Producers Consumers In Biology Overview Examples Lesson Study

Producers Decomposers Consumers Examples The producer definition in biology is an organism that makes its own food. an organism is any living thing, whether plant, animal, bacteria, fungi, etc. while plants are definitely producers. Short summary. in summary, producers are organisms that make their own food. producers create food for themselves and also provide energy for the rest of the ecosystem. any green plant, like a.
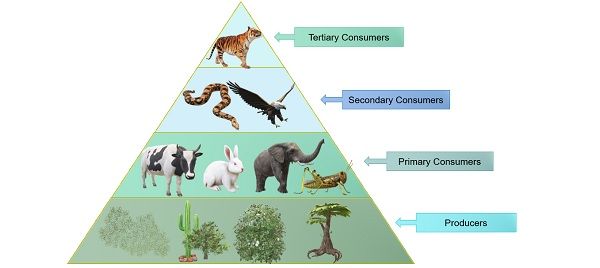
Producers And Consumers Summary. ecosystems require constant inputs of energy from sunlight or chemicals. producers use energy and inorganic molecules to make food. consumers take in food by eating producers or other living things. decomposers break down dead organisms and other organic wastes and release inorganic molecules back to the environment. Some examples of producer organisms include: trees. grass. algae. cyanobacteria. phytoplankton. all of these organisms are producers because they are able to make their own food. A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another. let's look at the parts of a typical food chain, starting from the bottom—the producers—and moving upward. at the base of the food chain lie the primary producers. Presentation, review with students the ecological role and examples of this in their local communities. 6. discuss the different ecological roles. have a whole class discussion about the different roles and the examples they gave. have students compare the local examples to the global examples for each. ask: which did they find.

Producers Consumers In Biology Overview Examples Lesson Study A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another. let's look at the parts of a typical food chain, starting from the bottom—the producers—and moving upward. at the base of the food chain lie the primary producers. Presentation, review with students the ecological role and examples of this in their local communities. 6. discuss the different ecological roles. have a whole class discussion about the different roles and the examples they gave. have students compare the local examples to the global examples for each. ask: which did they find. Many producers make their own food through the process of photosynthesis. the "food" the producers make is the sugar, glucose. producers make food for the rest of the ecosystem. as energy is not recycled, energy must consistently be captured by producers. this energy is then passed on to the organisms that eat the producers, and then to the. A. decomposers. b. primary consumers. c. primary producers. d. secondary consumers. what term describes animals which produce their own food? a. autotrophs b. chemoautotrophs c. chemotrophs d. heterotrophs; explain the difference between a food chain and a food web in an ecosystem. flora (plants) are a) heterotrophs b) homeotherms c) consumers.

Comments are closed.