Secondary Consumer In The Desert
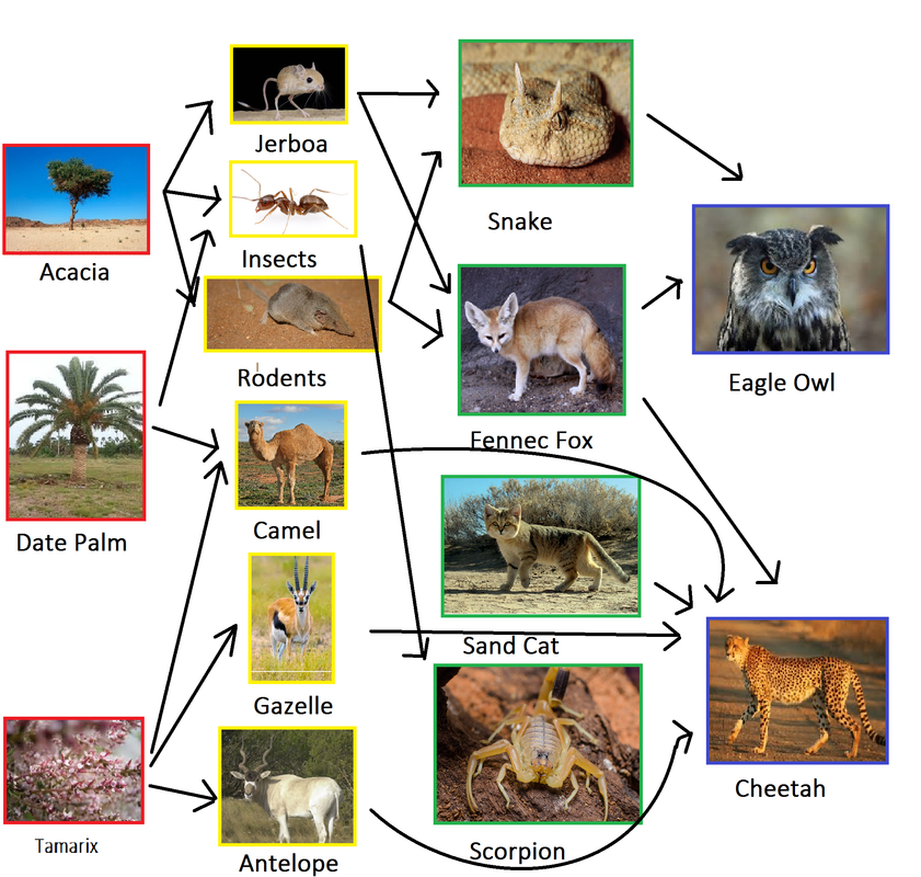
Food Chains Webs The Sahara Desertnorthern Africa Secondary consumers (omnivores) secondary consumers are mostly omnivores (plant and animal eaters), although a few may be carnivores (animal eaters). animals like lizards, coyotes, rattlesnakes, mongooses, tarantulas, and scorpions are some examples of secondary consumers in the desert. tertiary and apex consumers (carnivores). Plant eating animals – the herbivores, or “primary” consumers – become the second link in the food chain. flesh eating animals – the carnivores, or “secondary” and even “tertiary” consumers – become the next links. plant and flesh eaters – the omnivores, like human beings, for example – span two or three links.
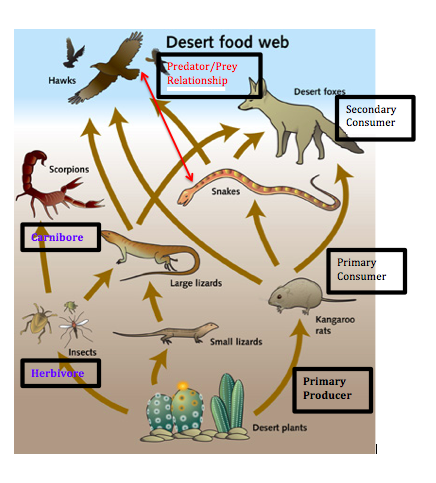
Food Chain And Food Web Desert Secondary consumers – omnivores of the desert. secondary consumers consist of omnivorous desert dwellers who eat plant and animal matter. these generalist feeders provide a vital link in the desert food chain. arachnids. arachnids such as spiders, scorpions, vinegaroons, and sun spiders consume insects, lizards, and vegetation when prey is. Consumers in the desert. there are three levels of consumers in the desert: primary, secondary and tertiary. primary consumers eat only producers. camels are an iconic example of a desert based. Both secondary and tertiary consumers depend on the energy and nutrients obtained from the animals they consume to survive and thrive in the desert environment. decomposers in the desert, decomposers are tiny organisms that play a crucial role in the ecosystem by breaking down dead plants and animals. Tertiary consumers eat both primary and secondary consumers. a desert biome food chain is unique because of the harsh environment of the desert. deserts have little rainfall, extreme temperatures.
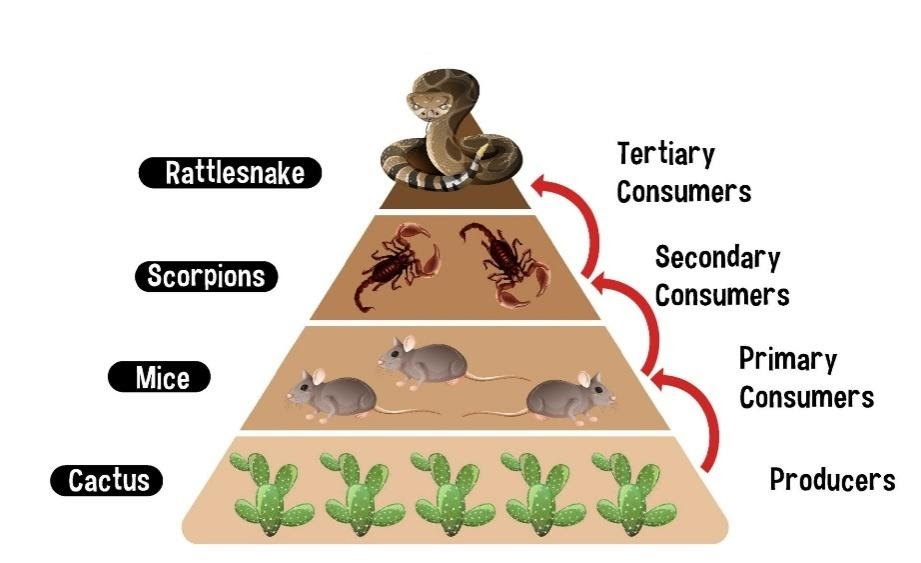
Desert Ecosystem Food Web Both secondary and tertiary consumers depend on the energy and nutrients obtained from the animals they consume to survive and thrive in the desert environment. decomposers in the desert, decomposers are tiny organisms that play a crucial role in the ecosystem by breaking down dead plants and animals. Tertiary consumers eat both primary and secondary consumers. a desert biome food chain is unique because of the harsh environment of the desert. deserts have little rainfall, extreme temperatures. Secondary consumers: these eat primary consumers. a snake is an example of a secondary consumer in a desert biome. tertiary consumers: organisms that consume primary and secondary consumers. in. Food web national geographic education.
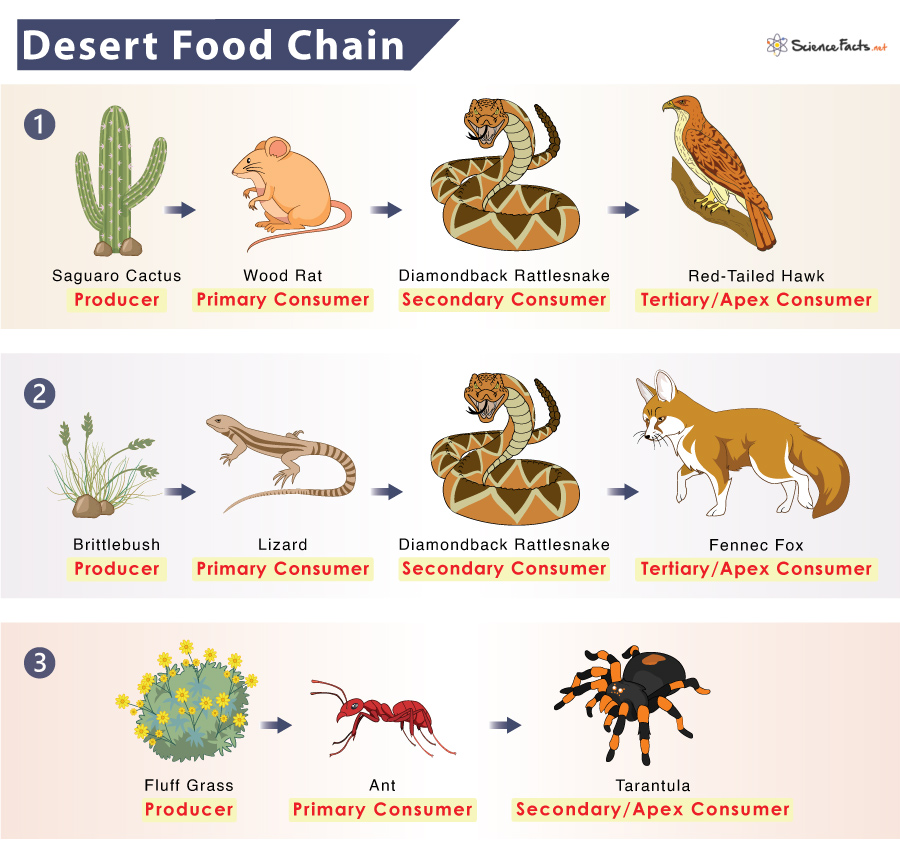
Desert Food Chain Example And Diagram Secondary consumers: these eat primary consumers. a snake is an example of a secondary consumer in a desert biome. tertiary consumers: organisms that consume primary and secondary consumers. in. Food web national geographic education.

Main Difference Between A Food Chain And A Food Web Yourdictionary

Comments are closed.