Trigeminal Nerve Dermatome
Trigeminal Nerve Dermatome Map The peripheral aspect of the trigeminal ganglion gives rise to 3 divisions: ophthalmic (v1), maxillary (v2) and mandibular (v3). the motor root passes inferiorly to the sensory root, along the floor of the trigeminal cave. its fibres are only distributed to the mandibular division. the ophthalmic nerve and maxillary nerve travel lateral to the. E. in neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve (lit. triplet nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve v, or simply cn v, is a cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves. its name (trigeminal, from latin tri 'three' and geminus.
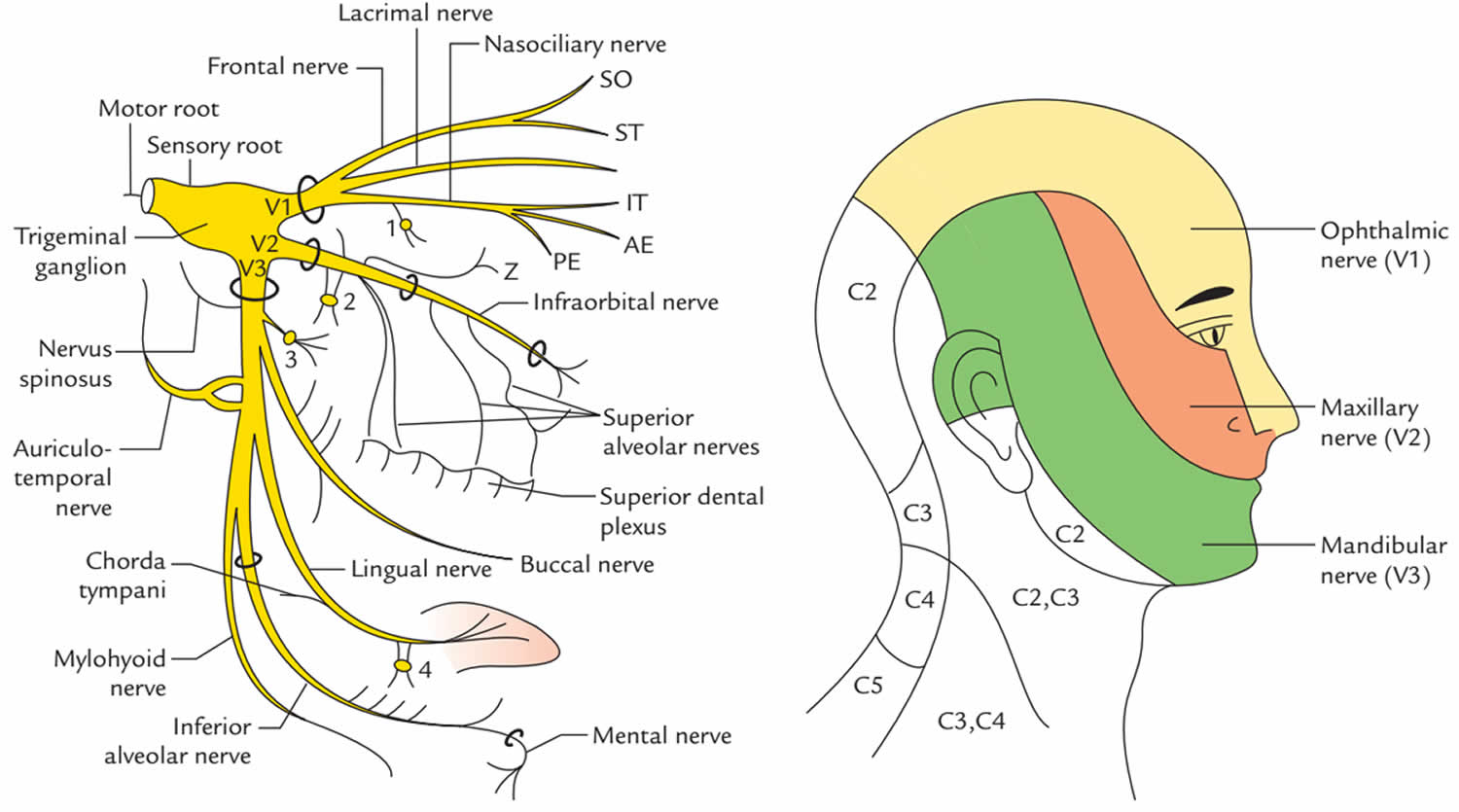
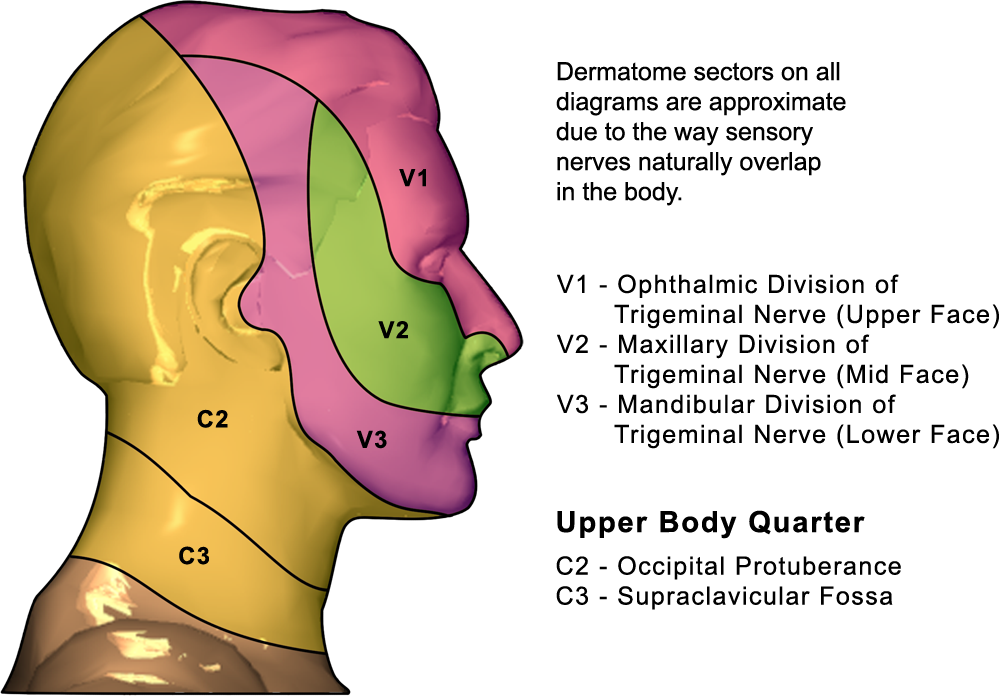
Trigeminal Nerve Dermatome Summary. a dermatome represents the area of skin that provides cutaneous innervation by fibers of a specific nerve. most of the skin on the body is innervated by spinal nerves, but the face receives cutaneous innervation from a cranial nerve (known as the trigeminal nerve). the trigeminal nerve is known as the 5th cranial nerve (cn v) and is. There are three dermatomes of the face, each of which are innervated by one of the three branches of the trigeminal nerve (cn v) and not spinal nerves. ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve (cn v1) forehead and nose; maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve (cn v2) skin over the cheek bones and maxilla (upper jaw). The trigeminal nerve is the 5th cranial nerve (cn v) and the largest of the cranial nerves (see image. cranial nerves in the orbit). cn v provides most of the face's sensory innervation and the mastication muscles' motor stimulation.[1] the nerve's 3 main branches are the ophthalmic (v1), maxillary (v2), and mandibular (v3) nerves. these branches join at the trigeminal ganglia within the. Started at 100mg one to two times per day. increase by 100 200mg every 3 days. usual maintenance dose is 400 800mg (rare >1500mg) metabolized by liver (cytochrome p450) lfts monitored on outpatient basis. pain relief occurs within several hours to days (94% within 48 hours) target serum concentration is 24 43 μmol l.
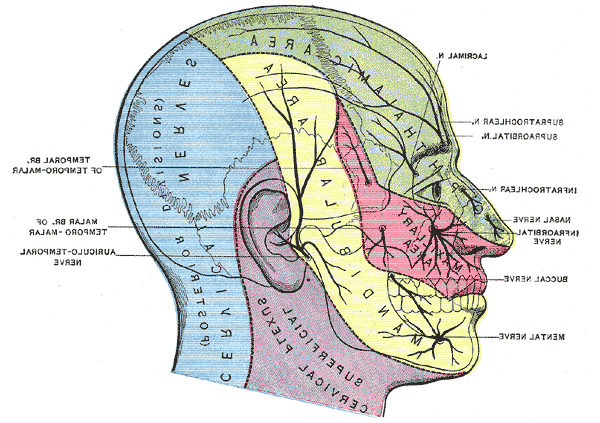
Trigeminal Nerve Dermatome The trigeminal nerve is the 5th cranial nerve (cn v) and the largest of the cranial nerves (see image. cranial nerves in the orbit). cn v provides most of the face's sensory innervation and the mastication muscles' motor stimulation.[1] the nerve's 3 main branches are the ophthalmic (v1), maxillary (v2), and mandibular (v3) nerves. these branches join at the trigeminal ganglia within the. Started at 100mg one to two times per day. increase by 100 200mg every 3 days. usual maintenance dose is 400 800mg (rare >1500mg) metabolized by liver (cytochrome p450) lfts monitored on outpatient basis. pain relief occurs within several hours to days (94% within 48 hours) target serum concentration is 24 43 μmol l. Dermatomes divide the skin according to sensory nerve distribution (see image. dermatome map). one of the first to map out and discuss the dermatomes is o. foerster in his 1933 publication entitled “the dermatomes in man” in the journal brain. some consider his work the foundation of dermatomal theory.[1] in 1948, j. keegan and f. garrett described spinal nerve distribution in the. A dermatome is an area of skin in which sensory nerves derive from a single spinal nerve root (see the following image). dermatomes of the head, face, and neck. the spinal cord has 31 segments, each with a pair (right and left) of ventral (anterior) and dorsal (posterior) nerve roots that innervate motor and sensory function, respectively.
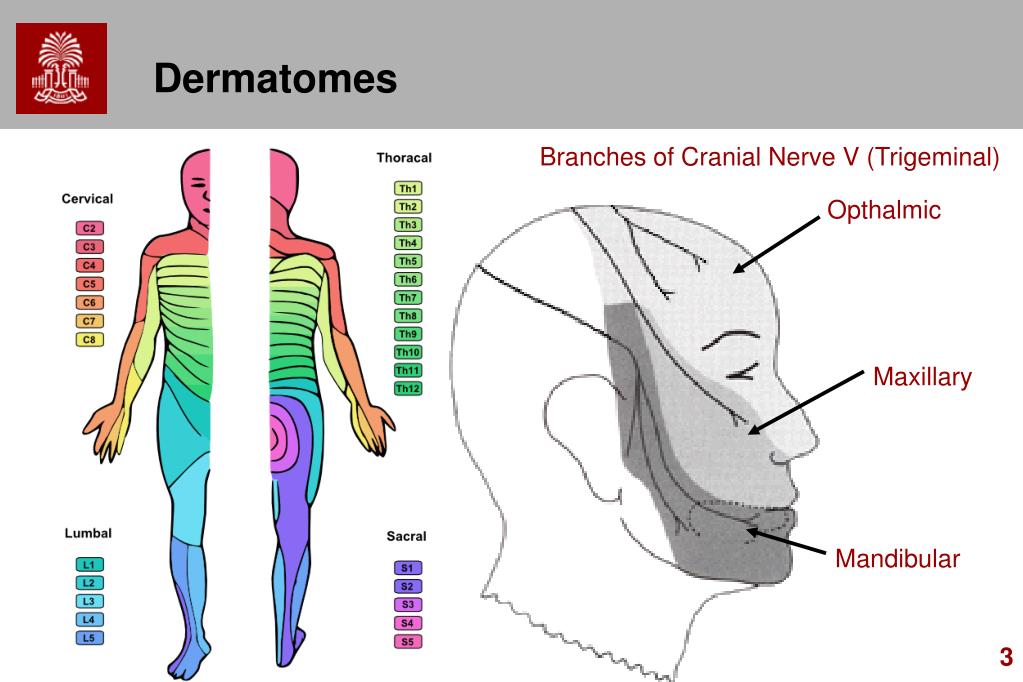
Trigeminal Nerve Dermatome Dermatomes divide the skin according to sensory nerve distribution (see image. dermatome map). one of the first to map out and discuss the dermatomes is o. foerster in his 1933 publication entitled “the dermatomes in man” in the journal brain. some consider his work the foundation of dermatomal theory.[1] in 1948, j. keegan and f. garrett described spinal nerve distribution in the. A dermatome is an area of skin in which sensory nerves derive from a single spinal nerve root (see the following image). dermatomes of the head, face, and neck. the spinal cord has 31 segments, each with a pair (right and left) of ventral (anterior) and dorsal (posterior) nerve roots that innervate motor and sensory function, respectively.

Trigeminal Nerve Sensory Distribution

Comments are closed.