Polysaccharides Examples And Structure Image Nutrients Review
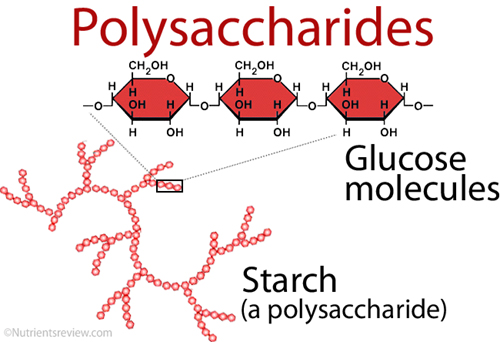
Polysaccharides Examples And Structure Image Nutrients Review Starch is in cereal grains (wheat, oats, rye, barley, buckwheat, rice, etc.), potatoes and legumes (beans, peas, lentils). fiber is mainly in whole grains (whole grain bread, brown rice, etc.), legumes, vegetables and fruits. animal foods are a poor source of polysaccharides: a small amount of glycogen is in shellfish and animal liver. A polysaccharide is a large molecule made of many smaller monosaccharides. monosaccharides are simple sugars, like glucose. special enzymes bind these small monomers together creating large sugar polymers, or polysaccharides. a polysaccharide is also called a glycan. a polysaccharide can be a homopolysaccharide, in which all the monosaccharides.
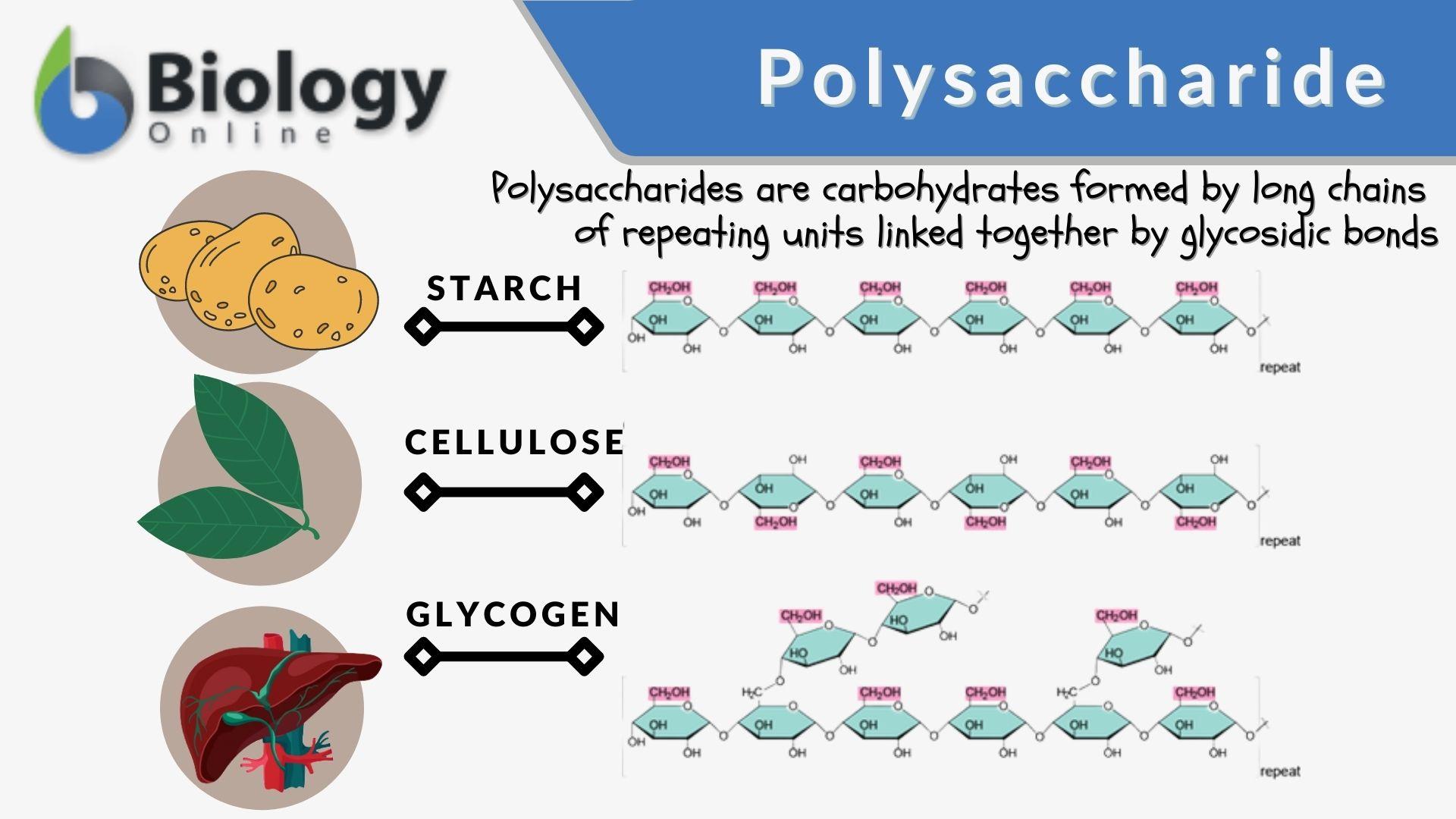
Polysaccharide Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary The structural classification of polysaccharides follows the suit of proteins and dnas, i.e., the structure of polysaccharides can be divided into primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures. 39. like other biomolecules, the higher structure of the polysaccharide chain is based on its primary structure. Structural polysaccharides are involved in providing support and structure to cells and tissues. they contribute to the formation of various structural components in organisms. examples of structural polysaccharides include: a. cellulose: cellulose is the most abundant structural polysaccharide found in plants. This chapter discusses the diversity in structure and properties that results when multiple monosaccharides (chapter 2) are linked together to form oligosaccharides and polysaccharides (the latter comprising much of the biomass on the planet). some examples of the more complex polymeric assemblies that occur in nature are presented, and how these remarkable structures are generated is discussed. Polysaccharides are polymers of sugars linked by glycosidic bonds. they have many nutritional benefits, including prebiotic effects, anti inflammation, and gut microbiota modulation. molecular structure investigation helps to understand polysaccharides’ functional, conformational properties and biological activities, facilitating their applications in food and nutraceuticals products. date.

Comments are closed.