Soil Based Ecosystem Services Ecosystem Functions And Soil Organisms

Soil Based Ecosystem Services Ecosystem Functions And Soil Organisms Eleven ecosystem functions regulated by soil organisms and belonging to a wide range of ecosystem services were included in this study: nutrient cycling (soil n and p availability), om. These soil attributes are associated with important ecosystem services and functions such as soil carbon sequestration (soil organic carbon content), nutrient cycling (soil total n, p, cu, mg, mn.

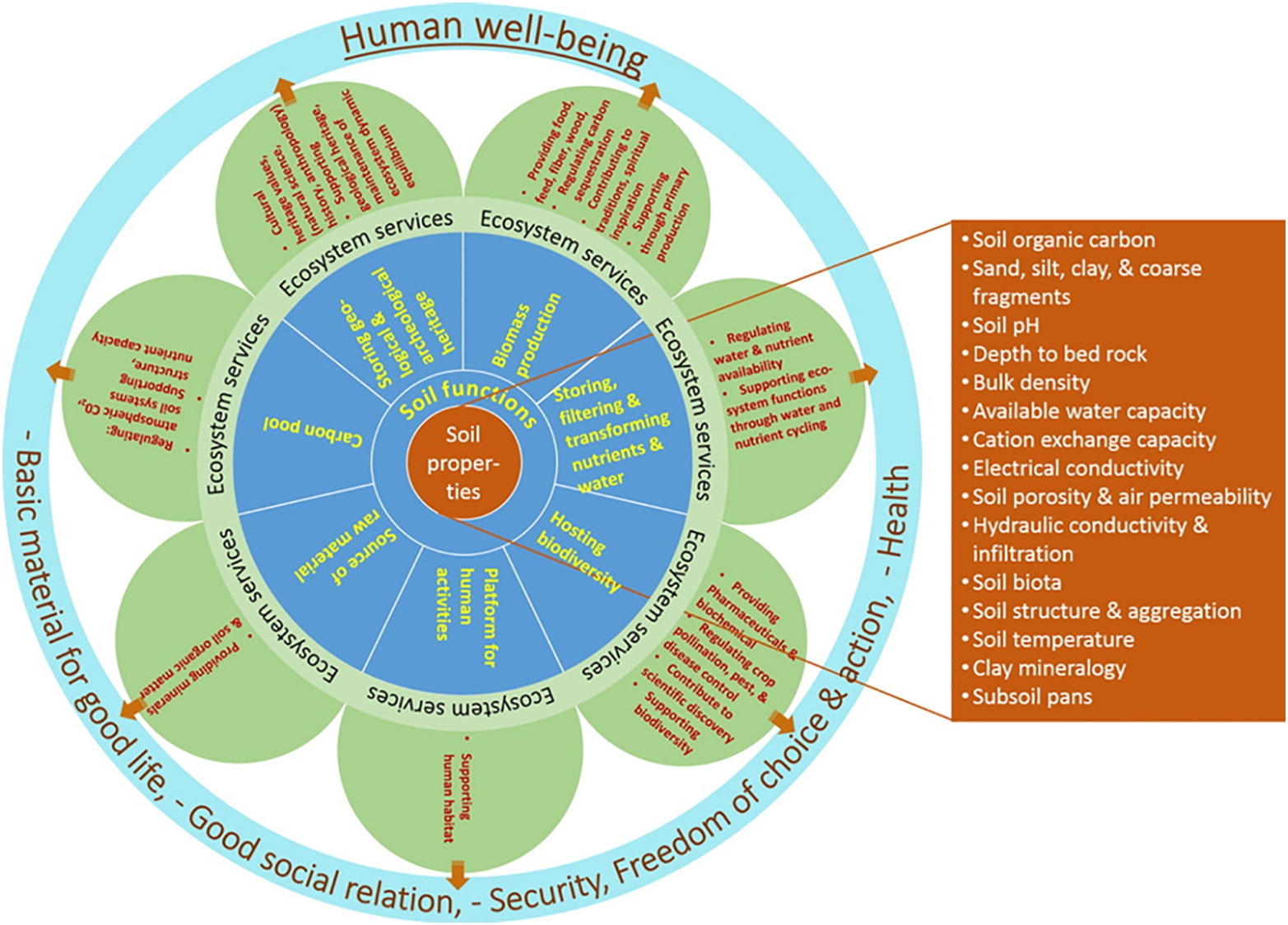
2 Schematic Diagram Of Soil Ecosystem Services Ecosystem Services Are Soil functions are directly related to ecosystem services ( 25 ). soils house a biodiversity pool, which includes ecosystems, species, and genes. soils directly facilitate the production of biomass, including that from agriculture and forestry. the soil stores, filter and transform nutrients, substances, and water. Fig. 1: microbial key functions in the plant–soil system. soil microorganisms play essential roles in ecosystem functioning. a, climate regulation. b, microbial nutrient cycling. c, plant growth. Soil microfauna support several ecosystem functions. their best known function is the promotion of nutrient cycling by feeding on various food sources and the release of nutrients via their excrements. the majority of microfauna feed on bacteria, fungi, and (dead) plant material (table 1.2.1; fig. 1.2.1 ). Abstract. the soil environment is likely the most complex biological community. soil organisms are extremely diverse and contribute to a wide range of ecosystem services that are essential to the sustainable function of natural and managed ecosystems. the soil organism community can have direct and indirect impacts on land productivity.
Frontiers The Role Of Soil Ecosystem Services In The Circular Bioeconomy Soil microfauna support several ecosystem functions. their best known function is the promotion of nutrient cycling by feeding on various food sources and the release of nutrients via their excrements. the majority of microfauna feed on bacteria, fungi, and (dead) plant material (table 1.2.1; fig. 1.2.1 ). Abstract. the soil environment is likely the most complex biological community. soil organisms are extremely diverse and contribute to a wide range of ecosystem services that are essential to the sustainable function of natural and managed ecosystems. the soil organism community can have direct and indirect impacts on land productivity. Soils are of central importance for delivering ecosystem services, such as food production and climate mitigation. these services strongly depend on carbon (c) sequestration and nutrient cycling, processes that are governed by soil biota. increasing demand for the production of food, fiber, and biofuel has resulted in intensification of. Therefore, ecological modules based on soil microbial co occurrence network analyses would be an employable strategy to investigate the relationship between soil microbiome and ecosystem multifunctionality. soil organisms live in a complex soil food web, such as numerous intra and inter connection between microbes and microfauna that impact.

Comments are closed.