Solved 1 Find The Vector Product Or Cross Product Of The Chegg
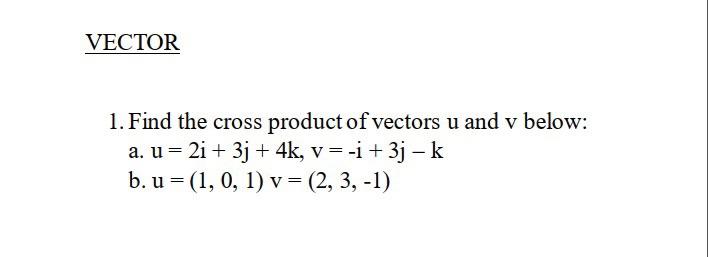
Solved Vector 1 Find The Cross Product Of Vectors U And V Your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: 1. find the cross product of the unit vector k × i. a. e. k 2. sketch the graph of the cross product of the unit vector kxi. here’s the best way to solve it. In the cross (or vector) product vec (f) = qvec (v) × vec (b) we know that. q = 1. vec (f) = 1 8 hat (i) 2. 0 hat (j) 2 5 hat (k) vec (v) = 3. 0 hat (i) 2. 0 widehat (j) 2. 0 hat (k) vec (b) = b x hat (i) b y hat (j) b z hat (k).
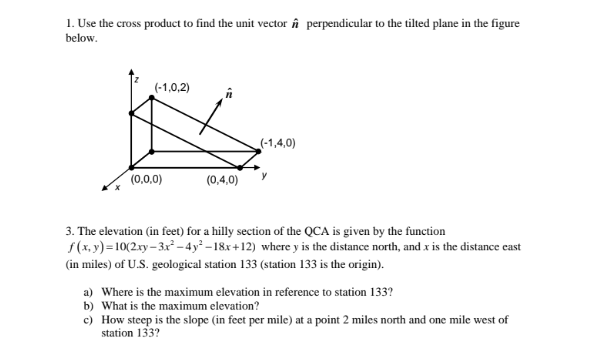
Solved 1 Use The Cross Product To Find The Unit Vector N Cheg Our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. question: 1. find the cross product a ⨯ b. a = 5j − 8k, b = −i 2j k verify that it is orthogonal to both a and b. (a ⨯ b) · a= (a ⨯ b) · b= 2. find a vector equation and. 1. find the cross product a ⨯ b. A. determine unit vector \(\vecs b(t)\) (called the binormal unit vector) that has the direction of cross product vector \(\vecs v(t)×\vecs a(t),\) where \(\vecs v(t)\) and \(\vecs a(t)\) are the instantaneous velocity vector and, respectively, the acceleration vector of the particle after \( t\) seconds. b. The cross product (purple) is always perpendicular to both vectors, and has magnitude zero when the vectors are parallel and maximum magnitude ‖ ⇀ a‖‖ ⇀ b‖ when they are perpendicular. (public domain; lucasvb). example 12.4.1: finding a cross product. let ⇀ p = − 1, 2, 5 and ⇀ q = 4, 0, − 3 (figure 12.4.1). 2.4.1 calculate the cross product of two given vectors. 2.4.2 use determinants to calculate a cross product. 2.4.3 find a vector orthogonal to two given vectors. 2.4.4 determine areas and volumes by using the cross product. 2.4.5 calculate the torque of a given force and position vector.
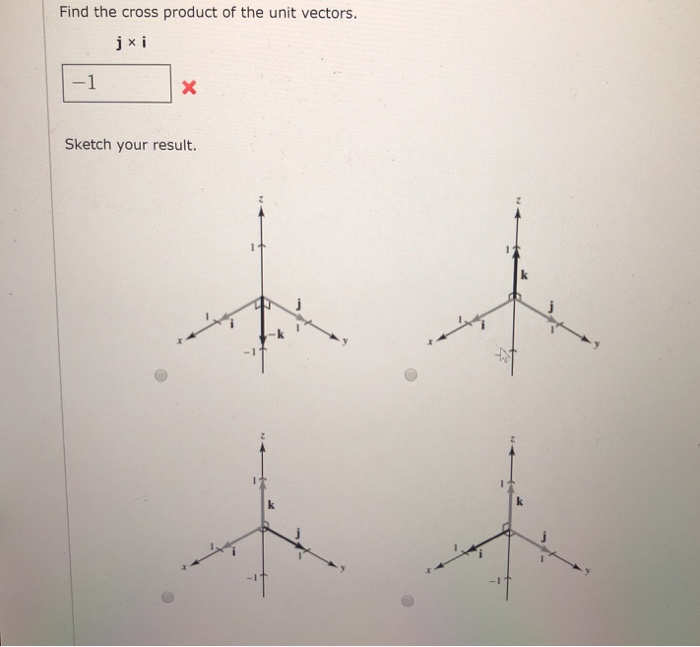
Solved Find The Cross Product Of The Unit Vectors Jx I 1 Cheg The cross product (purple) is always perpendicular to both vectors, and has magnitude zero when the vectors are parallel and maximum magnitude ‖ ⇀ a‖‖ ⇀ b‖ when they are perpendicular. (public domain; lucasvb). example 12.4.1: finding a cross product. let ⇀ p = − 1, 2, 5 and ⇀ q = 4, 0, − 3 (figure 12.4.1). 2.4.1 calculate the cross product of two given vectors. 2.4.2 use determinants to calculate a cross product. 2.4.3 find a vector orthogonal to two given vectors. 2.4.4 determine areas and volumes by using the cross product. 2.4.5 calculate the torque of a given force and position vector. The first step is to redraw the vectors →a and →b so that the tails are touching. then draw an arc starting from the vector →a and finishing on the vector →b . curl your right fingers the same way as the arc. your right thumb points in the direction of the vector product →a × →b (figure 3.28). figure 3.28: right hand rule. The cross product of two vectors and is given by. although this may seem like a strange definition, its useful properties will soon become evident. there is an easy way to remember the formula for the cross product by using the properties of determinants. recall that the determinant of a 2x2 matrix is. and the determinant of a 3x3 matrix is.
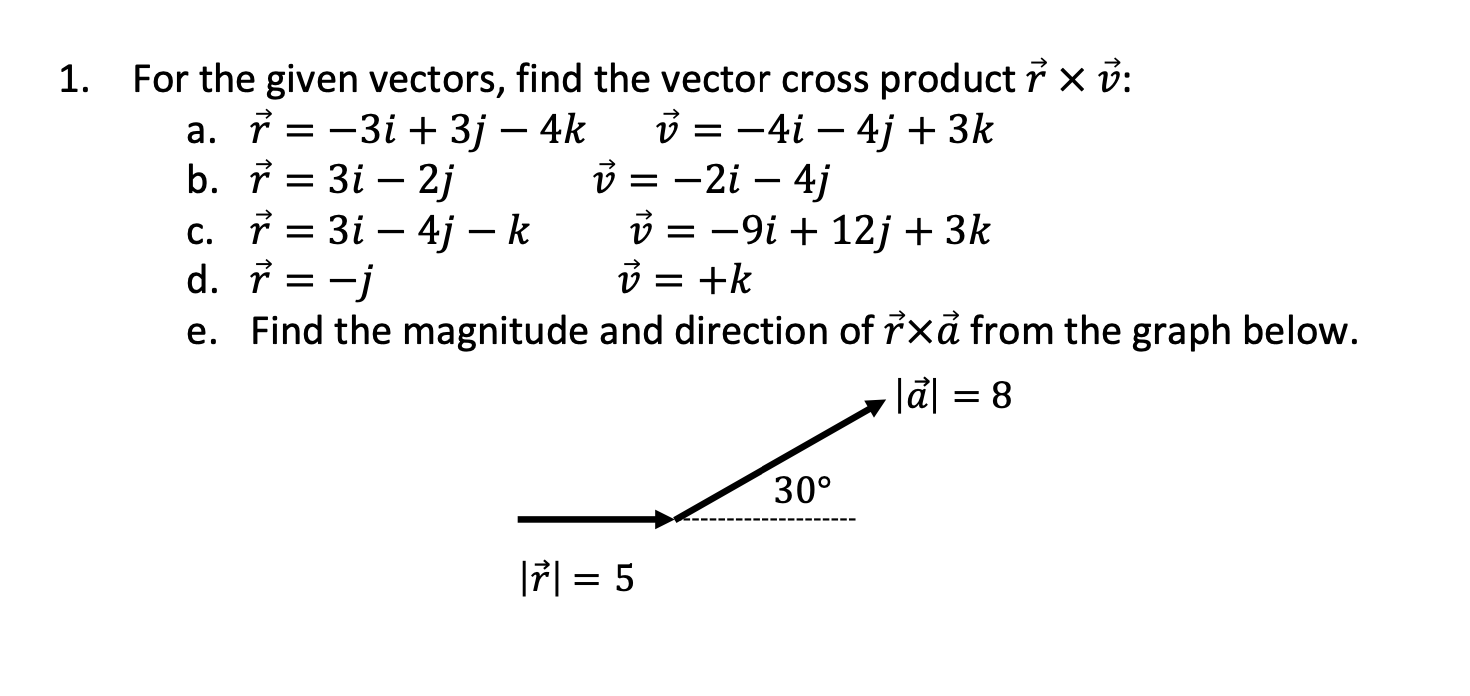
Solved 1 For The Given Vectors Find The Vector Cross Chegg The first step is to redraw the vectors →a and →b so that the tails are touching. then draw an arc starting from the vector →a and finishing on the vector →b . curl your right fingers the same way as the arc. your right thumb points in the direction of the vector product →a × →b (figure 3.28). figure 3.28: right hand rule. The cross product of two vectors and is given by. although this may seem like a strange definition, its useful properties will soon become evident. there is an easy way to remember the formula for the cross product by using the properties of determinants. recall that the determinant of a 2x2 matrix is. and the determinant of a 3x3 matrix is.

Comments are closed.