Rocks And The Rock Cycle
Rock Cycle вђ Definition Steps Importance Diagram Noun. rock formed from fragments of other rocks or the remains of plants or animals. weathering. noun. the breaking down or dissolving of the earth's surface rocks and minerals. the rock cycle is a series of processes that create and transform the types of rocks in earth’s crust. The rock cycle is the natural, continuous process that forms, breaks down, and reforms rock through geological, chemical, and physical processes. through the cycle, rocks convert between igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary forms. it is a dynamic system that recycles earth’s materials in different forms, from molten magma deep below the.

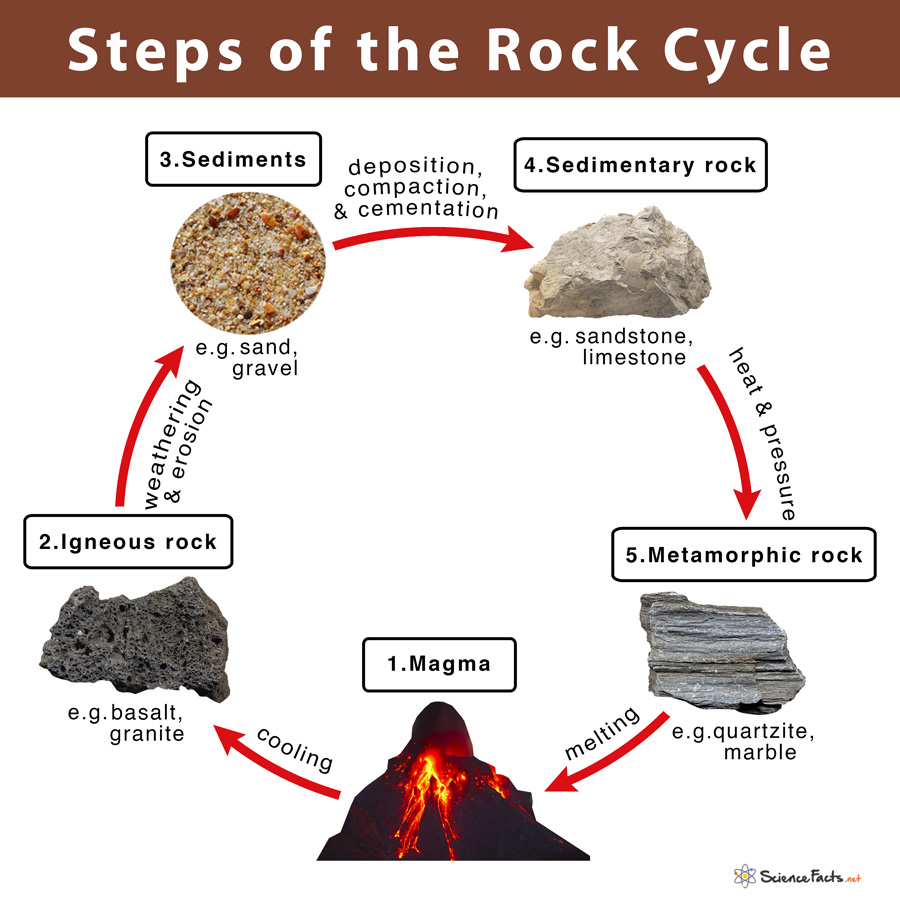
Rock Cycle Diagram Moomoomath And Science The rock cycle is a basic concept in geology that describes transitions through geologic time among the three main rock types: sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous. each rock type is altered when it is forced out of its equilibrium conditions. The rock cycle describes the processes through which the three main rock types (igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary) transform from one type into another. the formation, movement and transformation of rocks results from earth’s internal heat, pressure from tectonic processes, and the effects of water, wind, gravity, and biological. The rocks and the soil around us are the products of millions of years of transformation due to a variety of different geological processes. these geological processes can be referred to as the “rock cycle.” the discovery or description of the rock cycle is usually credited to james hutton, a geologist who lived during the 18th century. The rock cycle. many of earth’s key processes function in cycles and rock cycle is no exception. the rock cycle is a web of processes that outlines how each of the three major rock types—igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary—form and break down based on the different applications of heat and pressure over time.

Comments are closed.