Trigonometry Trigonometric Ratios Of Complementary Angles For
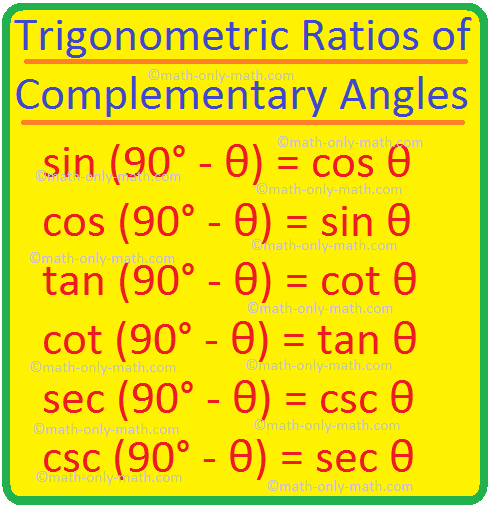
Trigonometric Ratios Of Complementary Angles Trig Ratios Of 90в In a right angle triangle, as the measure of the right angle is fixed, the remaining two angles always form the complementary as the sum of angles in a triangle is equal to 180°. finding trigonometric ratios of complementary angles. assume a triangle ∆abc, which is right angled at b. ∠a and ∠c form a complementary pair. ⇒ ∠a ∠c. But the value of this term is also 1. for this, please go through the trigonometric ratios of specific angles. thus, e = 1 e = 1. challenge 2: find the value of the following expression: e = tan48∘tan23∘tan42∘tan67∘ e = tan 48 ∘ tan 23 ∘ tan 42 ∘ tan 67 ∘. ⚡tip: pair up complementary angles.

Trigonometric Ratios Of Complementary Angles A Plus Topper The above explanation will help us to find the trigonometrical ratios of complementary angles. worked out problems on trigonometrical ratios of complementary angles: 1. without using trigonometric tables, evaluate tan65° cot25° t a n 65 ° c o t 25 °. solution: tan65° cot25° t a n 65 ° c o t 25 °. = tan65° cot(90°−65°) t a n 65 ° c. Ac remains the hypotenuse. so, the trigonometric ratios of reference angle 900 θ (i.e. complementary ratios) is given as: sine of an angle ‘ 90o − θ’ is given as. cosine of an angle ‘ 90o − θ’ is given as. cos(90o − θ) = adjacent hypotenuse = ab ac → (8) tangent of an angle ‘’ 90o − θ is given as. Therefore, m∠a m∠b = 90∘ m ∠ a m ∠ b = 90 ∘. angles a and b are complementary angles because their sum is 90∘ 90 ∘. in #1 you saw that sin a = cos b sin a = cos b and sin b = cos a sin b = cos a. this means that the sine and cosine of complementary angles are equal. 3. Since the measures of these acute angles of a right triangle add to 90º, we know these acute angles are complementary. ∠a is the complement of ∠b, and ∠b is the complement of ∠a. if we write, m∠b = 90º m∠a (or m∠a = 90º m∠b), and we substitute into the original observation, we have:.
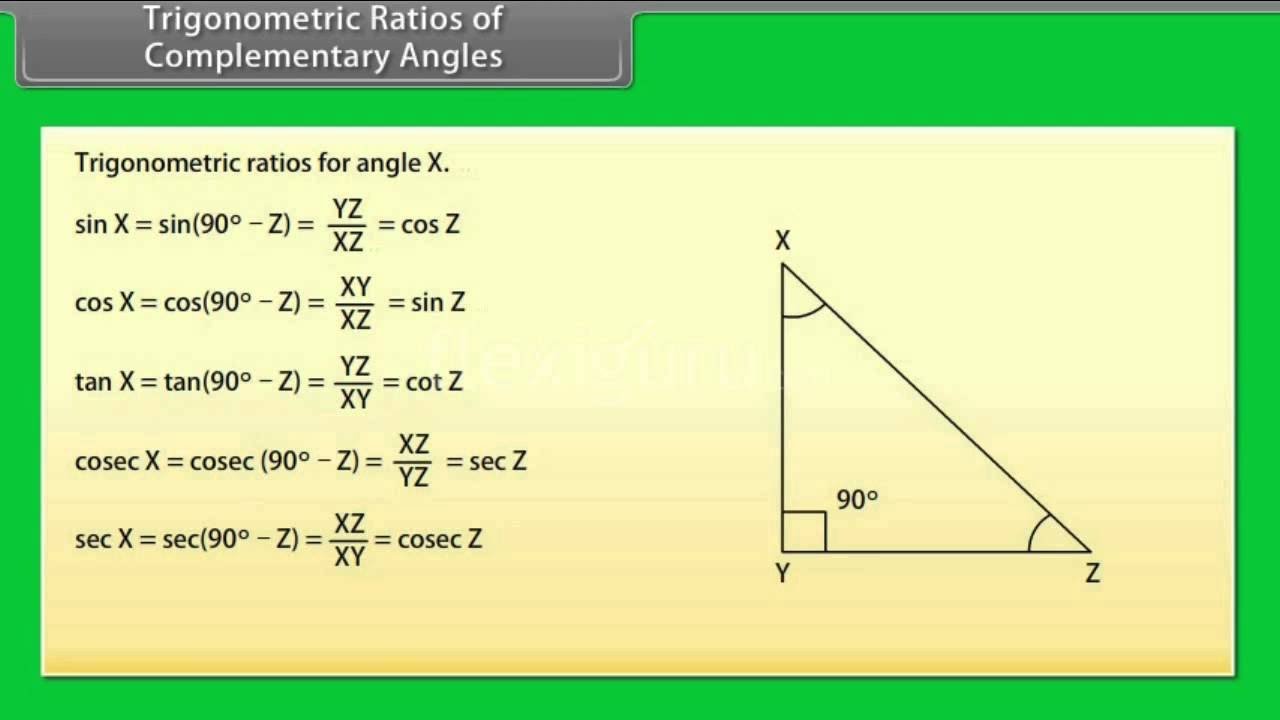
Trigonometric Ratios Of Complementary Angles Maths Class 10th Cbse Therefore, m∠a m∠b = 90∘ m ∠ a m ∠ b = 90 ∘. angles a and b are complementary angles because their sum is 90∘ 90 ∘. in #1 you saw that sin a = cos b sin a = cos b and sin b = cos a sin b = cos a. this means that the sine and cosine of complementary angles are equal. 3. Since the measures of these acute angles of a right triangle add to 90º, we know these acute angles are complementary. ∠a is the complement of ∠b, and ∠b is the complement of ∠a. if we write, m∠b = 90º m∠a (or m∠a = 90º m∠b), and we substitute into the original observation, we have:. Cot (90° β) = cot ( π 2 π 2 – β) = tan β. the values of trigonometrical ratios of 30° and 60°, which are complementary angles are compared below. this will help us to have a clear understanding of the relations shown before. sin 30° = cos 60° = 12 1 2. cos 30° = sin 60° = 3√ 2 3 2. tan 30° = cot 60° = 3√ 3 3 3. Since a right angle has a measure of 90 ∘, the remaining two angles in a right angled triangle must be complementary. trigonometric ratio of complementary angles. two angles are said to be complementary if their sum is 90 ∘. it follows from the above definition that θ and (90 ∘ − θ) are complementary angles for an acute angle θ.
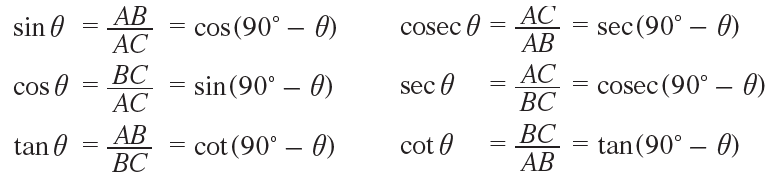
Complementary Angles In Trigonometry Cot (90° β) = cot ( π 2 π 2 – β) = tan β. the values of trigonometrical ratios of 30° and 60°, which are complementary angles are compared below. this will help us to have a clear understanding of the relations shown before. sin 30° = cos 60° = 12 1 2. cos 30° = sin 60° = 3√ 2 3 2. tan 30° = cot 60° = 3√ 3 3 3. Since a right angle has a measure of 90 ∘, the remaining two angles in a right angled triangle must be complementary. trigonometric ratio of complementary angles. two angles are said to be complementary if their sum is 90 ∘. it follows from the above definition that θ and (90 ∘ − θ) are complementary angles for an acute angle θ.
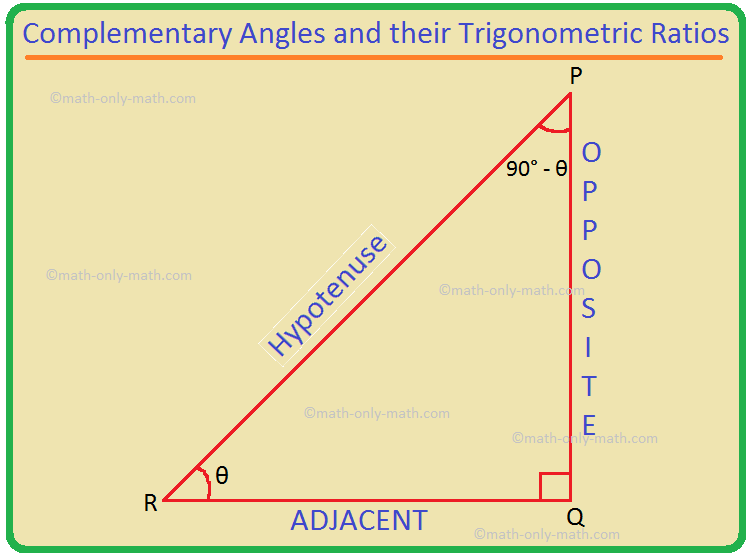
Trigonometric Ratios Of Complementary Angles Trig Ratios Of 90в

Comments are closed.