Ppt C1 Differentiation From First Principles Powerpoint Presentation

Ppt C1 Differentiation From First Principles Powerpoint Presentation Differentiation from first principles at the limit where δx→ 0, 6 δx→ 6. we write this as: 6 so the gradient of the tangent to the curve y = x2 at the point (3, 9) is 6. let’s apply this method to a general point on the curve y = x2. if we let the x coordinate of a general point a on the curve y = x2 be x, then the y coordinate will. Presentation on theme: "c1: differentiation from first principles"— presentation transcript: 1 c1: differentiation from first principles learning objective: to understand that differentiation is the process for calculating the gradient of a curve.
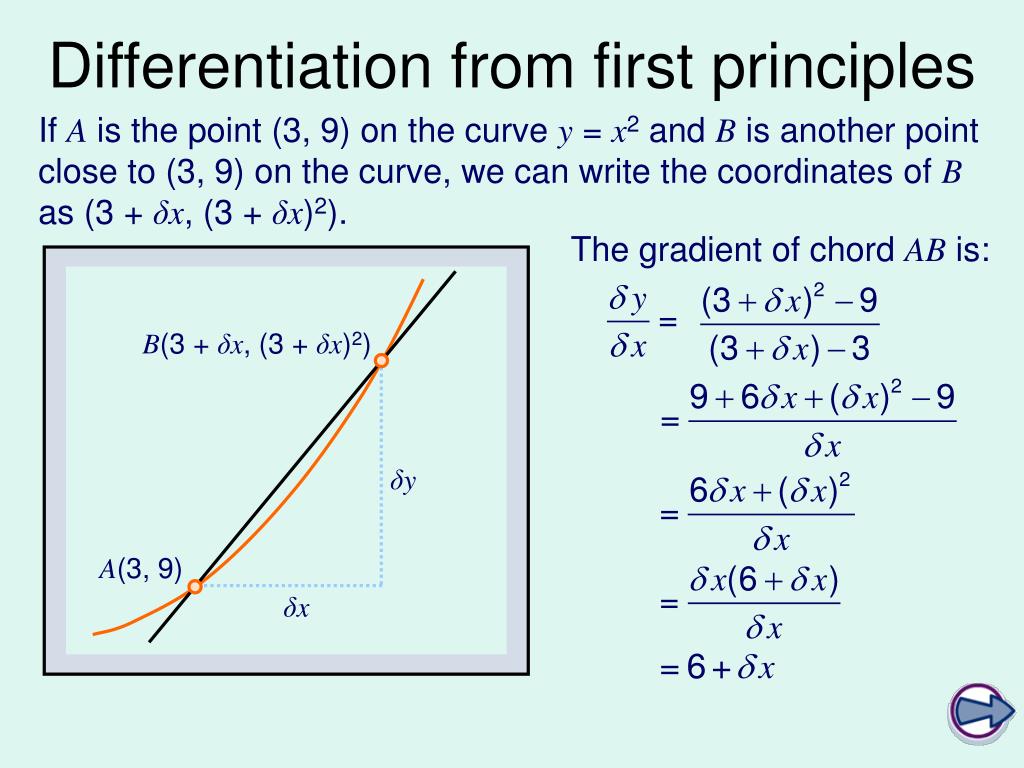
Ppt C1 Differentiation From First Principles Powerpoint Presentation Differentiation from first principles learning objective: to understand that differentiation is the process for calculating the gradient of a curve. the rate of change can be calculated from first principles by considering the limit of the function at any one point. rates of change 40 distance (m) 0 time (s) 5 this graph shows the distance that. Presentation on theme: "differentiation from first principles"— presentation transcript: 1 differentiation from first principles. f (x h) a f (x) x x h gradient of ap =. 2 differentiation from first principles. f (x h) a f (x) x x h gradient of ap =. 3 differentiation from first principles. f (x h) a f (x) x x h gradient of ap =. Ai enhanced description. the document discusses the concept of differentiability using limits and four examples: 1) the function f (x) = x 5 is not differentiable at x = 5 since the left and right hand derivatives are not equal. 2) the function f (x) = x^x, 0 ≤ x < 2 and f (x) = (x 1)x, 2 ≤ x < 3 is not differentiable at x = 2 since the. Resource type: lesson (complete) file previews. pdf, 393.23 kb. pptx, 1.24 mb. “ differentiation from first principles ” starts by illustrating the difficulty of finding a reliable answer for the gradient at a point on a curve by drawing a tangent to the curve. pupils compare their answers for the gradient at two points on a cubic graph.
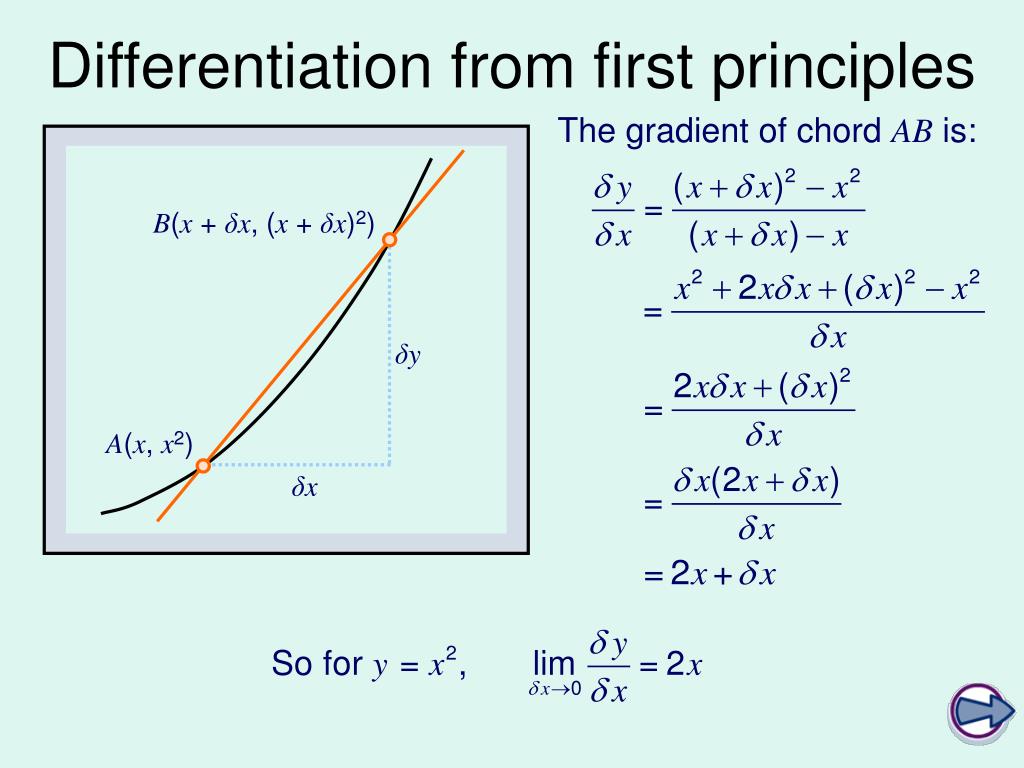
Ppt C1 Differentiation From First Principles Powerpoint Presentation Ai enhanced description. the document discusses the concept of differentiability using limits and four examples: 1) the function f (x) = x 5 is not differentiable at x = 5 since the left and right hand derivatives are not equal. 2) the function f (x) = x^x, 0 ≤ x < 2 and f (x) = (x 1)x, 2 ≤ x < 3 is not differentiable at x = 2 since the. Resource type: lesson (complete) file previews. pdf, 393.23 kb. pptx, 1.24 mb. “ differentiation from first principles ” starts by illustrating the difficulty of finding a reliable answer for the gradient at a point on a curve by drawing a tangent to the curve. pupils compare their answers for the gradient at two points on a cubic graph. On tes i have a wide range of resources for gcse and a level maths. year 1 powerpoint explains where the formula for differentiation from first principles comes from, and demonstrates how it’s used for positive integer powers of x. ends with some questions to practise the skills required (solutions provided in a separate pdf file as well as. The aim of differentiation is to find the gradient of the tangent lines to a curve. a tangent touches the curve at one point, and the gradient varies according to the touching coordinate. the tangents of the function f (x)=x² can be explored using the slider below. first principles differentiation first principles differentiation of x n maxima.

Comments are closed.