Trigonometric Ratios Of Angle A In Terms Of Tan A Physicscatalyst
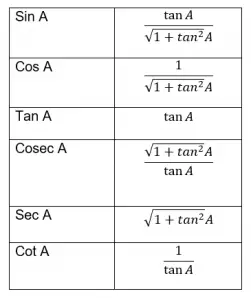
Trigonometric Ratios Of Angle A In Terms Of Tan A Physicscatalyst S Blog Here we would be focusing on acute angle a only. value of cos a in terms of tan a. from trigonometric identity $\sec ^2 a =1 \tan ^2 a$ or $\frac {1}{\cos ^2 a}= 1 \tan ^2 a$ $\cos a = \frac {1}{\sqrt { 1 \tan ^2 a}$ value of sin a in terms of tan a. Introduction. trigonometry (from greek trigõnon, "triangle" and metron, "measure") is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships involving lengths and angles of triangles. the field emerged during the 3 rd century bc from applications of geometry to astronomical studies. trigonometry is most simply associated with planar right angle.

Introduction To Trigonometric Functions Using Triangles Youtube Let us take an example of a right triangle with an acute angle a measuring 30 degrees. the complementary angle b will measure 60 degrees. using the formulas, we can find the trigonometry ratios of angle a and angle b. sin (30°) = cos (60°) = 1 2. cos (30°) = sin (60°) = √3 2 3 2. tan (30°) = cot (60°) = 1 √3 1 3. Trigonometric ratios identities. several trigonometric ratios identities make our calculations simpler such as: sin 2 θ cos 2 θ = 1; 1 tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ; 1 cot 2 θ = cosec 2 θ; there are also some variations of the above 3 identities, which are nothing but rearranging the ones given above. trigonometric ratios of complementary. In the trigonometric ratios table, we use the values of trigonometric ratios for standard angles 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90º. it is easy to predict the values of the table and to use the table as a reference to calculate values of trigonometric ratios for various other angles, using the trigonometric ratio formulas for existing patterns within trigonometric ratios and even between angles. The six trigonometric ratios are sine (sin), cosine (cos), tangent (tan), cotangent (cot), cosecant (cosec), and secant (sec). in geometry, trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the sides and angles of a right angled triangle. therefore, trig ratios are evaluated with respect to sides and angles.
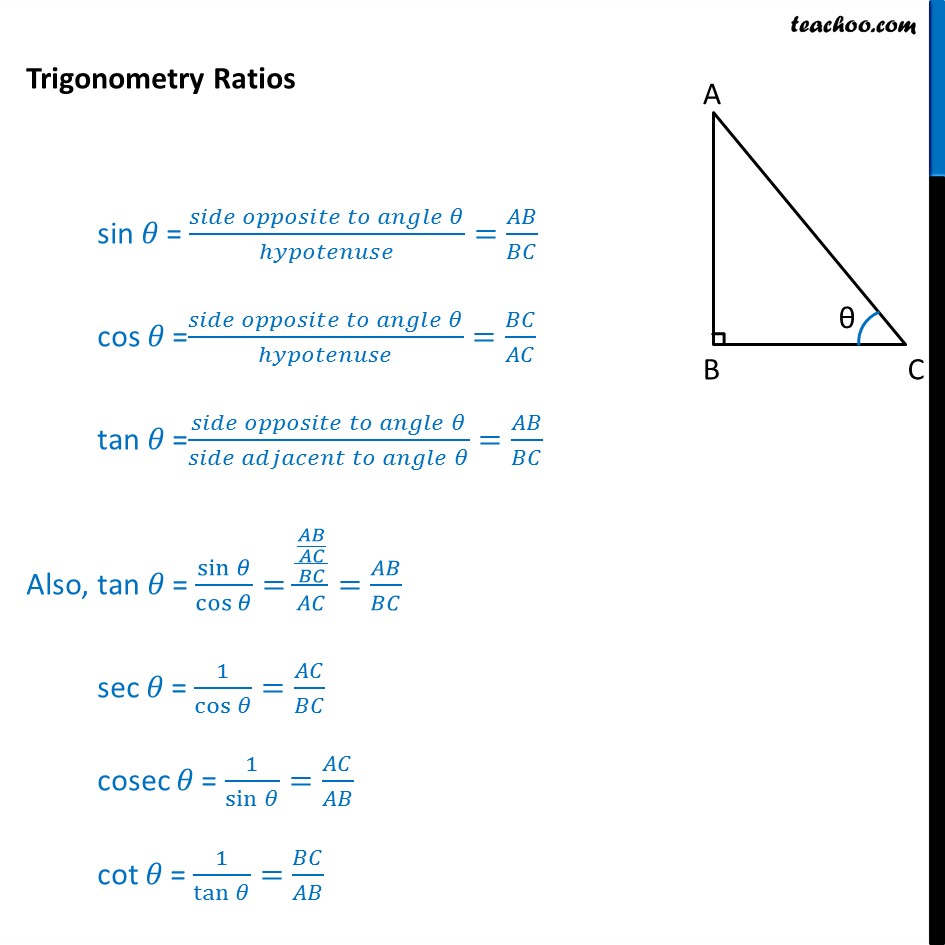
What Are Sin Cos Tan Chapter 8 Class 10 Trignometric Ratios In the trigonometric ratios table, we use the values of trigonometric ratios for standard angles 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90º. it is easy to predict the values of the table and to use the table as a reference to calculate values of trigonometric ratios for various other angles, using the trigonometric ratio formulas for existing patterns within trigonometric ratios and even between angles. The six trigonometric ratios are sine (sin), cosine (cos), tangent (tan), cotangent (cot), cosecant (cosec), and secant (sec). in geometry, trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the sides and angles of a right angled triangle. therefore, trig ratios are evaluated with respect to sides and angles. 2 write down the three trigonometric ratios for the angle † in terms of the sides of the triangle. a d b a c b d q p r c d d e 3 i nea chof t s r ig ld m. f a a 5 4 b a 6 8 c a 10 14 find the exact value of i sin • ii cos • iii tan •. 06 geometry1 and trigonometry 1. Trigonometric ratios are ratios between the side lengths of a right triangle. the six trigonometric ratios for an angle θ are sin θ, cos θ, tan θ, csc θ, sec θ, and cot θ.

Comments are closed.