The Theory Of Consumer Behavior Assumes That

Ppt The Theory Of Consumer Behavior Powerpoint Presentation Free Consumer theory is the study of how people decide to spend their money based on their individual preferences and budget constraints. it assumes that consumers are rational, non satiated, and have decreasing marginal utility. Unit 2: consumer theory. the second unit of the course introduces you to the analysis of consumer behavior. the decisions that individuals make about what and how much to consume are among the most important factors that shape the evolution of the overall economy, and we can analyze these decisions in terms of their underlying preferences. you.
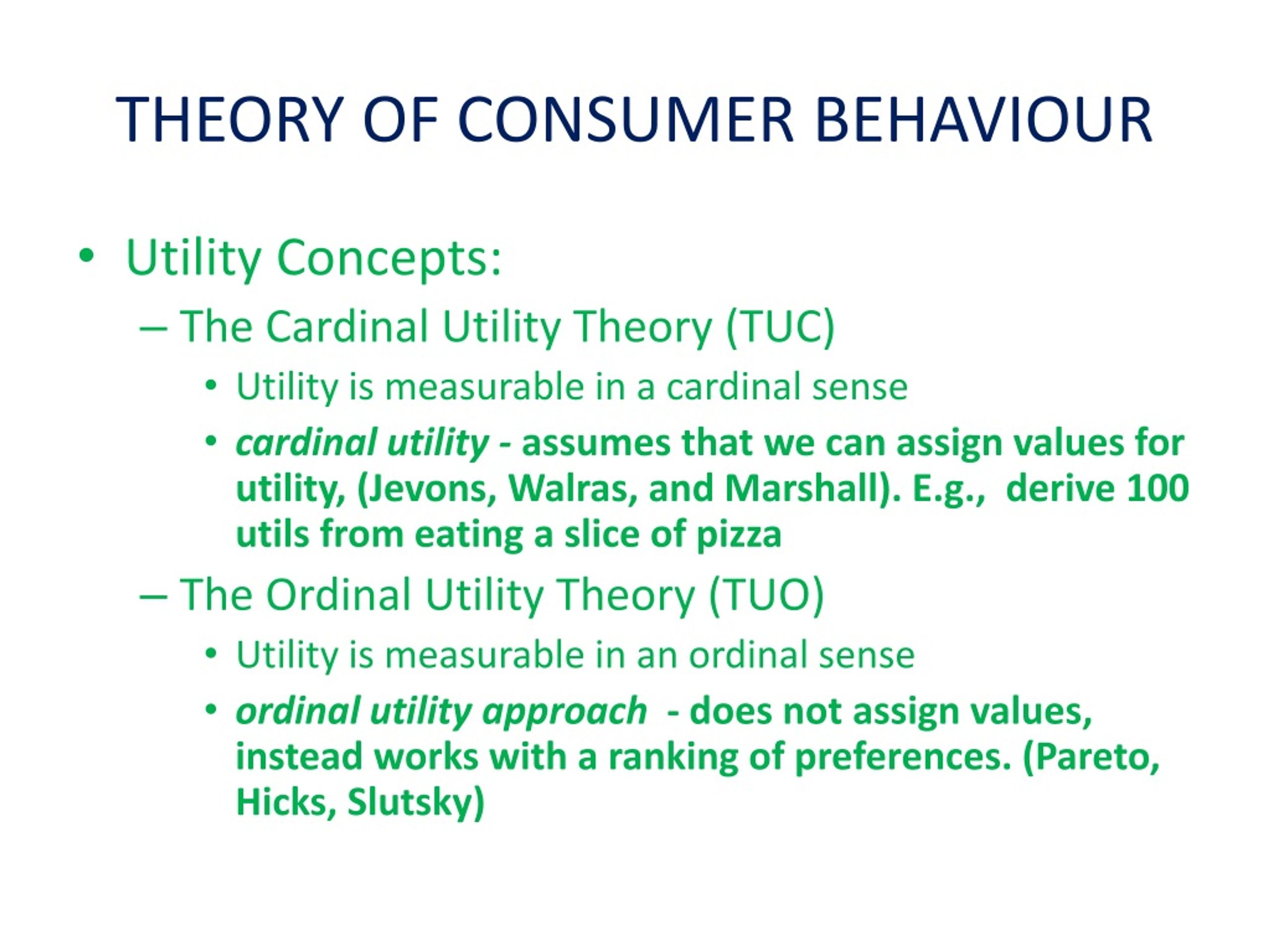
Ppt Theory Of Consumer Behaviour Powerpoint Presentation Free The review of the decision making models undertaken here highlights the complexity of consumer choices and identifies the key processes that lead to behaviour. a wide range of variables have been posited across the models, and each has evidence to justify its inclusion in attempts to explain behaviour. Assumptions: 1. rationality: the consumer is assumed to be rational he aims at the maximization of his utility, given his income and market prices. it is assumed he has full knowledge (certainty) of all relevant information. 2. utility is ordinal: it is taken as axiomatically true that the consumer can rank his preferences (order the various 'baskets of goods') according to the satisfaction of. Following are the three basic assumptions about consumer behaviour. utility maximization: the consumer theory assumes that a consumer always wants to maximize his or her utility as per taste and preferences and given budget. here the term utility refers to the satisfaction gained from the consumption of the commodity. Utility ordering seeks to rank goods based on the attractiveness of the characteristics of the good to the consumer. in his new model of consumer theory, lancaster 1966 assumed that the relationship between economic activity and goods consumed during an economic activity is linear. this is captured in eq. 6 below:.

Ppt Ch 21 Consumer Behavior Utility Maximization Powerpoint Following are the three basic assumptions about consumer behaviour. utility maximization: the consumer theory assumes that a consumer always wants to maximize his or her utility as per taste and preferences and given budget. here the term utility refers to the satisfaction gained from the consumption of the commodity. Utility ordering seeks to rank goods based on the attractiveness of the characteristics of the good to the consumer. in his new model of consumer theory, lancaster 1966 assumed that the relationship between economic activity and goods consumed during an economic activity is linear. this is captured in eq. 6 below:. Some basic assumptions about preferences. 1. completeness: preferences are assumed to be complete. in other words, consumers can compare and rank all possible baskets. thus, for any two market baskets a and b, a consumer will prefer a to b, will prefer b to a, or will be indifferent between the two. In almost all cases, consumer choices are driven by prices. as price goes up, the quantity that consumers demand goes down. this correlation between the price of goods and the willingness to make purchases is represented clearly by the generation of a demand curve (with price as the y axis and quantity as the x axis).

Comments are closed.