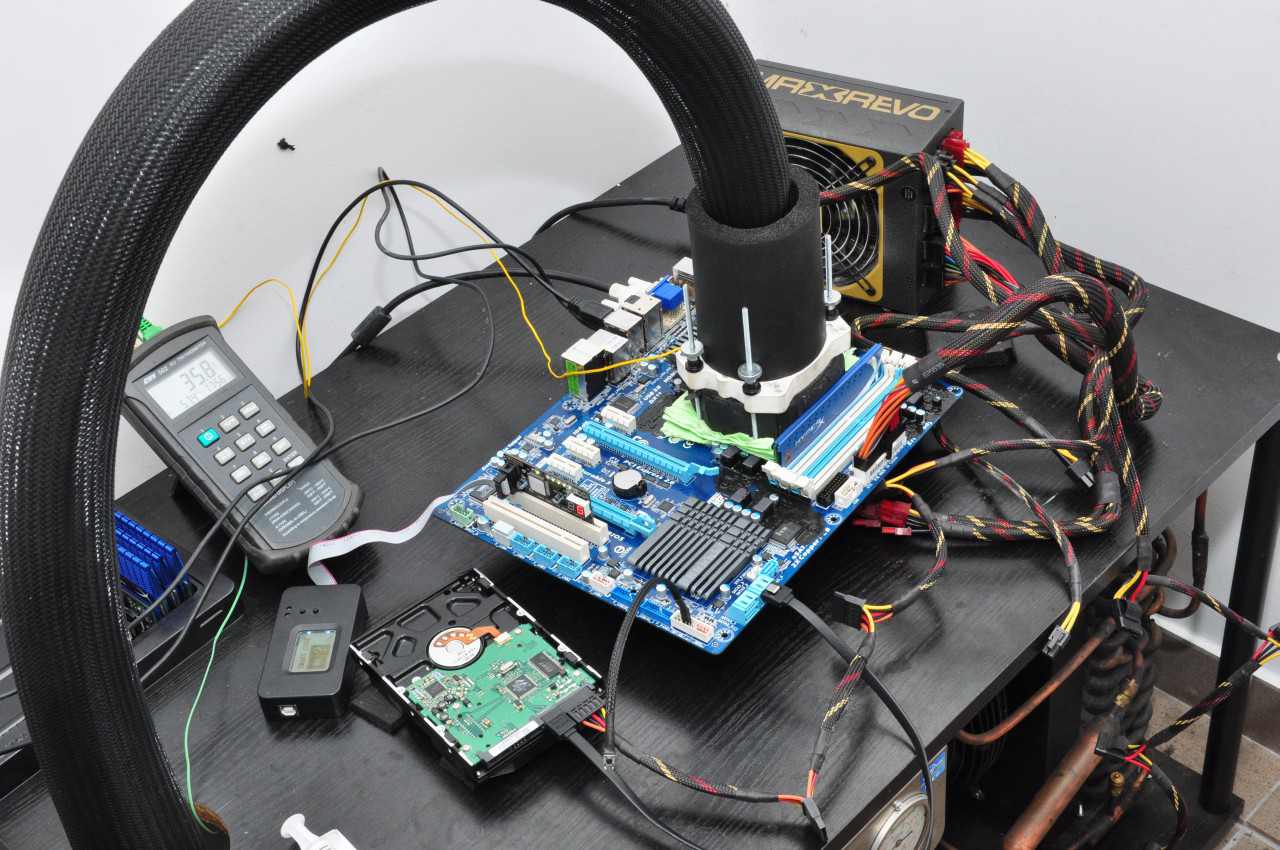
What Is Phase Change Explained By Thermal Engineers Solution: when two substances or objects at different temperatures are brought into contact, heat will flow from the warmer one to the cooler. the amount of heat that flows is given by. q = mcsΔt (16.3.1) (16.3.1) q = m c s Δ t. where q is heat, m is mass, cs is the specific heat, and Δ t is the temperature change. Heat exchanger calculations are based on the log mean temperature difference. = ∆ ∆ 2 − ∆ 1 ∆ = =. ∆ 2 Τ∆ 1. =. 1Τ h 1 Τ h. h, − , − h, − , h, − , ൗ h, − , hi and ho can be calculated using the nusselt number correlations shown earlier. another way to size a heat exchanger would be to use the effectiveness ntu method. A phase change material ( pcm) is a substance which releases absorbs sufficient energy at phase transition to provide useful heat or cooling. generally the transition will be from one of the first two fundamental states of matter solid and liquid to the other. the phase transition may also be between non classical states of matter, such as. A compressor and condenser turn gas into liquid, and an evaporator converts it back into gas, while absorbing heat from the cpu chip and other components. phase change cooling creates subzero.

Phase Change Diagrams вђ Overview Examples Expii A phase change material ( pcm) is a substance which releases absorbs sufficient energy at phase transition to provide useful heat or cooling. generally the transition will be from one of the first two fundamental states of matter solid and liquid to the other. the phase transition may also be between non classical states of matter, such as. A compressor and condenser turn gas into liquid, and an evaporator converts it back into gas, while absorbing heat from the cpu chip and other components. phase change cooling creates subzero.
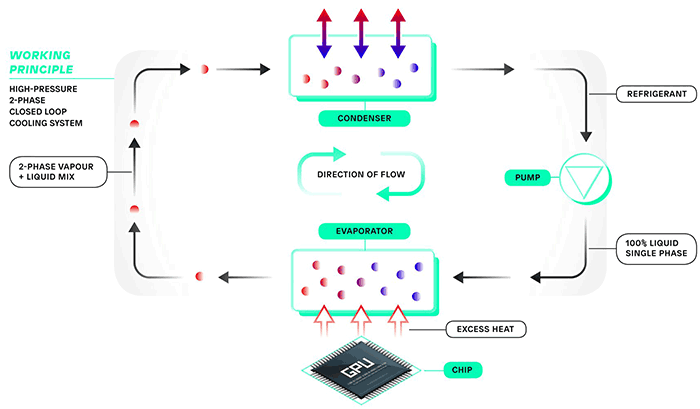
Gigabyte Works With Incooling For Phase Change Cooled Systems Cooling

Comments are closed.