What Is Ultraviolet Radiation Definition And Examples

What Is Ultraviolet Radiation Definition And Examples Ultraviolet radiation, that portion of the electromagnetic spectrum extending from the violet, or short wavelength, end of the visible light range to the x ray region. . ultraviolet (uv) radiation is undetectable by the human eye, although, when it falls on certain materials, it may cause them to fluoresce—i.e., emit electromagnetic radiation of lower energy, such as visible. Ultraviolet radiation is invisible energy in the wavelength range from 100 to 400 nanometers (nm). a nanometer is one billionth of a meter. uv radiation has a shorter wavelength and is more energetic than visible light. depending on its wavelength, it can get through the ozone layer and affect our health in different ways.

Ultraviolet Radiation Definition Examples Effects 58 Off Ultraviolet ( uv) light is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than x rays. uv radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the sun. it is also produced by electric arcs, cherenkov radiation, and. Ultraviolet radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation that has wavelengths which are a little shorter than the wavelengths of violet colored visible light. ultraviolet means "beyond violet. Ultraviolet (uv) radiation is one part of the electromagnetic spectrum of radiation that reaches earth from the sun. it is a form of light energy situated on the spectrum just beyond visible light. Ultraviolet radiation (uvr) can neither be seen nor felt. while some people are exposed to artificial uvr sources (e.g. in medicine, industry and for disinfection and cosmetic purposes), everyone is exposed to solar uvr. solar uvr levels are influenced by several factors: sun elevation: the higher the sun in the sky, the higher the uvr level.
.PNG)
Ultraviolet Presentation Physics Ultraviolet (uv) radiation is one part of the electromagnetic spectrum of radiation that reaches earth from the sun. it is a form of light energy situated on the spectrum just beyond visible light. Ultraviolet radiation (uvr) can neither be seen nor felt. while some people are exposed to artificial uvr sources (e.g. in medicine, industry and for disinfection and cosmetic purposes), everyone is exposed to solar uvr. solar uvr levels are influenced by several factors: sun elevation: the higher the sun in the sky, the higher the uvr level. The sun releases ultraviolet (uv) radiation, which provides vitamin d to your body. but too much sun exposure can cause wrinkles and skin cancer. you can protect your skin from too much uv exposure by wearing sunscreen when you go outside. skin cancer from uv radiation is treatable and leads to a good prognosis if detected early. Solar emissions include visible light, heat and ultraviolet (uv) radiation. just as visible light consists of different colours that become apparent in a rainbow, the uv radiation spectrum is divided into three regions called uva, uvb and uvc. as sunlight passes through the atmosphere, all uvc and most uvb is absorbed by ozone, water vapour.
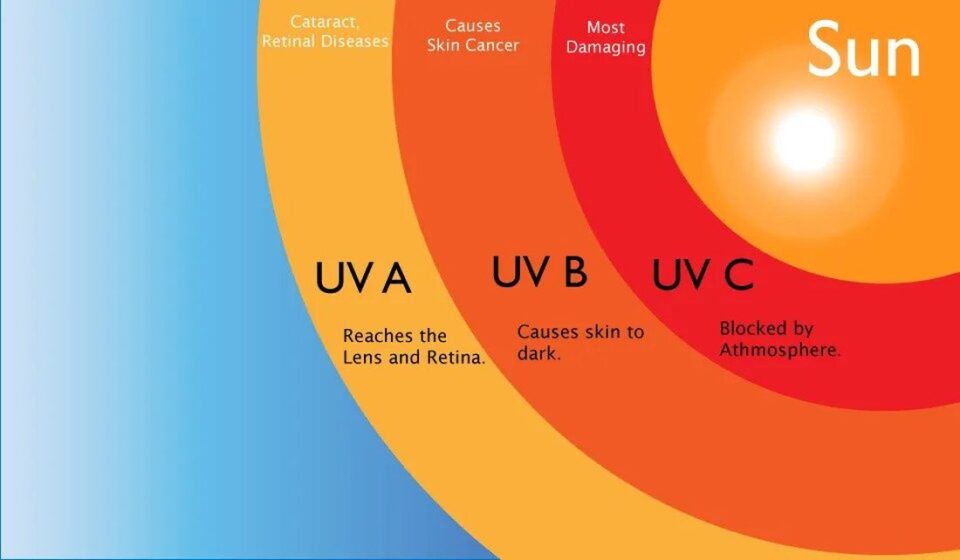
How To Protect Your Child S Skin From Too Much Ultraviolet Uv The sun releases ultraviolet (uv) radiation, which provides vitamin d to your body. but too much sun exposure can cause wrinkles and skin cancer. you can protect your skin from too much uv exposure by wearing sunscreen when you go outside. skin cancer from uv radiation is treatable and leads to a good prognosis if detected early. Solar emissions include visible light, heat and ultraviolet (uv) radiation. just as visible light consists of different colours that become apparent in a rainbow, the uv radiation spectrum is divided into three regions called uva, uvb and uvc. as sunlight passes through the atmosphere, all uvc and most uvb is absorbed by ozone, water vapour.

Comments are closed.