Power Electronics Thermal Management And Heatsink Design

Power Electronics Thermal Management And Heatsink Design Youtube This video discusses thermal management and demonstrates th join dr. martin ordonez and dr. rouhollah shafaei in a lesson on mosfet heat transfer mechanisms. Heat sink architecture for power electronics. heat is transferred through three primary mechanisms: conduction, convection, and radiation. the thermal effectiveness of a heat sink is established by summing up the thermal resistances within the network of interest (electronics, heat sink, and surroundings) and then multiplying this value (in oc w) by the heat source's maximum power output (tdp.
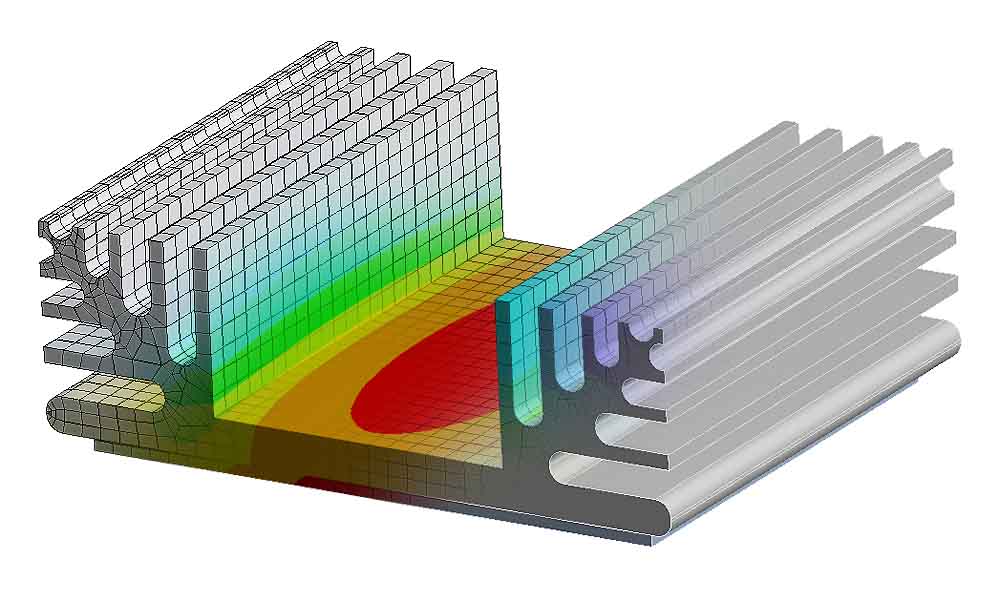
Thermal Management And Design Of Heat Sinks Cademix Institute Of Heat sink design facts & guidelines for thermal analysis. Limited thermal budget and space make the choice of a particular type of heatsink very important. this is where the volume of the heatsink becomes relevant. the volume of a heatsink for a given flow condition can be obtained by using the following equation: volume(heatsink) = volumetric resistance (cm3 °c w) thermal resistance θ sa (°c w). This depends on the amount of power dissipation and the thermal resistance between the junction and the package surface (referred to as “case” hereafter), an ambient and some other specified reference point. this chapter introduces the thermal management, design, and cooling methods for power electronic packaging. The amount the surface temperature rises above ambient, divided by the heat dissipated, gives a result for thermal impedance at that specific operating condition. here, the dispersed heat is 2.78 w, resulting in a surface temperature rise above ambient of 53°c. dividing 53°c by 2.78 w will result in a sink to ambient thermal impedance of 19.1.
Advanced Thermal Solutions Releases Heat Sinks For High Component This depends on the amount of power dissipation and the thermal resistance between the junction and the package surface (referred to as “case” hereafter), an ambient and some other specified reference point. this chapter introduces the thermal management, design, and cooling methods for power electronic packaging. The amount the surface temperature rises above ambient, divided by the heat dissipated, gives a result for thermal impedance at that specific operating condition. here, the dispersed heat is 2.78 w, resulting in a surface temperature rise above ambient of 53°c. dividing 53°c by 2.78 w will result in a sink to ambient thermal impedance of 19.1. Abstract. power electronics are vital for the generation, conversion, transmission, and distribution of electrical energy. improving the efficiency, power density, and reliability of power electronics is an important challenge that can be addressed with electrothermal codesign and optimization. current thermal management approaches utilize metallic heat sinks (hss), resulting in parasitic load. Overview of heat sink design basics and principles. it’s important for electrical engineers to remember the basics and how they affect our designs. when it comes to thermal management, thermal resistance, and heat sinks, the three main phenomena that drive heat transfer are convection, conduction, and radiation.
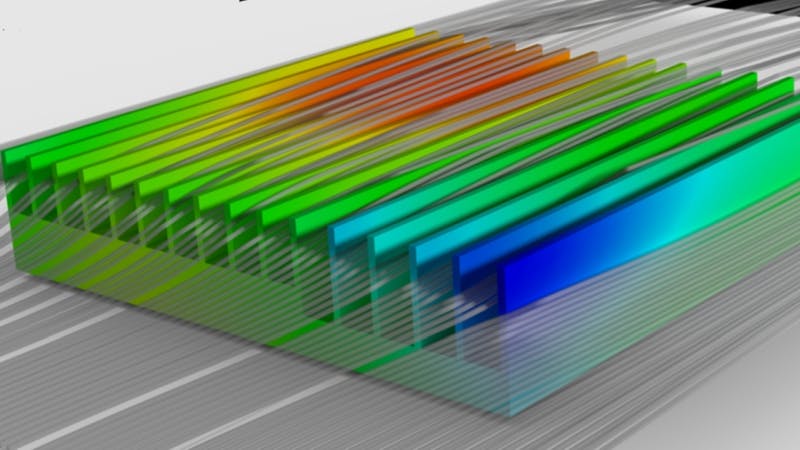
Heatsink Thermal Design Considerations For Electronics Cooling Abstract. power electronics are vital for the generation, conversion, transmission, and distribution of electrical energy. improving the efficiency, power density, and reliability of power electronics is an important challenge that can be addressed with electrothermal codesign and optimization. current thermal management approaches utilize metallic heat sinks (hss), resulting in parasitic load. Overview of heat sink design basics and principles. it’s important for electrical engineers to remember the basics and how they affect our designs. when it comes to thermal management, thermal resistance, and heat sinks, the three main phenomena that drive heat transfer are convection, conduction, and radiation.

Solidworks Tutorial 023t Cpu Heatsink With Thermal Heat Simulation

Comments are closed.