The Vector Cross Product
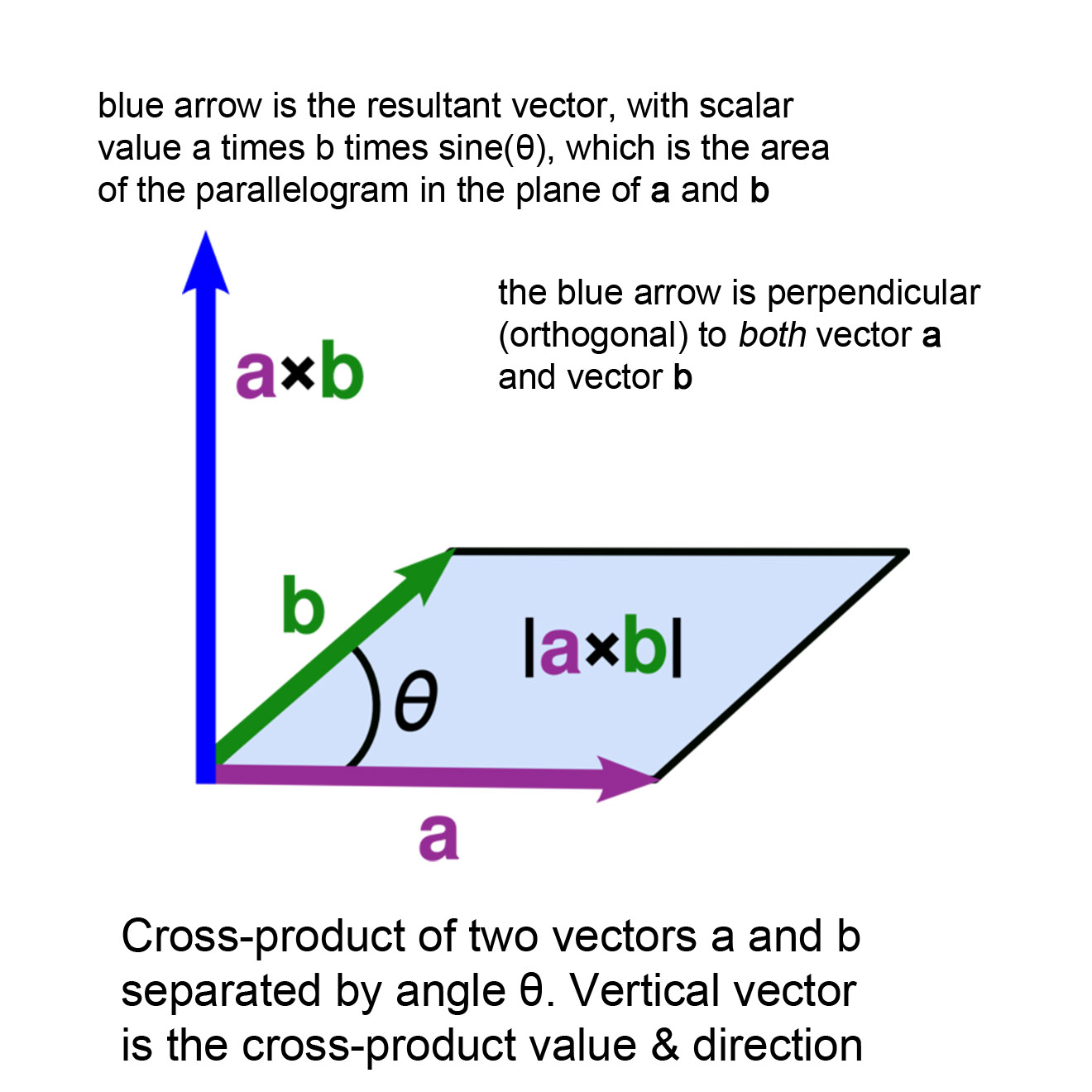
Cross Product In Vector Algebra вђ The Thunderbolts Projectв ў Cross product. in mathematics, the cross product or vector product (occasionally directed area product, to emphasize its geometric significance) is a binary operation on two vectors in a three dimensional oriented euclidean vector space (named here ), and is denoted by the symbol . Cross product is a binary operation on two vectors in three dimensional space. it results in a vector that is perpendicular to both vectors. the vector product of two vectors, a and b, is denoted by a × b. its resultant vector is perpendicular to a and b. vector products are also called cross products.
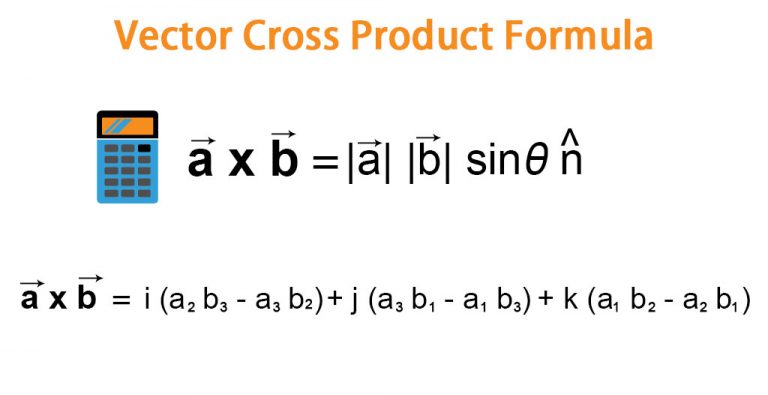
Vector Cross Product Formula Examples With Excel Template The cross product could point in the completely opposite direction and still be at right angles to the two other vectors, so we have the: "right hand rule" with your right hand, point your index finger along vector a , and point your middle finger along vector b : the cross product goes in the direction of your thumb. The cross product (purple) is always perpendicular to both vectors, and has magnitude zero when the vectors are parallel and maximum magnitude ‖ ⇀ a‖‖ ⇀ b‖ when they are perpendicular. (public domain; lucasvb). example 12.4.1: finding a cross product. let ⇀ p = − 1, 2, 5 and ⇀ q = 4, 0, − 3 (figure 12.4.1). Defining the cross product. the dot product represents the similarity between vectors as a single number: for example, we can say that north and east are 0% similar since (0, 1) ⋅ (1, 0) = 0. or that north and northeast are 70% similar (cos (45) =.707, remember that trig functions are percentages.) the similarity shows the amount of one. A cross product is denoted by the multiplication sign(x) between two vectors. it is a binary vector operation, defined in a three dimensional system. the resultant product vector is also a vector quantity. understand its properties and learn to apply the cross product formula.

Cross Product Of Two Vectors Explained Youtube Defining the cross product. the dot product represents the similarity between vectors as a single number: for example, we can say that north and east are 0% similar since (0, 1) ⋅ (1, 0) = 0. or that north and northeast are 70% similar (cos (45) =.707, remember that trig functions are percentages.) the similarity shows the amount of one. A cross product is denoted by the multiplication sign(x) between two vectors. it is a binary vector operation, defined in a three dimensional system. the resultant product vector is also a vector quantity. understand its properties and learn to apply the cross product formula. Cross product. for vectors and in , the cross product in is defined by. where is a right handed, i.e., positively oriented, orthonormal basis. this can be written in a shorthand notation that takes the form of a determinant. where , , and are unit vectors. here, is always perpendicular to both and , with the orientation determined by the right. The vector c c (in red) is the cross product of the vectors a a (in blue) and b b (in green), c = a ×b c = a × b. the parallelogram formed by a a and b b is pink on the side where the cross product c c points and purple on the opposite side. using the mouse, you can drag the arrow tips of the vectors a a and b b to change these vectors.

Comments are closed.