View In Full Resolution Emt Study Shock Symptoms Types Of Shock

Types Of Shock Comparison There are three stages of shock: stage i also called compensated, or nonprogressive. stage ii also called decompensated or progressive. stage iii also called irreversible. in stage i shock. A blood clot that occurs in the pulmonary circulation that blocks the flow of blood through the pulmonary vessels. three of the most common examples of obstructive shock. 1 cardiac tamponade. 2 tension pneumothorax. 3 pulmonary embolism.

Types Of Shock And Symptoms Chapter 13: shock. chapter 13 shock unit summary. after students complete this chapter and the related course work, they will have an understanding of the different types and causes of shock, the process of perfusion, the signs and symptoms associated with shock, application of the assessment process with the shock patient, and the general and specific emergency medical care provided to. Pulse ÷ systolic. shock is a progressive state of cellular hypoperfusion in which insufficient oxygen is available to meet tissue demands. it is key to understand that when shock occurs, the body is in distress. the shock response is mounted by the body to attempt to maintain systolic blood pressure and brain perfusion during times of. Treatment of septic shock. transport promptly, administer oxygen en route, provide full ventilatory support, consider elevating legs, keep patient warm. treatment of neurogenic shock. secure airway, spinal stabilization, assist ventilations, administer high flow oxygen, preserve body heat, transport promptly. treatment of anaphylactic shock. Learn more (video study course): prepareforems the "life saving video vault" ems students use to pass school & nremt on easy mode.(without com.
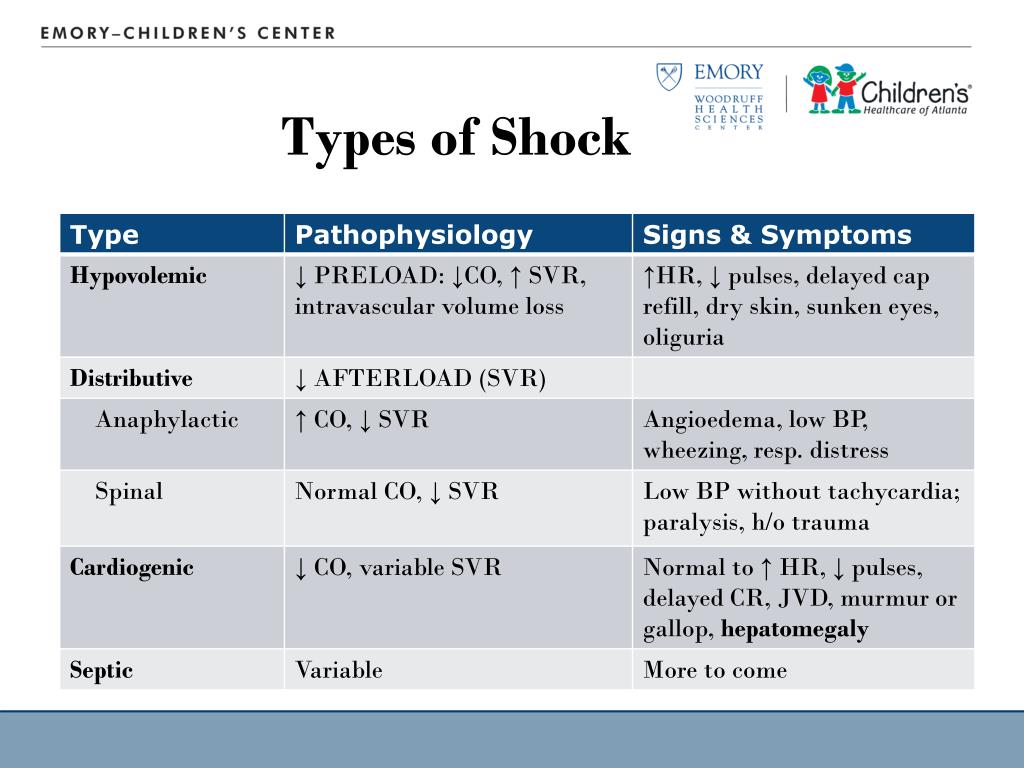
Types Of Shock Stages Comparison Cheat Sheet Vrogue Co Treatment of septic shock. transport promptly, administer oxygen en route, provide full ventilatory support, consider elevating legs, keep patient warm. treatment of neurogenic shock. secure airway, spinal stabilization, assist ventilations, administer high flow oxygen, preserve body heat, transport promptly. treatment of anaphylactic shock. Learn more (video study course): prepareforems the "life saving video vault" ems students use to pass school & nremt on easy mode.(without com. Obstructive shock. due to a pump problem caused by a mechanical obstruction of the heart. two types of obstructive shock. cardiac tamponade and tension pneumothorax. distributive shock. blood vessel problem due to widespread vasodilation. four types of distributive shock. anaphylactic. Hypovolemic shock is a type of shock in which the body loses fluid volume. if the body loses 20% or more of its volume, it can be enough to affect its ability to perfuse the tissues. hypovolemic shock can be hemorrhagic or non hemorrhagic by nature. non hemorrhagic shock can be caused by severe dehydration from sweating, vomiting, or diarrhea.

Summary Table Of Types Of Shock Obstructive shock. due to a pump problem caused by a mechanical obstruction of the heart. two types of obstructive shock. cardiac tamponade and tension pneumothorax. distributive shock. blood vessel problem due to widespread vasodilation. four types of distributive shock. anaphylactic. Hypovolemic shock is a type of shock in which the body loses fluid volume. if the body loses 20% or more of its volume, it can be enough to affect its ability to perfuse the tissues. hypovolemic shock can be hemorrhagic or non hemorrhagic by nature. non hemorrhagic shock can be caused by severe dehydration from sweating, vomiting, or diarrhea.

Comments are closed.