Transmission Electron Microscopy 01 Basics
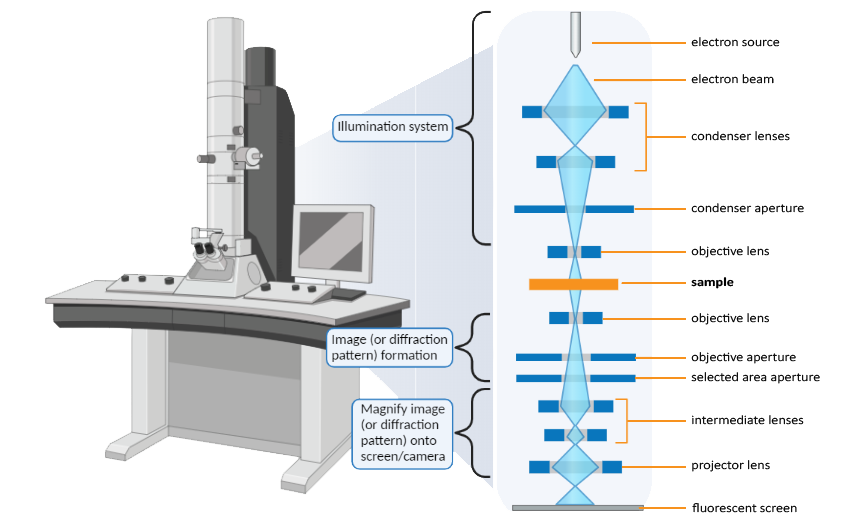
Transmission Electron Microscopy Nanoscience Instruments The working principle of the transmission electron microscope (tem) is similar to the light microscope. the major difference is that light microscopes use light rays to focus and produce an image while the tem uses a beam of electrons to focus on the specimen, to produce an image. electrons have a shorter wavelength in comparison to light which. Transmission electron microscopy (tem) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. the specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a grid. an image is formed from the interaction of the electrons with the sample as the beam is transmitted.
Microscopes вђ General Microbiology Transmission electron microscope (tem) science info. Tem: an overview. transmission electron microscopy (tem) is a form of microscopy which in which a beam of electrons transmits through an extremely thin specimen, and then interacts with the specimen when passing through it. the formation of images in a tem can be explained by an optical electron beam diagram in figure 8.2.1 8.2. 1. The transmission electron microscope1. electron microscopechapter previewa typical commercial transmission electron microscope (tem) costs about $5 for each electron volt (ev) of energy in the beam and, if you add on all available options, it can easily cost up to $10 per ev. as you’ll see, we use beam energies in the range from 100,000 to. Profusely illustrated, transmission electron microscopy: a textbook for materials science provides the necessary instructions for successful hands on application of this versatile materials characterization technique. for this first new edition in 12 years, many sections have been completely rewritten with all others revised and updated.

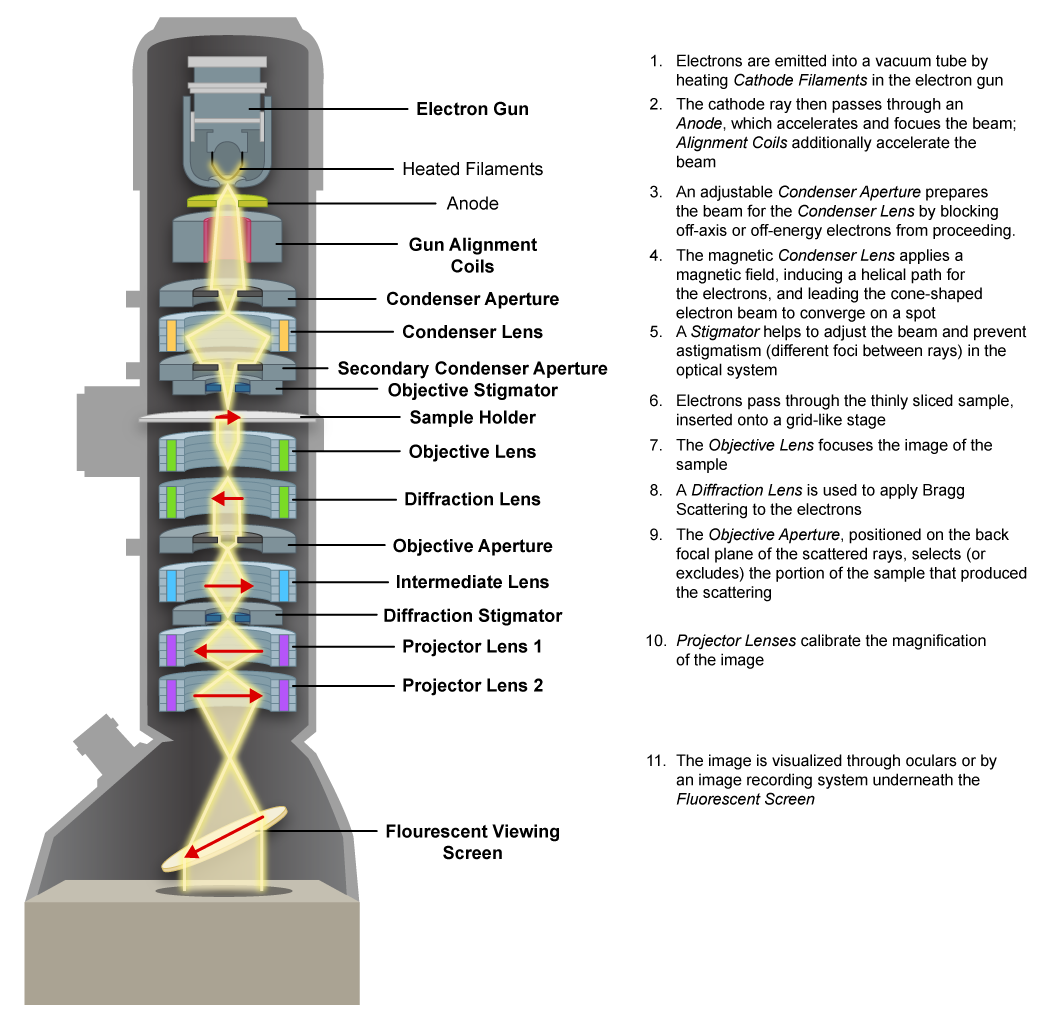
The Components Of A Transmission Electron Microscope Tem Stock Photo The transmission electron microscope1. electron microscopechapter previewa typical commercial transmission electron microscope (tem) costs about $5 for each electron volt (ev) of energy in the beam and, if you add on all available options, it can easily cost up to $10 per ev. as you’ll see, we use beam energies in the range from 100,000 to. Profusely illustrated, transmission electron microscopy: a textbook for materials science provides the necessary instructions for successful hands on application of this versatile materials characterization technique. for this first new edition in 12 years, many sections have been completely rewritten with all others revised and updated. 1 introduction. since its invention by ernst ruska in 1931, 1 transmission electron microscopy (tem) greatly influenced the course of modern day science. while initially the high vacuum and radiation damage where thought to strongly limit its usability, the development of sample preparation techniques led to tem playing a significant role in material sciences, physics, chemistry and biology. How does the transmission electron microscope (tem) work? the tem uses a beam of electrons to resolve structures far beyond the resolution of conventional light microscopy (less than 200 nm). electrons produced by heating a filament (tungsten or lab6) at voltages ranging from 60 120kv, are fired towards the sample down a column held under vacuum.

Comments are closed.