Solving An Undecic Polynomial Equation

Pin On Algebra Ii Explained 🤩 hello everyone, i'm very excited to bring you a new channel (sybermath shorts).enjoy and thank you for your support!!! 🧡🥰🎉🥳🧡 .co. This video is about a rational equation that can be solved with an algebraic trick.follow me: twitter sybermathsubscribe!!!: .

Solving Polynomial Equations Youtube 🤩 hello everyone, i'm very excited to bring you a new channel (aplusbi)enjoy and thank you for your support!!! 🧡🥰🎉🥳🧡. To solve a polynomial equation write it in standard form (variables and canstants on one side and zero on the other side of the equation). factor it and set each factor to zero. solve each factor. the solutions are the solutions of the polynomial equation. a polynomial equation is an equation formed with variables, exponents and coefficients. Polynomial equations of degree one are linear equations are of the form ax b = c. we are now going to solve polynomial equations of degree two. a polynomial equation of degree two is called a quadratic equation. listed below are some examples of quadratic equations: x2 5x 6 = 0 3y2 4y = 10 64u2 − 81 = 0 n(n 1) = 42. Step 1: check for common factors. if the terms have common factors, then factor out the greatest common factor (gcf). step 2: determine the number of terms in the polynomial. factor four term polynomials by grouping. factor trinomials (3 terms) using “trial and error” or the ac method.

Polynomial Equation Definition Solving Polynomial Equations Polynomial equations of degree one are linear equations are of the form ax b = c. we are now going to solve polynomial equations of degree two. a polynomial equation of degree two is called a quadratic equation. listed below are some examples of quadratic equations: x2 5x 6 = 0 3y2 4y = 10 64u2 − 81 = 0 n(n 1) = 42. Step 1: check for common factors. if the terms have common factors, then factor out the greatest common factor (gcf). step 2: determine the number of terms in the polynomial. factor four term polynomials by grouping. factor trinomials (3 terms) using “trial and error” or the ac method. If you’re solving an equation, you can throw away any common constant factor. (technically, you’re dividing left and right sides by that constant factor.) but if you’re factoring a polynomial, you must keep the common factor. example: to solve 8 x ² 16 x 8 = 0, you can divide left and right by the common factor 8. More than just an online equation solver. wolfram|alpha is a great tool for finding polynomial roots and solving systems of equations. it also factors polynomials, plots polynomial solution sets and inequalities and more. learn more about: equation solving; tips for entering queries. enter your queries using plain english.

22 Gcf Polynomial Calculator Gaylewillow If you’re solving an equation, you can throw away any common constant factor. (technically, you’re dividing left and right sides by that constant factor.) but if you’re factoring a polynomial, you must keep the common factor. example: to solve 8 x ² 16 x 8 = 0, you can divide left and right by the common factor 8. More than just an online equation solver. wolfram|alpha is a great tool for finding polynomial roots and solving systems of equations. it also factors polynomials, plots polynomial solution sets and inequalities and more. learn more about: equation solving; tips for entering queries. enter your queries using plain english.
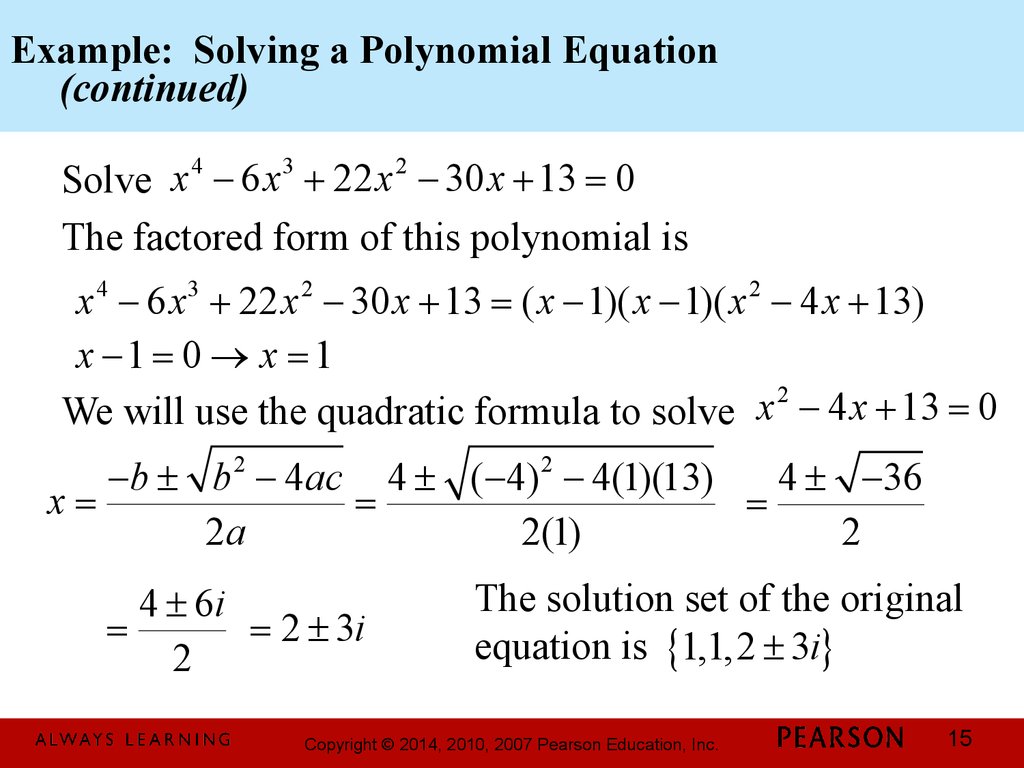
Chapter 3 Polynomial And Rational Functions 3 4 Zeros Of Polynomial

Comments are closed.