What Is Isometric Projection Principle Of Isometric Projections
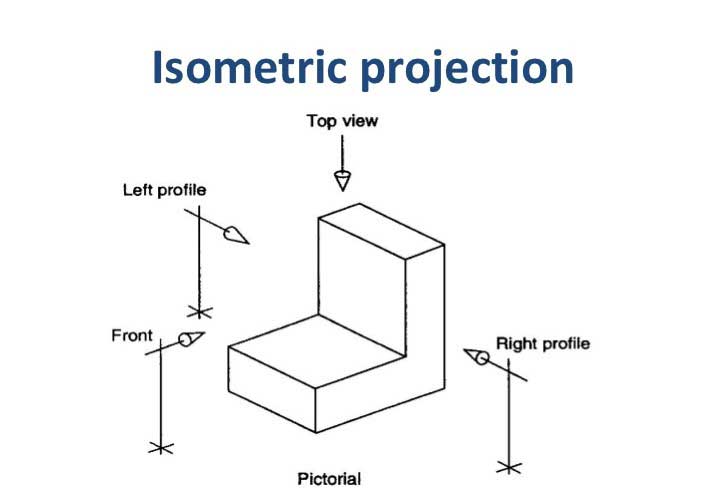
Isometric Drawing Projection Its Types Methods 1 principle of isometric projections it’s a pictorial orthographic projection, or isometric projection in engineering drawing , of an object where a transparent cube containing the object is tilted before one of those solid diagonals of the cube becomes perpendicular to the vertical plane along with the three axes are equally inclined to. Isometric drawing, also commonly called isometric projection. isometric projection is a method of graphic representation of three dimensional objects through drawing. isometric drawing is used by engineers, technical painters, and architects. in isometric projection, the plan shows the three visible sides of the object from the same angle to.
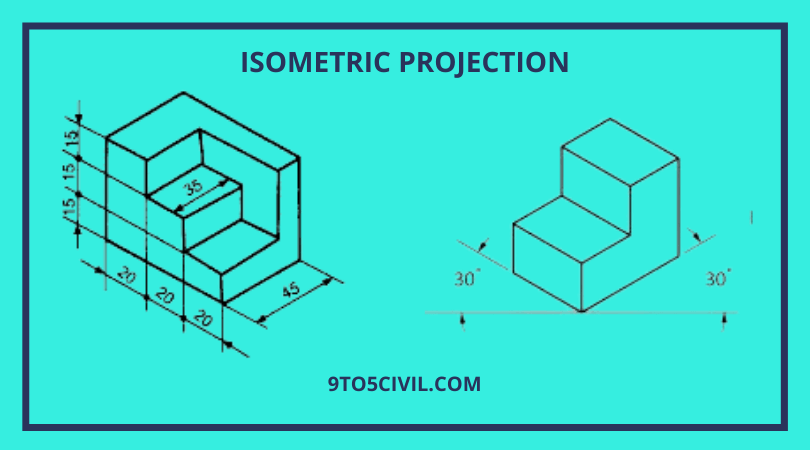
What Is Isometric Projection Principle Of Isometric Projections To find the length of the edges in the isometric projection: to find the extent to which the lengths of the edges are foreshortened. draw a square d’ab’c od sides equal to the actual length of the edges of the cube with d’b’ as the common diagonal. d’c is the actual length of the edge, whereas corresponding edge d’c’ in the. The term "isometric" comes from the greek for "equal measure", reflecting that the scale along each axis of the projection is the same (unlike some other forms of graphical projection). an isometric view of an object can be obtained by choosing the viewing direction such that the angles between the projections of the x , y , and z axes are all. The isometric is one class of orthographic projections. (in making an orthographic projection, any point in the object is mapped onto the drawing by dropping a perpendicular from that point to the plane of the drawing.) an isometric projection results if the plane is oriented so that it makes equal angles (hence “isometric,” or “equal. Principle of isometric projections. it’s a pictorial orthographic projection of an object where a transparent cube containing the object is tilted before one of those solid diagonals of the cube becomes perpendicular to the vertical plane along with the three axes are equally inclined to this vertical plane. lines in isometric projection.

A Beginner S Guide To Isometric Projection With Examples The isometric is one class of orthographic projections. (in making an orthographic projection, any point in the object is mapped onto the drawing by dropping a perpendicular from that point to the plane of the drawing.) an isometric projection results if the plane is oriented so that it makes equal angles (hence “isometric,” or “equal. Principle of isometric projections. it’s a pictorial orthographic projection of an object where a transparent cube containing the object is tilted before one of those solid diagonals of the cube becomes perpendicular to the vertical plane along with the three axes are equally inclined to this vertical plane. lines in isometric projection. Isometric projection is a technique for visualising a three dimensional object in two dimensions. it is a type of axonometric projection, which means that all three principal axes of the object. Isometric projection of a pyramid rotating around z axis. isometric projection is one of the ways to map a 3d point on a 2d plane. it is a linear transformation, which means it can be represented by a 2 by 3 matrix. a common way to explain the projection and derive the matrix is via using a composition of rotations a 3d vector is linearly.

What Is Isometric Projection Principle Of Isometric Projections Isometric projection is a technique for visualising a three dimensional object in two dimensions. it is a type of axonometric projection, which means that all three principal axes of the object. Isometric projection of a pyramid rotating around z axis. isometric projection is one of the ways to map a 3d point on a 2d plane. it is a linear transformation, which means it can be represented by a 2 by 3 matrix. a common way to explain the projection and derive the matrix is via using a composition of rotations a 3d vector is linearly.

Comments are closed.