Stress And Strain Definition Stress Strain Curve Hooke S Law Si Unit

юааstressюаб юааand Strainюаб юааdefinitionюаб юааstressюаб юааstrainюаб юааcurveюаб юааhookeтащsюаб Definition, stress strain curve, hooke's law, si units. Stress strain curve is a very crucial concept in the study of material science and engineering. it describes the relationship between stress and the strain applied on an object. we know that stress is the applied force on the material, and strain, is the resulting change (deformation or elongation) in the shape of the object.

юааhookeтащsюаб юааlawюаб A юааstressюаб юааstrainюаб Relationship Formula Explanation The simplest oscillations occur when the restoring force is directly proportional to displacement. when stress and strain were covered in newton’s third law of motion, the name was given to this relationship between force and displacement was hooke’s law:. When stress and strain were covered in newton’s third law of motion, the name was given to this relationship between force and displacement was hooke’s law: f = −kx (16.1.1) (16.1.1) f = − k x. here, f f is the restoring force, x x is the displacement from equilibrium or deformation, and k k is a constant related to the difficulty in. Stress–strain curve. Young’s modulus y is the elastic modulus when deformation is caused by either tensile or compressive stress, and is defined by equation 12.4.4. dividing this equation by tensile strain, we obtain the expression for young’s modulus: y = tensile stress tensile strain = f ⊥ a Δl l0 = f ⊥ a × l0 Δl.
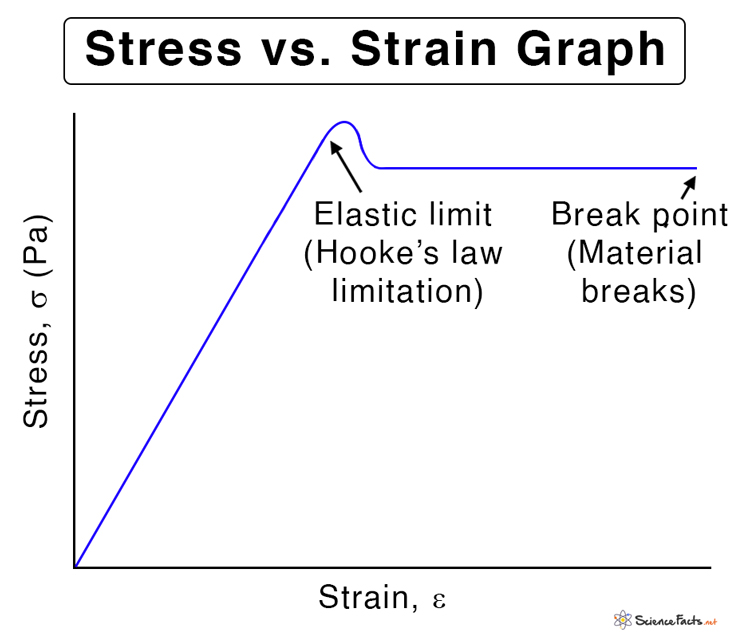
юааhookeтащsюаб юааlawюаб Statement Formula And Diagram Stress–strain curve. Young’s modulus y is the elastic modulus when deformation is caused by either tensile or compressive stress, and is defined by equation 12.4.4. dividing this equation by tensile strain, we obtain the expression for young’s modulus: y = tensile stress tensile strain = f ⊥ a Δl l0 = f ⊥ a × l0 Δl. 12.3 stress, strain, and elastic modulus. Another biological example of hooke’s law occurs in tendons. functionally, the tendon (the tissue connecting muscle to bone) must stretch easily at first when a force is applied, but offer a much greater restoring force for a greater strain. figure 5.15 shows a stress strain relationship for a human tendon. some tendons have a high collagen.

State And Explain Hooke S Law Draw Stress And Strain Curve With 12.3 stress, strain, and elastic modulus. Another biological example of hooke’s law occurs in tendons. functionally, the tendon (the tissue connecting muscle to bone) must stretch easily at first when a force is applied, but offer a much greater restoring force for a greater strain. figure 5.15 shows a stress strain relationship for a human tendon. some tendons have a high collagen.

Comments are closed.