Rna Polymerase In Prokaryotes

Rna Polymerase In Prokaryotes Prokaryotic and eukaryotic rna polymerase. Prokaryotic rna polymerase. prokaryotes use the same rna polymerase to transcribe all of their genes. in e. coli, the polymerase is composed of five polypeptide subunits, two of which are identical. four of these subunits, denoted α, α, β, and β' comprise the polymerase core enzyme. these subunits assemble every time a gene is transcribed.
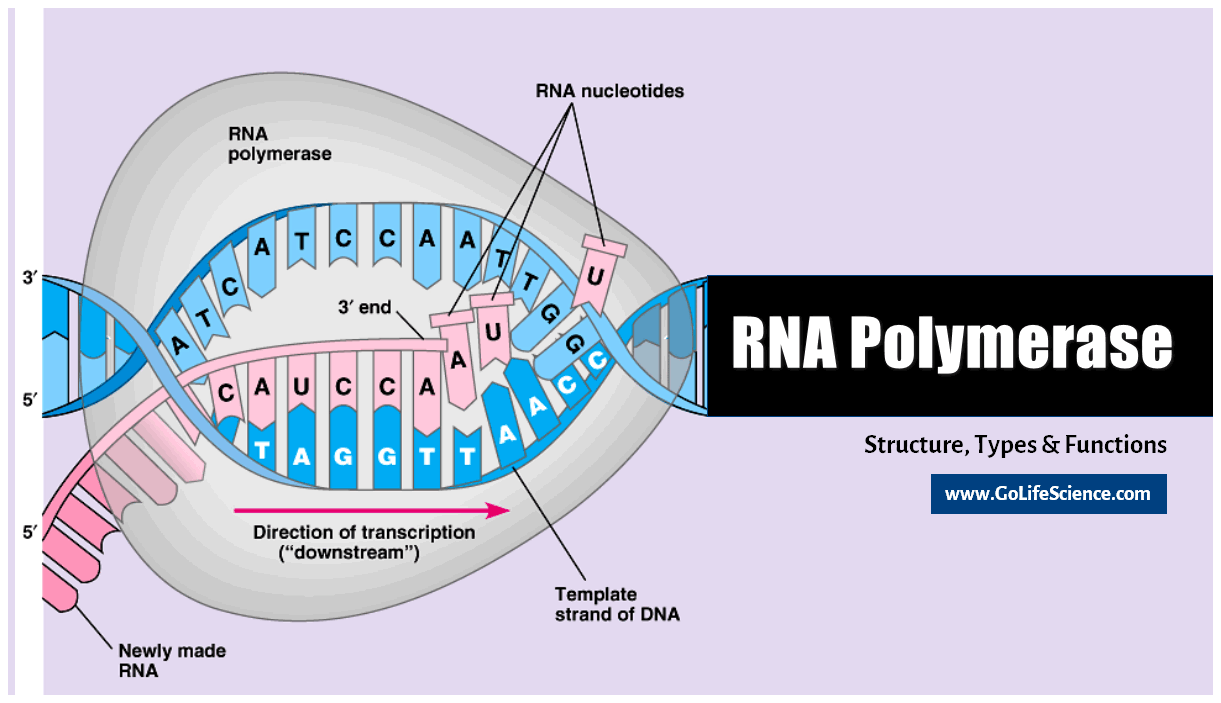
Rna Polymerase In Prokaryotes In most prokaryotes, a single rna polymerase species transcribes all types of rna. rna polymerase "core" from e. coli consists of five subunits: two alpha (α) subunits of 36 kda, a beta (β) subunit of 150 kda, a beta prime subunit (β′) of 155 kda, and a small omega (ω) subunit. a sigma (σ) factor binds to the core, forming the holoenzyme. Eukaryotic cells are more complex than bacteria in many ways, including in terms of transcription. specifically, in eukaryotes, transcription is achieved by three different types of rna polymerase. Essential and fundamental to all organisms, transcription is the process for rna synthesis from template dna. at the heart of this activity is the large multisubunit enzyme called rna polymerase. rna polymerase, abbreviated rnap and officially known as dna directed rna polymerase, is found in all living organisms as well as many viruses. present in bacteria, archaea, and even eukaryotes, these. The transcription initiation phase ends with the production of abortive transcripts, which are polymers of approximately 10 nucleotides that are made and released. figure 15.4.1 15.4. 1: promoter: the σ subunit of prokaryotic rna polymerase recognizes consensus sequences found in the promoter region upstream of the transcription start sight.

Rna Polymerase In Prokaryotes Essential and fundamental to all organisms, transcription is the process for rna synthesis from template dna. at the heart of this activity is the large multisubunit enzyme called rna polymerase. rna polymerase, abbreviated rnap and officially known as dna directed rna polymerase, is found in all living organisms as well as many viruses. present in bacteria, archaea, and even eukaryotes, these. The transcription initiation phase ends with the production of abortive transcripts, which are polymers of approximately 10 nucleotides that are made and released. figure 15.4.1 15.4. 1: promoter: the σ subunit of prokaryotic rna polymerase recognizes consensus sequences found in the promoter region upstream of the transcription start sight. The major function of rna polymerase is to transcribe a specific gene in the dna and synthesize rna. this synthesis is characterized by the unwinding of that specific portion of the dna and taking it as a template to transcribe the gene directed rnas. rna polymerase Ι. this enzyme is responsible for synthesizing ribosomal rna. Transcription in prokaryotes the cell.

Prokaryotic Transcription And Translation Biology For Majors I The major function of rna polymerase is to transcribe a specific gene in the dna and synthesize rna. this synthesis is characterized by the unwinding of that specific portion of the dna and taking it as a template to transcribe the gene directed rnas. rna polymerase Ι. this enzyme is responsible for synthesizing ribosomal rna. Transcription in prokaryotes the cell.

Comments are closed.