T T 0
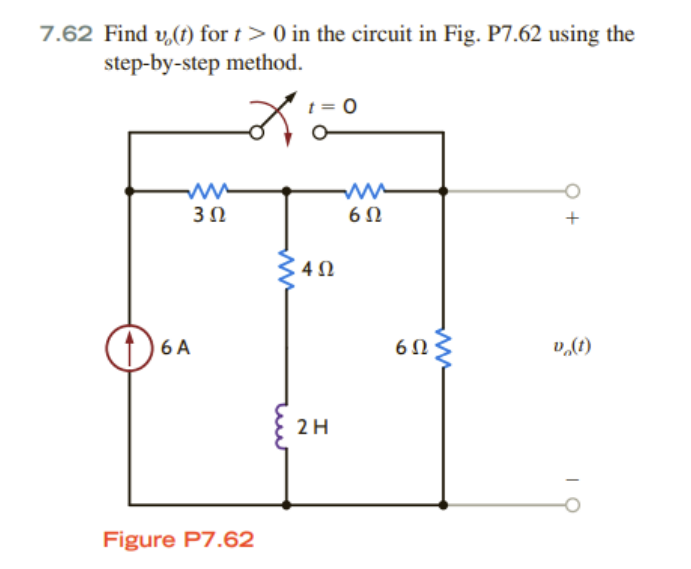
Solved 7 62 Find Vo T For T 0 In The Circuit In Fig P7 62 Chegg Capacitor acts like short circuit at t=0, the reason that capacitor have leading current in it. the inductor acts like an open circuit initially so the voltage leads in the inductor as voltage appears instantly across open terminals of inductor at t=0 and hence leads. Thus \(\vecs a (t) = 0\vecs t(t) 3\vecs n(t) = 3\vecs n(t)\), which is clearly the case. what is the practical interpretation of these numbers? \(a \text{t}=0\) means the object is moving at a constant speed, and hence all acceleration comes in the form of direction change.

T 1 T 2 1 оє 0 2475 Download Scientific Diagram In c (and many other languages), you can insert hard to see type characters using \ notation: \a is alert bell. \b is backspace rubout. \n is newline. \r is carriage return (return to left margin) \t is tab. you can also specify the octal value of any character using \0 nnn, or the hexadecimal value of any character with \x nn. For all u u and w w it is tu, w = 0 t u, w = 0. this gives t = 0 t = 0. in the real case you need to assume for example that t t is self adjoint (the above identity then just lacks the imaginary part). this identity, i think, assumes conjugate linearity in the second argument. beware that you need to switch some minus signs around if your. The equation for calculating time dilation is as follows: t = t 0 (1 v 2 c 2) 1 2. where: t = time observed in the other reference frame. t 0 = time in observers own frame of reference (rest time) v = the speed of the moving object. c = the speed of light in a vacuum. so in our problem we will let v = .95c, t 0 = 10 years and we will solve. We use the same letter to denote that one function is the laplace transform of the other. for example f(s) is the laplace transform of f(t). let us define the transform. l{f(t)} = f(s)def = ∫∞ 0e − stf(t)dt. we note that we are only considering t ≥ 0 in the transform.

Comments are closed.