What Animals Are Secondary Consumers
Secondary Consumers Definition Types And Examples Learn what secondary consumers are, how they function in the food chain, and what types of animals are secondary consumers. find out how secondary consumers can switch between being primary or tertiary consumers depending on the environment. Learn what secondary consumers are, how they fit into the trophic pyramid, and what types of animals are secondary consumers. find out the importance of secondary consumers for energy flow, biodiversity, and nutrient cycling in ecosystems.
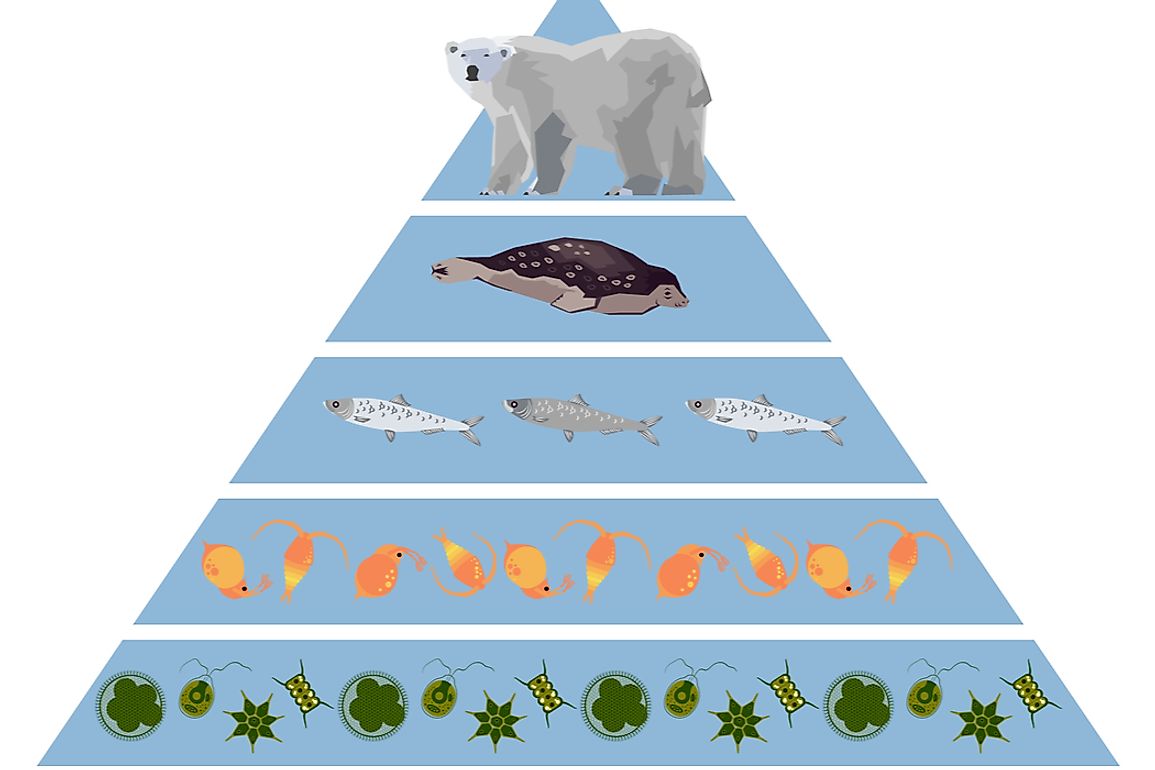
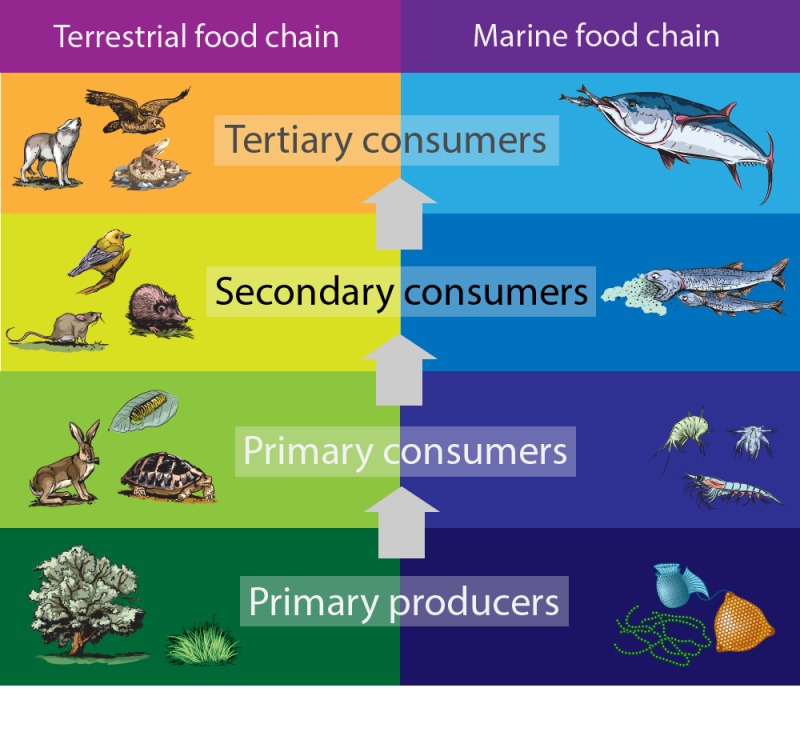
What Are Secondary Consumers Worldatlas Learn what secondary consumers are, how they feed on primary consumers, and why they are important for ecosystems. find out examples of aquatic and terrestrial secondary consumers, and how they can switch between trophic levels. Definition of secondary consumers. secondary consumers are organisms that primarily feed on primary consumers, which are herbivores, in a food chain. they occupy the third trophic level and can be either carnivores, who eat only other animals, or omnivores, who consume both animal and plant matter. their role is vital in transferring energy. Secondary consumers are organisms that receive their energy from primary consumers. most secondary consumers are carnivores, meaning they survive by eating animal tissues. carnivores can be. This is also the amount of energy per year that's made available to the primary consumers, which eat the primary producers. the 10% rule would predict that the primary consumers store only 2,000 kcal m 2 year of energy in their own bodies, making energy available to their predators—secondary consumers—at a lower rate.

Secondary Consumer Definition Examples Food Chain Lesson Study Secondary consumers are organisms that receive their energy from primary consumers. most secondary consumers are carnivores, meaning they survive by eating animal tissues. carnivores can be. This is also the amount of energy per year that's made available to the primary consumers, which eat the primary producers. the 10% rule would predict that the primary consumers store only 2,000 kcal m 2 year of energy in their own bodies, making energy available to their predators—secondary consumers—at a lower rate. Animals, fungi, and many bacteria are heterotrophs. when we're talking about their role in food chains, we can call heterotrophs consumers. as we'll see shortly, there are many different kinds of consumers with different ecological roles, from plant eating insects to meat eating animals to fungi that feed on debris and wastes. Some secondary consumers eat both plants and animals. they are called omnivores , from the latin words that mean “eats everything.” a raccoon is an example of an omnivore; it eats plant matter such as berries and acorns, but it also catches crayfish, frogs, fish, and other small animals.

Comments are closed.