Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Understanding The 3 Main Branches

Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Understanding The 3 Main Branches The trigeminal nerve is a mixed cranial nerve that has both sensory and motor functions. there are three divisions of the trigeminal nerve: ophthalmic division (cn v1 or va), maxillary division (cn v2 or vb), mandibular division (cn v3 or vc). the acronym mom can be used to recall the three branches of the trigeminal nerve. The peripheral aspect of the trigeminal ganglion gives rise to 3 divisions: ophthalmic (v1), maxillary (v2) and mandibular (v3). the motor root passes inferiorly to the sensory root, along the floor of the trigeminal cave. its fibres are only distributed to the mandibular division. the ophthalmic nerve and maxillary nerve travel lateral to the.
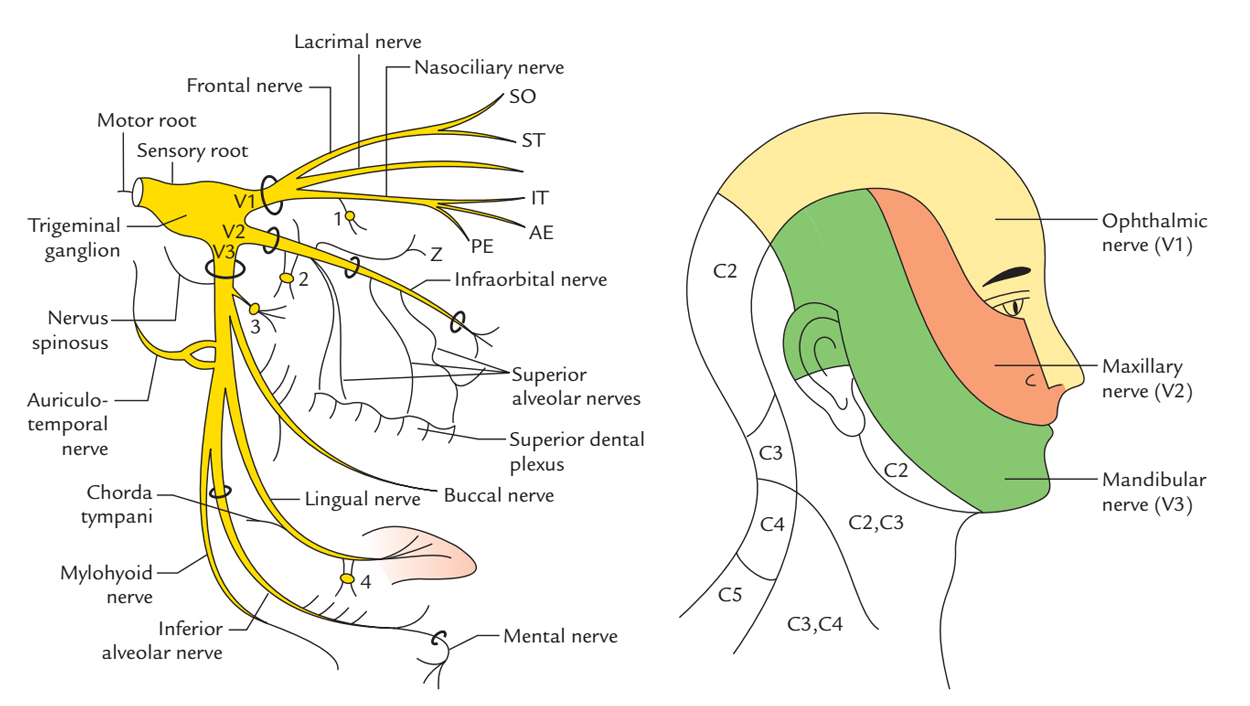
Trigeminal Nerve вђ Earth S Lab The trigeminal nerve is responsible for carrying most of the sensation of the face to the brain. the sensory trigeminal nerve branches of the trigeminal nerve are the ophthalmic, the maxillary, and the mandibular nerves, which correspond to sensation in the v1, v2, and v3 regions of the face, respectively. ophthalmic nerve: this nerve detects. The trigeminal nerve is the 5th cranial nerve (cn v) and the largest of the cranial nerves (see image. cranial nerves in the orbit). cn v provides most of the face's sensory innervation and the mastication muscles' motor stimulation.[1] the nerve's 3 main branches are the ophthalmic (v1), maxillary (v2), and mandibular (v3) nerves. these branches join at the trigeminal ganglia within the. Cranial nerve v is known as the trigeminal nerve. it is the largest (in diameter) of the cranial nerves and contains sensory fibres for the face, as well as a motor segment important for mastication (chewing). understanding the embryology can assist in appreciating the course and innervation of cranial nerves v and vii, the facial nerve. Gross anatomy. the trigeminal nerve is the largest and most complex of the 12 cranial nerves (cns). it supplies sensations to the face, mucous membranes, and other structures of the head. it is the motor nerve for the muscles of mastication and contains proprioceptive fibers. it exits the brain by a large sensory root and a smaller motor root.

Branches Of The Trigeminal Nerve All Branches Of Cranial nerve v is known as the trigeminal nerve. it is the largest (in diameter) of the cranial nerves and contains sensory fibres for the face, as well as a motor segment important for mastication (chewing). understanding the embryology can assist in appreciating the course and innervation of cranial nerves v and vii, the facial nerve. Gross anatomy. the trigeminal nerve is the largest and most complex of the 12 cranial nerves (cns). it supplies sensations to the face, mucous membranes, and other structures of the head. it is the motor nerve for the muscles of mastication and contains proprioceptive fibers. it exits the brain by a large sensory root and a smaller motor root. Your trigeminal nerve provides motor (movement) and sensory information for different aspects of your head and face. motor nerve fibers tell your muscles when and how to move. sensory nerve fibers send pain, touch and temperature sensations from your skin to your brain. your trigeminal nerve consists of three branches:. The trigeminal nerve is the fifth cranial nerve. it is also represented as cn v. it is the largest of all the cranial nerves. it is the most complex of all the cranial nerves due to it's extensive anatomic course. this nerve is a mixed nerve having both sensory and motor fibres.

Trigeminal Nerve вђ Anatomy Qa Your trigeminal nerve provides motor (movement) and sensory information for different aspects of your head and face. motor nerve fibers tell your muscles when and how to move. sensory nerve fibers send pain, touch and temperature sensations from your skin to your brain. your trigeminal nerve consists of three branches:. The trigeminal nerve is the fifth cranial nerve. it is also represented as cn v. it is the largest of all the cranial nerves. it is the most complex of all the cranial nerves due to it's extensive anatomic course. this nerve is a mixed nerve having both sensory and motor fibres.

Comments are closed.