Types Of Fracture Ortho X Ray Medschool
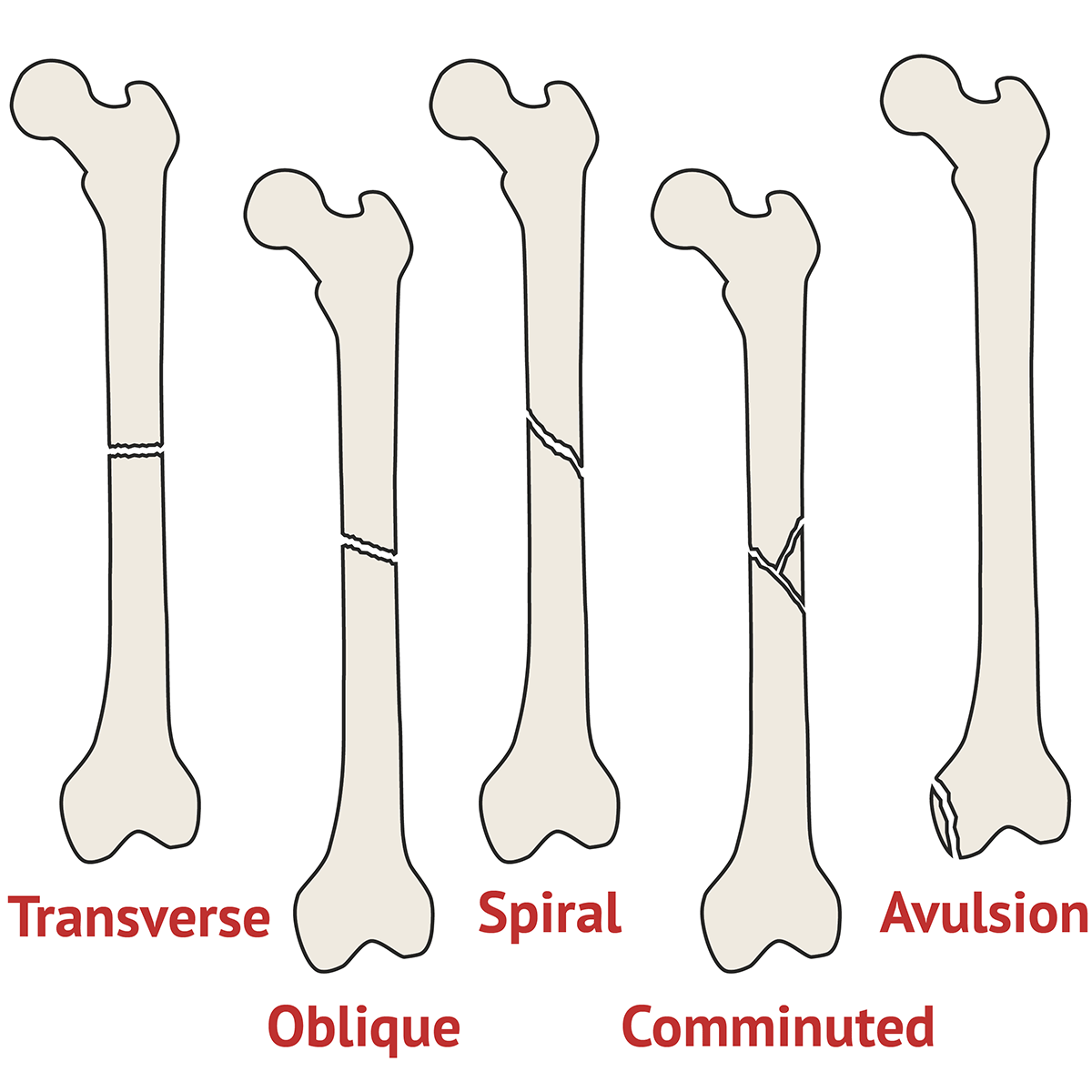
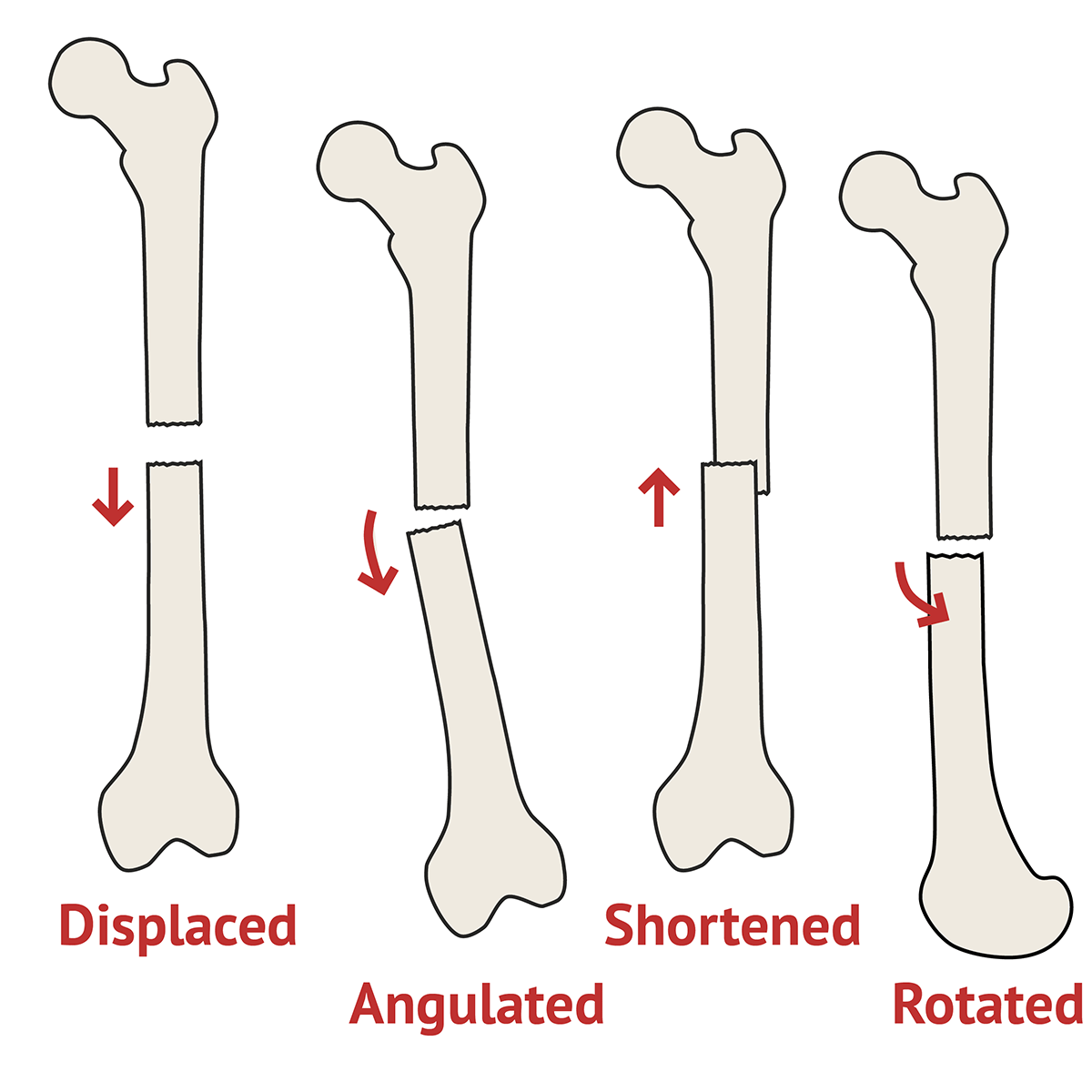
Types Of Fracture Ortho X Ray Medschool Transverse fracture a fracture straight across the bone. oblique fracture a fracture at an angle to the bone. spiral fracture a corkscrew shaped fracture around the bone occurs due to twisting of a long bone. comminuted fracture the bone has been shattered into multiple pieces. avulsion fracture avulsion of a fragment of bone away. Types of fracture deformity. displacement dorsal (posterior), volar (anterior) or lateral displacement of the distal fragment with respect to the proximal fragment. shortening overlapping of fracture ends. angulation the angle created between the distal fragment and the proximal fragment due to the fracture.
Deformity Of Fracture Ortho X Ray Medschool Orthopaedic x ray interpretation. x rays are commonly used in clinical practice to diagnose fractures. characteristics of the fracture such as the type, deformity and soft tissue joint involvement are used to guide management. Describing a fracture (an approach) | radiology reference. Improve article. musculoskeletal (msk) x ray interpretation can occasionally feature in osces and therefore it’s important to practice this skill to develop a structured approach. this guide provides a brief overview of msk x ray interpretation, including a structured approach you can apply to most x rays and examples of relevant pathology. Line in the proximal tibia and the presence or absence of a depressed. segment of the articular surface of the proximal tibia (see fig. 53 9). this fracture classification is not dependent on the amount of displacement or depression. of the articular fractures, but only on the location of the fracture. lines.
Types Of Fracture Ortho X Ray Medschool Improve article. musculoskeletal (msk) x ray interpretation can occasionally feature in osces and therefore it’s important to practice this skill to develop a structured approach. this guide provides a brief overview of msk x ray interpretation, including a structured approach you can apply to most x rays and examples of relevant pathology. Line in the proximal tibia and the presence or absence of a depressed. segment of the articular surface of the proximal tibia (see fig. 53 9). this fracture classification is not dependent on the amount of displacement or depression. of the articular fractures, but only on the location of the fracture. lines. Sanders classification. type i: all fractures with <2mm displacement. type ii: two part fractures of the posterior facet. type iii: three part fractures of the posterior facet. type iv: highly comminuted fracture with four or more fracture lines. dirschl dr. Fractures (broken bones) orthoinfo aaos.

Complete Fracture Diagram Sanders classification. type i: all fractures with <2mm displacement. type ii: two part fractures of the posterior facet. type iii: three part fractures of the posterior facet. type iv: highly comminuted fracture with four or more fracture lines. dirschl dr. Fractures (broken bones) orthoinfo aaos.
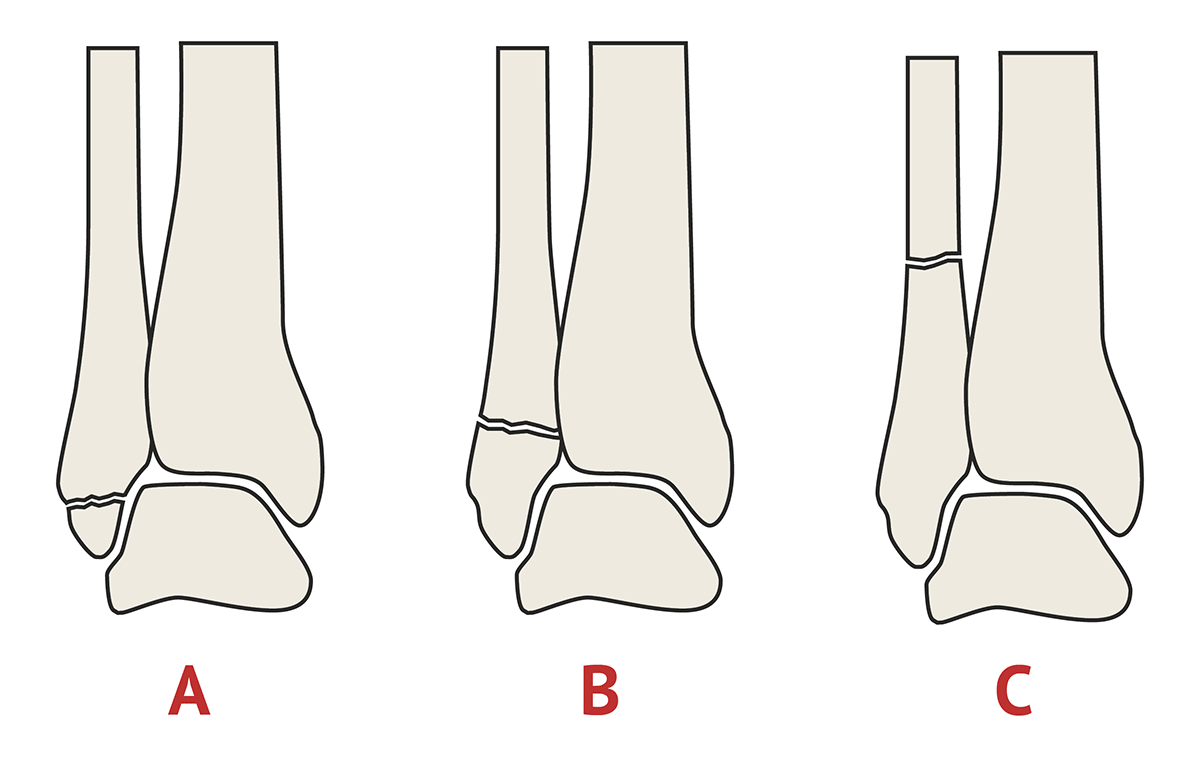
Weber Classification Orthopaedic X Ray Interpretation Medschool

Comments are closed.