What Is Meant By The Initial Point Of A Vector
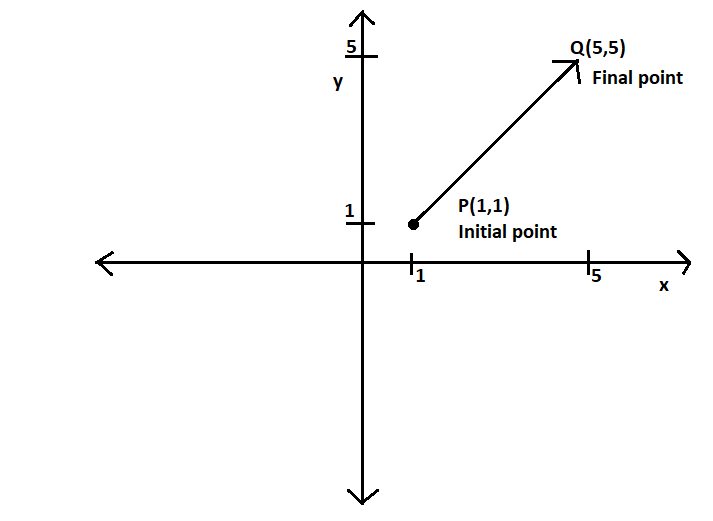
What Is Meant By The Initial Point Of A Vector We call a vector with its initial point at the origin a standard position vector. because the initial point of any vector in standard position is known to be \((0,0)\), we can describe the vector by looking at the coordinates of its terminal point. thus, if vector \(\vecs{v}\) has its initial point at the origin and its terminal point at \((x,y. Example of initial point of a vector. in the above figure, pq is a vector and p the initial point of the vector. solved example on initial point of a vector ques: identify the value of initial point from the given vector . choices: a. (3, 4) b. (4, 5) c. (3, 5) d. none of these correct answer: a. solution:.
11 1 Vectors In The Plane Mathematics Libretexts But it has a different initial point. geometrically, a vector is a length in a direction. a vector is (or can be thought of as) a directed line segment. a vector (unlike a line segment) goes from one point to another. a line segment has two endpoints and a length. it is a length in a particular location. a vector has only a length and a direction. Because of this, the head to tail rule is also known as the parallelogram law: the vector \(\vec u \vec v\) is defined by forming the parallelogram defined by the vectors \(\vec u\) and \(\vec v\); the initial point of \(\vec u \vec v\) is the common initial point of parallelogram, and the terminal point of the sum is the common terminal point. Parallelogram law of addition of vectors: the law states that if two co initial vectors acting simultaneously are represented by the two adjacent sides of a parallelogram, then the diagonal of the parallelogram represents the sum of the two vectors, that is, the resultant vector starting from the same initial point. subtraction of vectors. A vector with an initial point and terminal point that are the same is called the zero vector, denoted 0. 0. the zero vector is the only vector without a direction, and by convention can be considered to have any direction convenient to the problem at hand.

Vectors With Different Initial Points Youtube Parallelogram law of addition of vectors: the law states that if two co initial vectors acting simultaneously are represented by the two adjacent sides of a parallelogram, then the diagonal of the parallelogram represents the sum of the two vectors, that is, the resultant vector starting from the same initial point. subtraction of vectors. A vector with an initial point and terminal point that are the same is called the zero vector, denoted 0. 0. the zero vector is the only vector without a direction, and by convention can be considered to have any direction convenient to the problem at hand. A vector is the equivalence class of all directed segments of the same length and direction. we can represent a vector by writing the unique directed line segment that has its initial point at the origin. the vector between. p = (2, 3) and q = ( − 1, 4) is equivalent to the directed line segment. q − p = − 3, 1 . A vector is a directed line segment with an initial point and a terminal point. vectors are identified by magnitude, or the length of the line, and direction, represented by the arrowhead pointing toward the terminal point. the position vector has an initial point at (0, 0) (0, 0) and is identified by its terminal point (a, b). (a, b).

Figuring Out Vector Initial Point Vectors Precalculus Khan A vector is the equivalence class of all directed segments of the same length and direction. we can represent a vector by writing the unique directed line segment that has its initial point at the origin. the vector between. p = (2, 3) and q = ( − 1, 4) is equivalent to the directed line segment. q − p = − 3, 1 . A vector is a directed line segment with an initial point and a terminal point. vectors are identified by magnitude, or the length of the line, and direction, represented by the arrowhead pointing toward the terminal point. the position vector has an initial point at (0, 0) (0, 0) and is identified by its terminal point (a, b). (a, b).

Comments are closed.