The H R Diagram Astronomy Course Hero
The H R Diagram Astronomy Course Hero Ejnar hertzspung plotted the first such diagram in 1911, and henry norris russell in developed one similar in 1913. it is a "two dimensional" plot for the observed stars and represents one of the greatest observational syntheses in astronomy and astrophysics! the important things to note about such a diagram is that: most of the stars in the. Hipparcos satellite (1989) – plotted accurate distances to the nearest stars. h r diagrams • luminosity class – 90% of all stars lie on the main sequence • 10% are either giant or dwarf class stars. binary stars • most stars are part of multiple star systems • ex.alpha centauri a, b & c (or “proxima” centauri).

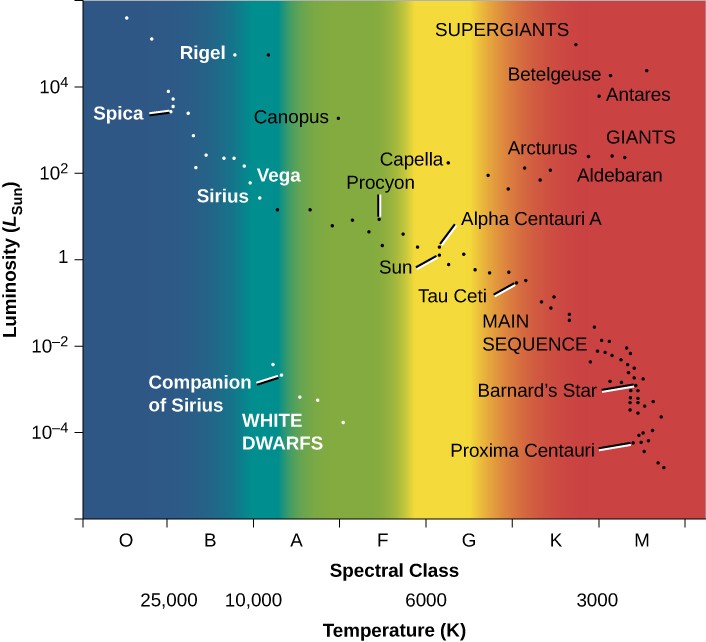
H R Diagrams Lab Figures Docx Figure 1 H R Diagram With Region L A b3 star: 2.1 a g8 star: 5.5 task #7 to make your hr diagram complete, add the following “freak” stars to your hr diagram: spectral class absolute magnitude k0 0.5 m0 0.5 b0 8.5 label this star a “white dwarf” task #8 with all the answers typed in appropriately above, save this document to your hard drive. Key concepts and summary. the hertzsprung–russell diagram, or h–r diagram, is a plot of stellar luminosity against surface temperature. most stars lie on the main sequence, which extends diagonally across the h–r diagram from high temperature and high luminosity to low temperature and low luminosity. Henry norris russell. one of the most useful and powerful plots in astrophysics is the hertzsprung russell diagram (hereafter called the h r diagram). it originated in 1911 when the danish astronomer, ejnar hertzsprung, plotted the absolute magnitude of stars against their colour (hence effective temperature). independently in 1913 the american. Features of the h–r diagram. following hertzsprung and russell, let us plot the temperature (or spectral class) of a selected group of nearby stars against their luminosity and see what we find (figure 18.14). such a plot is frequently called the hertzsprung–russell diagram, abbreviated h–r diagram. it is one of the most important and.

Understanding The H R Diagram Pdf Nam Homew R R N Er An Ng N R Henry norris russell. one of the most useful and powerful plots in astrophysics is the hertzsprung russell diagram (hereafter called the h r diagram). it originated in 1911 when the danish astronomer, ejnar hertzsprung, plotted the absolute magnitude of stars against their colour (hence effective temperature). independently in 1913 the american. Features of the h–r diagram. following hertzsprung and russell, let us plot the temperature (or spectral class) of a selected group of nearby stars against their luminosity and see what we find (figure 18.14). such a plot is frequently called the hertzsprung–russell diagram, abbreviated h–r diagram. it is one of the most important and. An actual h r diagram is provided in the upper right panel with an active location indicated by a red x. this active location can be dragged around the diagram. the options panel allows you control the variables plotted on the x axis: (temperature, b v, or spectral type) and those plotted on the y axis (luminosity or absolute magnitude). Thus, its position on the h–r diagram, in which luminosity is plotted against temperature, also changes. as a star ages, we must replot it in different places on the diagram. therefore, astronomers often speak of a star moving on the h–r diagram, or of its evolution tracing out a path on the diagram. in this context, “tracing out a path.

H R Diagram Construction No Calculations1 Docx Esc13000 Esc13100 An actual h r diagram is provided in the upper right panel with an active location indicated by a red x. this active location can be dragged around the diagram. the options panel allows you control the variables plotted on the x axis: (temperature, b v, or spectral type) and those plotted on the y axis (luminosity or absolute magnitude). Thus, its position on the h–r diagram, in which luminosity is plotted against temperature, also changes. as a star ages, we must replot it in different places on the diagram. therefore, astronomers often speak of a star moving on the h–r diagram, or of its evolution tracing out a path on the diagram. in this context, “tracing out a path.

Comments are closed.