Refrigeration As Refrigeration

Hvac Refrigeration Cycle Refrigeration, the process of removing heat from an enclosed space or from a substance for the purpose of lowering the temperature. in the industrialized nations and affluent regions in the developing world, refrigeration is chiefly used to store foodstuffs at low temperatures, thus inhibiting the destructive action of bacteria, yeast, and mold. Refrigeration is any of various types of cooling of a space, substance, or system to lower and or maintain its temperature below the ambient one (while the removed heat is ejected to a place of higher temperature). [1][2] refrigeration is an artificial, or human made, cooling method. [1][2] refrigeration refers to the process by which energy.
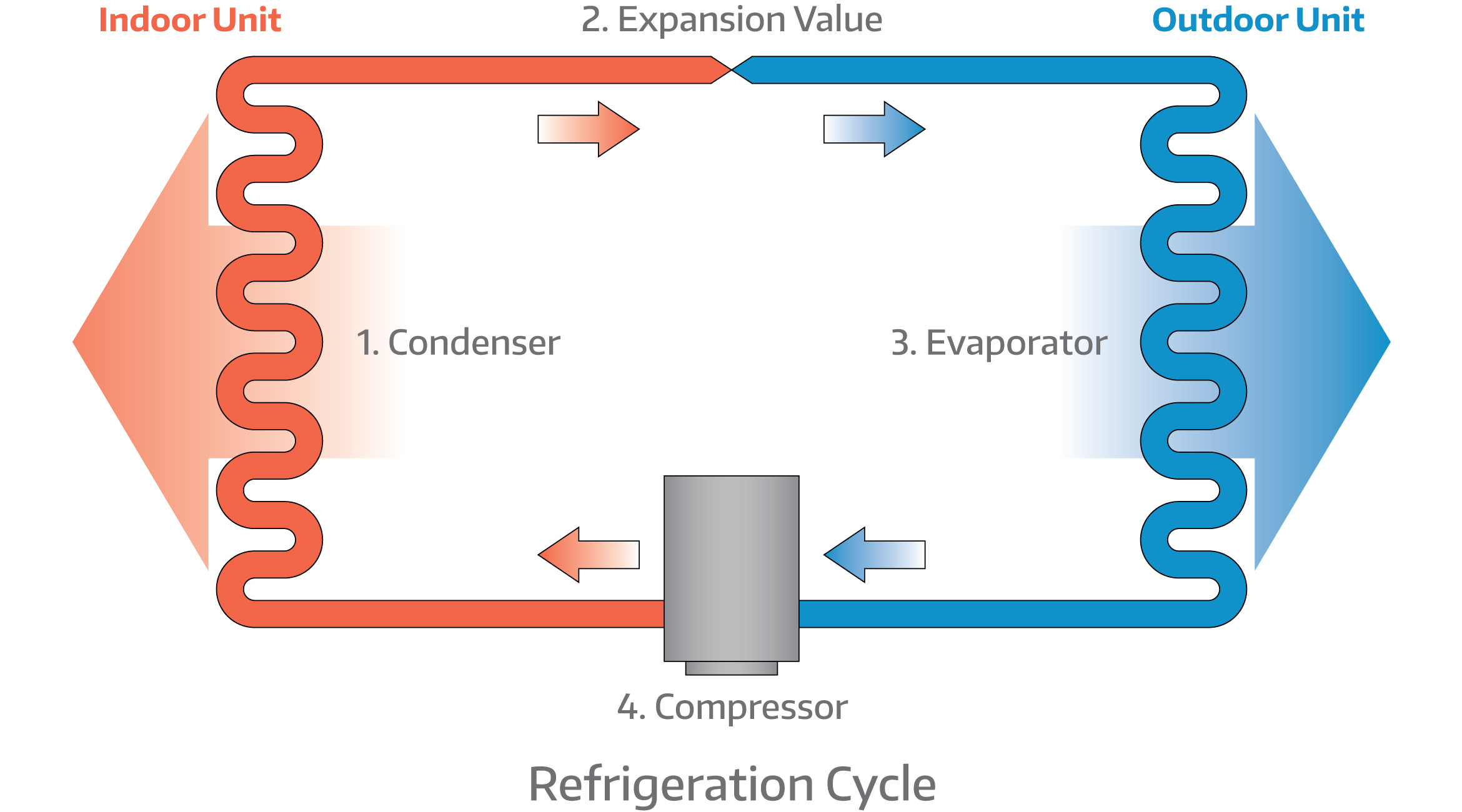
Refrigeration Cycle Real Refrigeration Types of refrigeration systems vapor compression refrigeration. vapor compression refrigeration is the rockstar behind most fridges and ac units. picture it as a cycle of transformation – the refrigerant starts as a cool, low pressure gas in the evaporator, absorbing heat and turning into a warm gas. Refrigeration effect "ton" a common term that has been used in refrigeration work to define and measure capacity or refrigeration effect is called a ton of refrigeration. it is the amount of heat absorbed in melting a tone of ice (2,000 lb) over a 24 hour period. the ton of refrigeration is equal to 288,000 btu. this may be calculated by. This cycle involves four key phases: evaporation, compression, condensation, and expansion. evaporation: the refrigeration cycle begins in the evaporator with a low pressure liquid refrigerant absorbing heat from its surrounding environment. as the refrigerant absorbs heat, it changes state from a liquid to a vapor. Generally, refrigeration is the action of cooling, and in practice, this requires the removal of heat and discarding it at a higher temperature. therefore, refrigeration is the device of moving heat from a lower temperature to a higher temperature. in addition to cooling applications, refrigeration is utilized in air conditioning and heat pumps.

Refrigeration Refrigeration Schematic This cycle involves four key phases: evaporation, compression, condensation, and expansion. evaporation: the refrigeration cycle begins in the evaporator with a low pressure liquid refrigerant absorbing heat from its surrounding environment. as the refrigerant absorbs heat, it changes state from a liquid to a vapor. Generally, refrigeration is the action of cooling, and in practice, this requires the removal of heat and discarding it at a higher temperature. therefore, refrigeration is the device of moving heat from a lower temperature to a higher temperature. in addition to cooling applications, refrigeration is utilized in air conditioning and heat pumps. One ton of refrigeration: it can be defined as the amount of refrigeration effect produced by the uniform melting of one tone of ice (1000 kg) from and at 0°c in 24 hrs. 1 tonne of refrigeration (tr)= (335x1000) 24. where latent heat of ice= 335 kj kg= 13958.333 kj hr= 13958.333 24 kj min. 1 tonne of refrigeration (tr)= 232.6 kj min. Flashing lowers the coolant temperature to a saturation temperature at the low side pressure. b→ c: low temperature refrigerant receives heat from the environment and continues to evaporate as it flows at constant pressure through the evaporator. refrigeration cycle: hvac system basics and refrigerant charging from r hvac.

Hvac R Refrigerant Cycle Basics Hvac School One ton of refrigeration: it can be defined as the amount of refrigeration effect produced by the uniform melting of one tone of ice (1000 kg) from and at 0°c in 24 hrs. 1 tonne of refrigeration (tr)= (335x1000) 24. where latent heat of ice= 335 kj kg= 13958.333 kj hr= 13958.333 24 kj min. 1 tonne of refrigeration (tr)= 232.6 kj min. Flashing lowers the coolant temperature to a saturation temperature at the low side pressure. b→ c: low temperature refrigerant receives heat from the environment and continues to evaporate as it flows at constant pressure through the evaporator. refrigeration cycle: hvac system basics and refrigerant charging from r hvac.

Comments are closed.